Method for degrading streptococcus suis biofilm by applying phage lyase
A technology of phage lyase and biofilm, which is applied in the field of phage lyase to degrade Streptococcus suis biofilm, can solve the problems such as difficult to degrade Streptococcus suis, and achieve the effect of high-efficiency lysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Cleavage spectrum of biofilm by lyase:
[0033] Step 1, cultivation of biofilm
[0034] Inoculate 20 μL of Streptococcus suis overnight on a shaker at 37°C into each well containing 2 mL of THB medium (add 3 g of yeast extract, 20 g of tryptone, 5 g of beef extract, 2 g of glucose, 10 g of NaCl, and 2 CO 3 2.5 g, 1.0008 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 20 mL of calf serum, adjust the pH value to 7.5) in a 24-well cell culture plate (purchased from Cellstar Company), cover and culture in a 37°C incubator for 3 days. Wells containing only THB medium were used as control wells. After 3 days, the cell culture plate was taken out, the free medium was discarded with a pipette and washed gently twice with sterilized PBS buffer (pH7.2) to remove free bacteria, and a mature biofilm was obtained.
[0035] Step 2, expression and purification of phage lyase LySMP
[0036] The plasmid used for the prokaryotic expression is pET-28a(+), and the expressed cleavage enzyme molecule...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The dose-effect relationship of lyase cleavage biofilm:
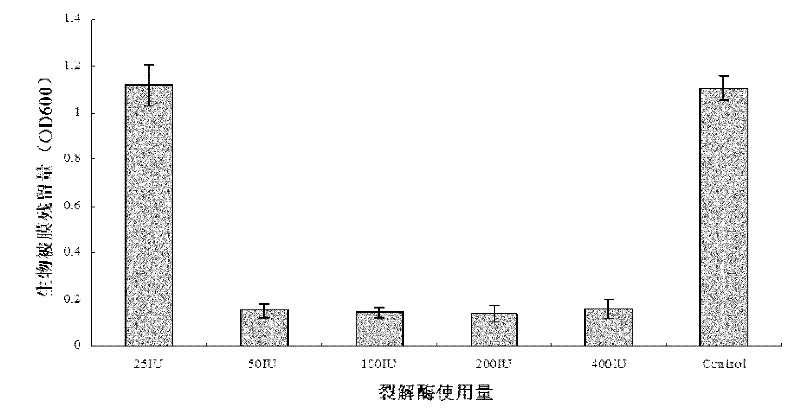
[0053] Step 1, dilute the purified LySMP with elution buffer to 50IU / mL, 100IU / mL, 200IU / mL, 400IU / mL, 800IU / mL. Add 0.5 mL of LySMP at different concentrations to the biofilm, that is, add 25 IU, 50 IU, 100 IU, 200 IU, and 400 IU to each well.
[0054] Step 2: After using LySMP to act on the biofilm for 6 hours in a 37° C. incubator, use the crystal violet staining method (same as Example 1) to semi-quantitatively measure the biofilm residual amount.
[0055] Such as figure 2 As shown, 25IU lyase has almost no cracking effect on biofilm. When it is greater than 50IU, the cleavage effect of the lyase is stronger.
Embodiment 3
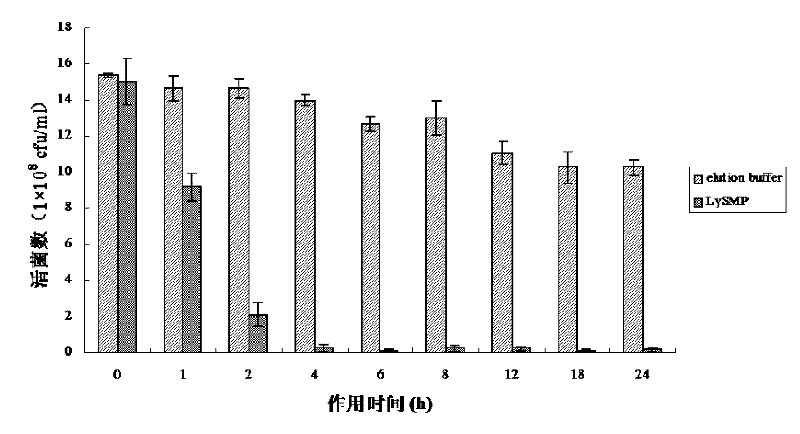
[0057] The number of residual viable bacteria after the lyase acts on the SS2-4 biofilm:
[0058] Step 1, make MTT colorimetric test standard curve according to MTT colorimetric test method
[0059] In step 2, the Streptococcus suis biofilm treated with LySMP for 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 18, and 24 hours was gently washed twice with sterile PBS buffer (pH 7.2) to remove free bacteria. Resuspend residual biofilm in 1 mL of sterile PBS buffer per well.
[0060] Step 3: Use a pipette to draw 100 μL of the bacterial resuspension, and add it to a 96-well microtiter plate, and make 3 replicate wells for each sample solution, and set a negative control with PBS buffer. Then add 20 μL of MTT application solution (100 mg MTT in 20 mL PBS buffer solution, MTT purchased from sigma company) to each well, put it in a constant temperature incubator at 37 °C for 2 hours, take it out, and add 100 μL of DMSO (purchased from sigma company), the OD value was measured at 570nm with an automatic micro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com