Optical receiving system of doppler wind lidar
A Doppler wind measurement and lidar technology, which is applied in the field of Doppler wind measurement and lidar optical receiving systems, can solve the problems of decreased receiving efficiency of an optical path receiving device, loss of backscattered light signals, unfavorable FP etalon processing, etc. , to achieve the effect of being beneficial to the adjustment of the optical path, reducing the loss of the optical signal, and improving the frequency locking efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] In order to make the above objects, features and advantages of the present application more obvious and comprehensible, the present application will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific implementation methods.
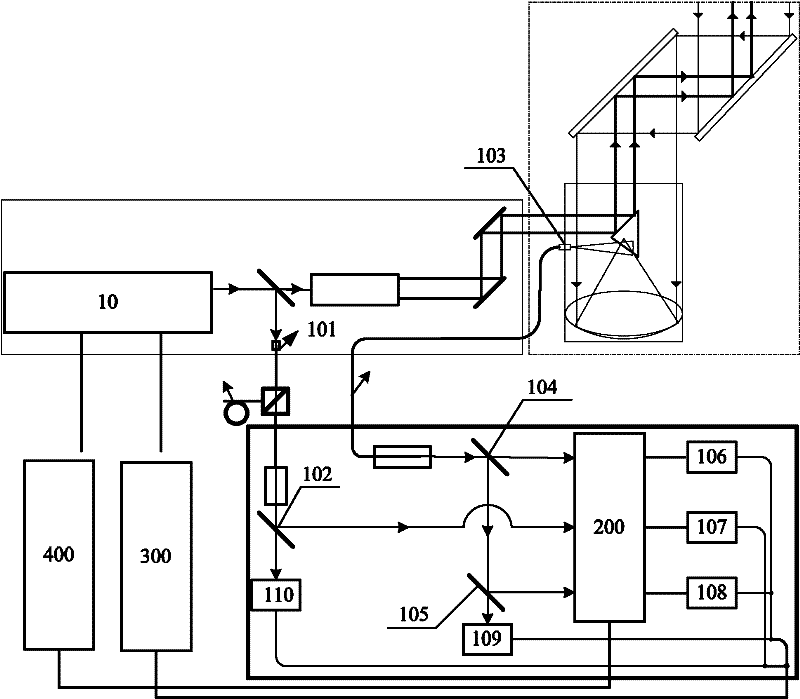
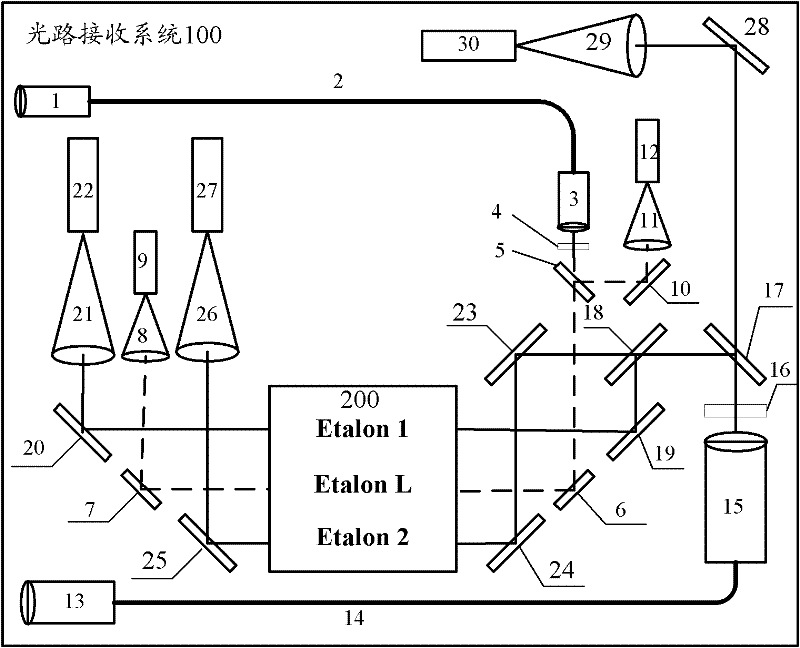
[0045] See figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic structural diagram of a Doppler wind lidar optical receiving system according to an embodiment of the present application. The system includes:
[0046] Receiving optical path system 100, FP etalon 200, detection acquisition system 300, and control system 400, wherein:
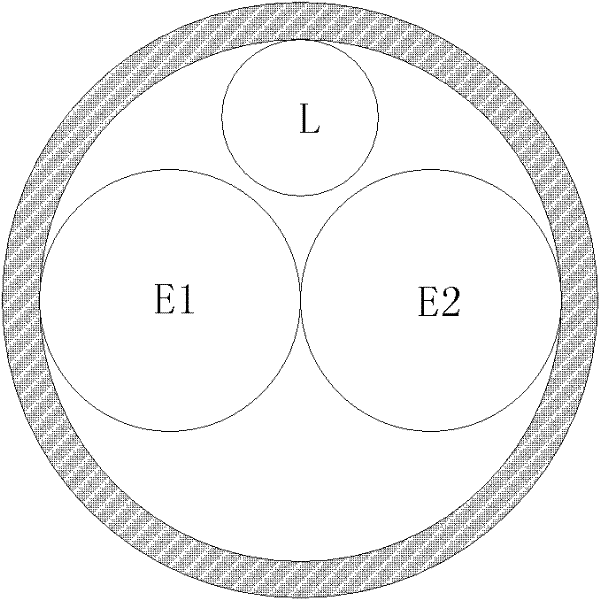
[0047] The FP etalon 200 includes three channels, namely the first signal channel E1, the second signal channel E2 and the locking channel L, wherein: the first signal channel E1 and the second signal channel E2 are located side by side on the center line of the FP etalon aperture, The locking channel L is located above the first signal channel E1 and the second signal channel E2, so tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com