Method for increasing incidence rate of isolated microspore embryos of Brassica campestris var. peruviridis
A technology of microspores and occurrence rate, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low culture efficiency and achieve the effect of improving the embryo formation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The method for improving the induction rate of embryos cultured with free microspores of Chinese cabbage includes:
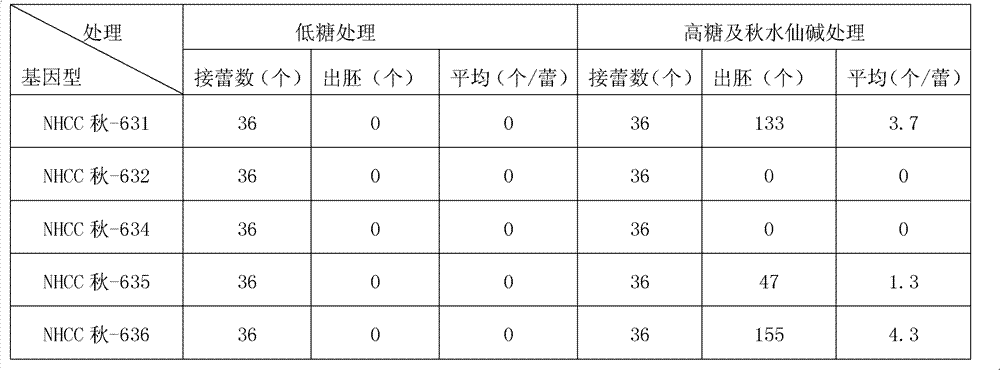
[0021] 1 Genotype: NHCC Autumn-631; NHCC Autumn-632; NHCC Autumn-634; NHCC Autumn-635; NHCC Autumn-636.
[0022] 2 Configuration and sterilization of medium
[0023] The basic medium is NLN medium with halved macroelements, that is, 1 / 2NLN medium;
[0024] ① High-sugar medium (1 / 2NLN-17): 1 / 2NLN+17% sucrose+0.8mg / L colchicine, pH 6.0;
[0025] ②Low-sugar medium (1 / 2NLN-13): 1 / 2NLN+13% sucrose+0.8g / L activated carbon with a pH of 6.0;
[0026] The above medium was sterilized by suction filtration through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane.
[0027] ③ microspore extract (B 5 -13 medium): B 5 Basic medium + 13% sucrose, pH 5.8;
[0028] ④Differentiation medium: B 5 Basic medium+13% sucrose+0.2mg / L 6-BA+0.02mg / L NAA+0.8% agar+0.5g / L activated carbon, pH 5.8;
[0029] The microspore extract and differentiation culture above are sterilized at 121°C and 1.1M...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The method for improving the induction rate of embryos cultured with free microspores of Chinese cabbage includes:
[0043] 1 Genotype: NHCC Autumn-633; NHCC Autumn-607; Elysium.
[0044] 2 Materials collection: Flower buds with a length of 2-3mm were selected in January 2011, and the flower buds were kept moist and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for 24 hours.
[0045] 3 Disinfection: The selected flower buds are disinfected with 75% alcohol for 30s, and then sterilized with 0.1% HgCl 2 Disinfect for 6 minutes, and finally rinse with sterile water 3 times for use;
[0046] 4 Separation and purification of microspores: put the sterilized flower buds in a mortar, add microspore extract (B 5-13 culture medium), the microspores were dissociated by the extrusion method, then filtered with a 400-mesh filter, the filtrate was collected in a centrifuge tube, centrifuged at 800rpm for 5min, the supernatant was discarded, and repeated 3 times;
[0047] 5 Suspend the purified ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] The method for improving the induction rate of embryos cultured with free microspores of Chinese cabbage includes:
[0063] 1 Genotype: NHCC Autumn-633.
[0064] 2 Materials collection: Flower buds with a length of 2-3mm were selected in January 2011, and the flower buds were kept moist and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for 24 hours.
[0065] 3 Disinfection: The selected flower buds are disinfected with 75% alcohol for 30s, and then sterilized with 0.1% HgCl 2 Disinfect for 6 minutes, and finally rinse with sterile water 3 times for use;
[0066] 4 Separation and purification of microspores: put the sterilized flower buds in a mortar, add microspore extract (B 5 -13 culture medium), the microspores were dissociated by the extrusion method, then filtered with a 400-mesh filter, the filtrate was collected in a centrifuge tube, centrifuged at 800rpm for 5min, the supernatant was discarded, and repeated 3 times;
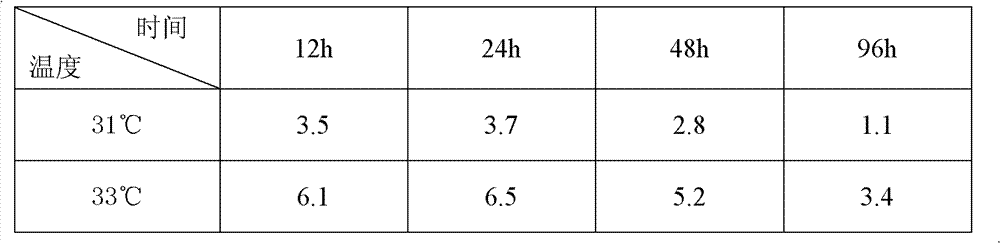
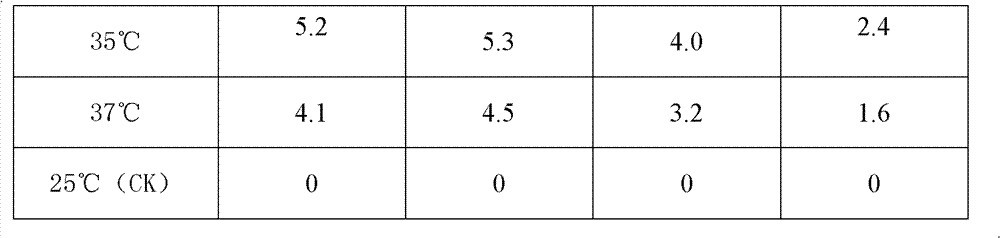
[0067] 5. High sugar and colchicine treatment: suspend ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com