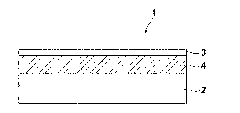
Semiconductor device, method for producing the semiconductor device, substrate for semiconductor element and method for producing the substrate
A technology for semiconductors and components, applied in the field of substrates for semiconductor components, can solve the problems of semiconductor production and processing temperature limit, difficulty in forming strong bonds, and decrease in contact area, and achieve the effects of improving electron mobility, improving performance, and suppressing separation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
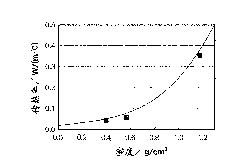
[0100] 15 parts of 10 mM acetic acid solution, 2 parts of Pluronic F-127 (block copolymer surfactant from BASF), 1 part of urea and 9 parts of methyltrimethoxysilane were mixed to obtain a clear solution. Place the solution in a semi-hermetically sealed Teflon TM In the container, a gelation reaction was performed at 80° C. for 2 days. Surfactants were removed from the wet gel by washing in boiling water, and solvent exchange was performed with methanol and fluorosolvent (Novec-7100 from Sumitomo 3M). The gel was dried to obtain a transparent xerogel porous structure formed of polymethylsilsesquioxane. The density ρ of the xerogel measured by the Archimedes method is 0.40 g / cm 3 .
Embodiment approach 2
[0102] A translucent xerogel formed of polymethylsilsesquioxane was obtained by the same procedure as Embodiment 1 (except that the amount of Pluronic F-127 was changed to 1.5 parts). The density ρ of the dry gel measured by the Archimedes method is 0.57g / cm 3 .
Embodiment approach 3
[0104] By the same procedure as Embodiment 1 (the difference is that by mixing 35 parts of 10 mM acetic acid solution, 16 parts of tetramethoxysilane, 10 parts of methyltrimethoxysilane, 5.5 parts of Pluronic F-127 and 2.5 parts Parts of urea to obtain a transparent solution) to obtain a transparent xerogel formed from a copolymer of methylsilsesquioxane and siloxane. The weight ratio of siloxane skeleton / silsesquioxane skeleton calculated from the mixing ratio was 61 / 39. The density ρ of the xerogel measured by the Archimedes method is 0.40 g / cm 3 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal degradation temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com