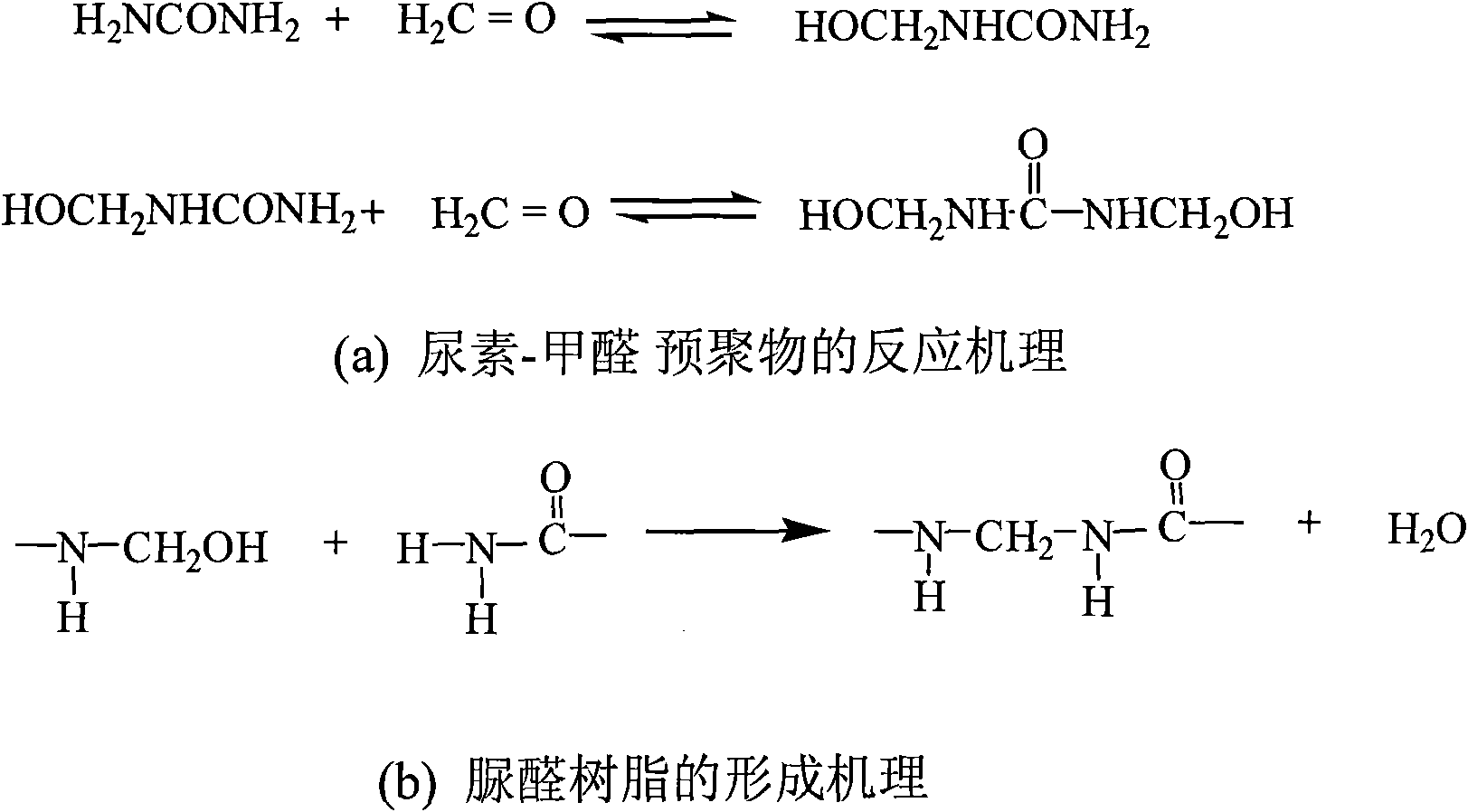
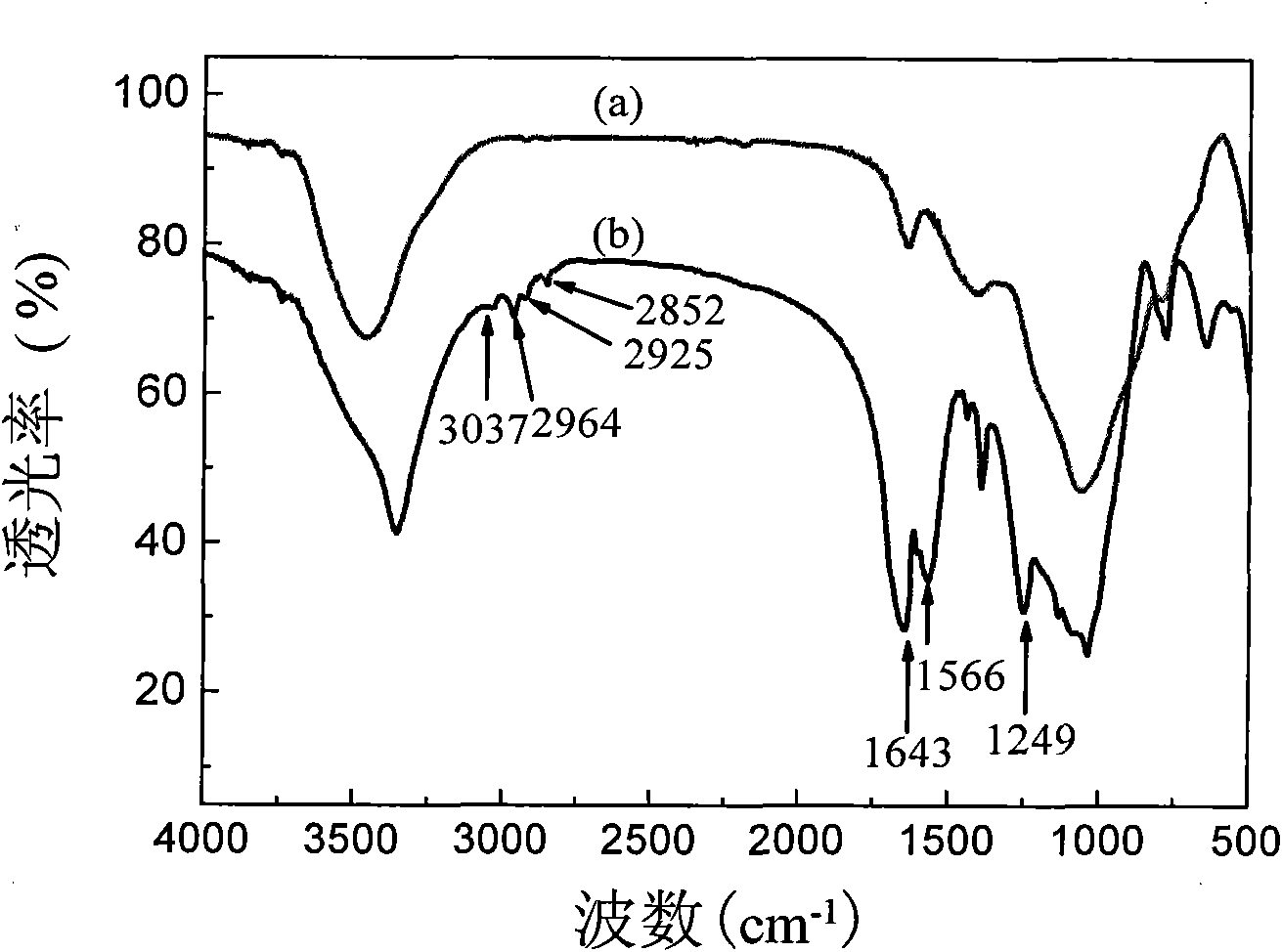
Method for in situ polymerization of surface modified hollow micro glass bead from urea-formaldehyde resin
A technology of hollow glass microspheres and urea-formaldehyde resin, which is applied in the treatment of dyed polymer organic compounds and fibrous fillers, etc., which can solve the problems of limited effect and reduction compared to the base material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0022] Example 2: 30g of urea, 60g of formaldehyde and 400g of distilled water are fully mixed, and after the urea is dissolved, the pH of the system is adjusted to 7.5-8 with triethanol diamine, and the urea-formaldehyde prepolymerization is obtained after keeping at 65-70°C for 2 hours thing. Then add 5g of Tween 60 and 95g of hollow glass microspheres into the above prepolymer, and adjust the pH of the system to 3-4 after fully stirring; after 1.5h, filter, wash and dry the white product to obtain the modified product. Hollow glass microspheres with a core-shell structure—urea-formaldehyde resin products.
example 2
[0023] Example 3: 30g of urea, 30g of formaldehyde and 400g of distilled water are fully mixed, and after the urea is dissolved, the pH of the system is adjusted to 7.5-8 with triethanol diamine, and the urea-formaldehyde prepolymerization is obtained after keeping at 65-70°C for 2 hours things. Then add 2g Tween into 80g and 80g hollow glass microspheres into the above prepolymer, adjust the pH of the system to 3~4 after stirring thoroughly; after 1.5h, filter, wash and dry the white product to obtain the modified Good, hollow glass microspheres with core-shell structure - urea-formaldehyde resin products.
example 3
[0024] Example 4: 30g of urea, 60g of formaldehyde and 400g of distilled water are fully mixed, and after the urea is dissolved, the pH of the system is adjusted to 7.5-8 with triethylene glycol diamine, and the urea-formaldehyde prepolymerization is obtained after keeping at 65-70°C for 2 hours thing. Then add 5g of Tween 85 and 105g of hollow glass microspheres into the above prepolymer, and adjust the pH of the system to 3-4 after fully stirring; after 1.5h, filter, wash and dry the white product to obtain the modified product. Hollow glass microspheres with a core-shell structure—urea-formaldehyde resin products.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com