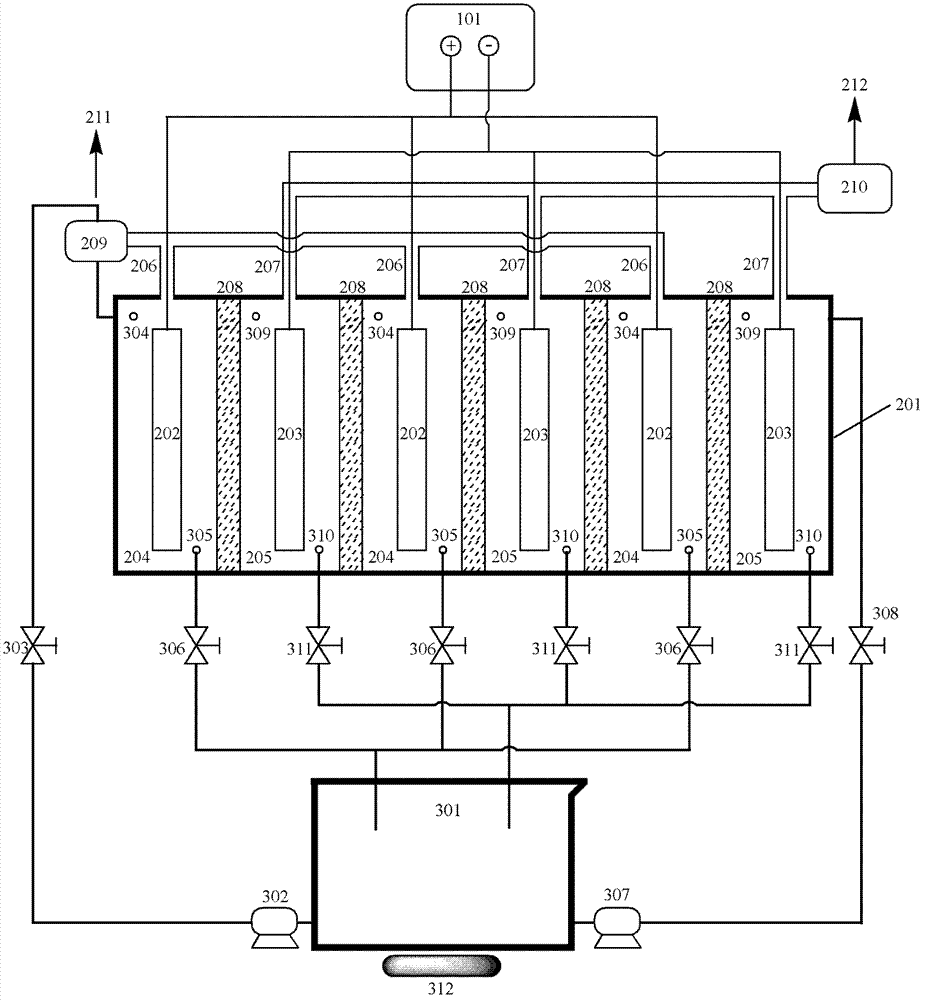
Device and method for treating waste water and preparing hydrogen simultaneously
A technology for wastewater and electrolysis devices, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0100] Example 1: Treatment of high-concentration organic wastewater containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
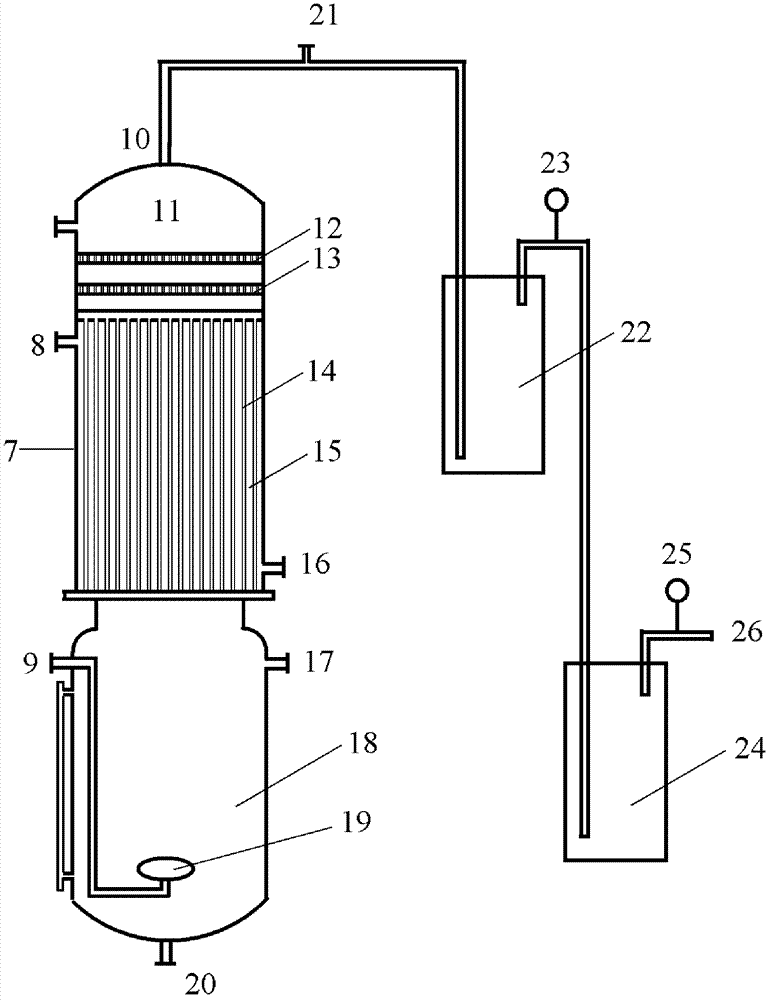
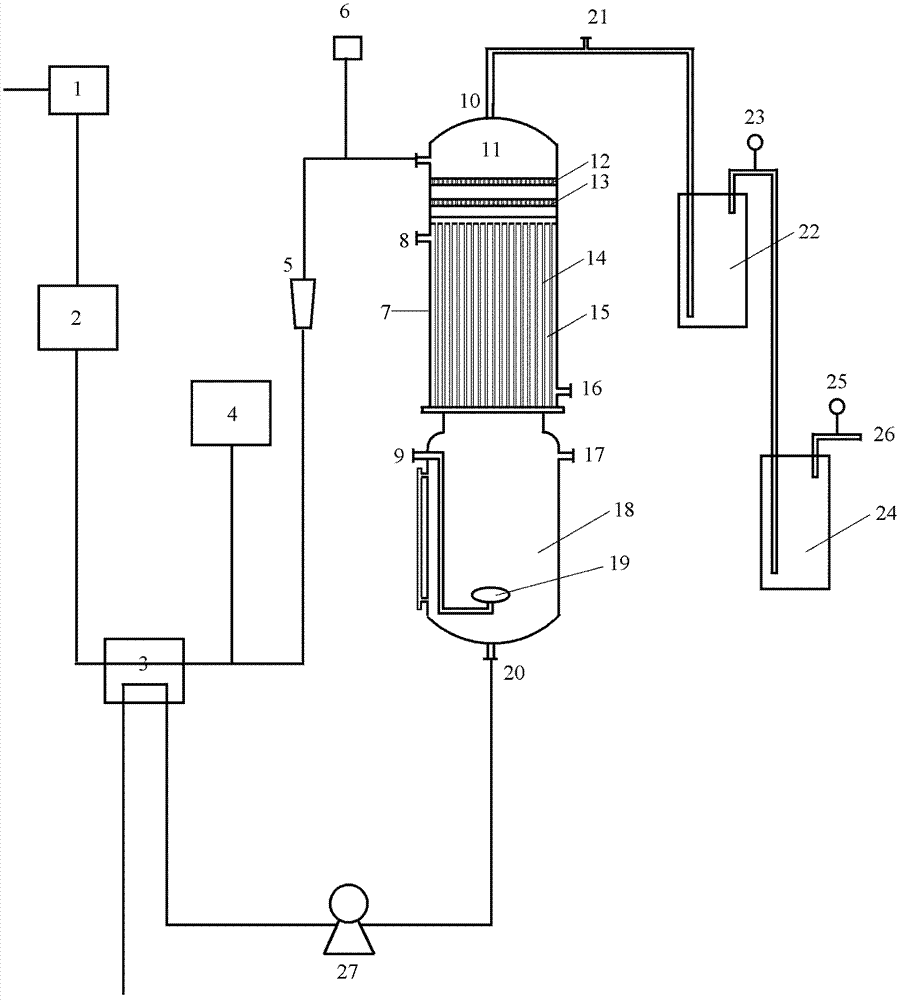
[0101] Using the device (attached image 3 ) to treat organic wastewater with a COD concentration of 13270mg / L, the voltage is 20V (the voltage fluctuates slightly during the treatment process), and the electrolyte is Na 2 SO 4 The concentration is 10%, after a period of electrolysis, the current is reduced from 0.7A to 0.05A, and the single-electrode COD removal rate and hydrogen production change with time are shown in Figure 7. The purity of hydrogen produced by the electrolysis cathode is greater than 97%, the average energy efficiency is 30%, and the hydrogen production volume is 3400mL.
Embodiment 2
[0102] Example 2: Wastewater containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and ammonia nitrogen mixture
[0103] Using the device (attached Figure 5 ) to treat organic wastewater with an ammonia nitrogen concentration of 1000mg / L and a COD concentration of 13331mg / L. The voltage is 10V. After a period of electrolysis, the current is reduced from 0.5A to 0.05A. The changes in ammonia nitrogen removal rate and hydrogen production over time are shown in the table Show. The single-electrode COD removal rate is 70%, the hydrogen production is 4460mL, and the energy efficiency is 25%.
[0104]
example 3
[0105] Example 3: Treatment of wastewater containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons under different electrolyte conditions
[0106] Using the device (attached image 3 ) to treat organic wastewater with a COD concentration of 13331mg / L, the electrolytes were 10% sodium sulfate and 10% sodium chloride, and the voltage was 4V. After a period of electrolysis, the current was reduced from 0.5A to 0.05A and 0.04A, and the energy efficiency was 33% and 25%, single-electrode COD removal rate and hydrogen production are shown in the table below. The ultraviolet spectrum of different electrolytes is shown in Figure 8. From the spectrum, it can be seen that different electrolytes have different mechanisms for the degradation of organic matter; the hydrogen production efficiency of sodium sulfate and sodium chloride as electrolyte electrolysis has decreased significantly over time. Hydrogen production efficiency is lower in NaCl electrolyte devices.
[0107]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com