LED (Light-Emitting Diode) heat dissipation base plate, LED packaging structure, and manufacturing method of LED heat dissipation base plate and LED packaging structure
A technology for a heat dissipation substrate and a manufacturing method, which is applied in the directions of electrical components, electrical solid devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of complicated manufacturing process of silicon substrate, unsuitable for popularization and use, complicated design, etc., and achieves clear steps, simple structure, and easy operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] (Example 1, LED heat dissipation substrate, using SOI wafer as the base material)
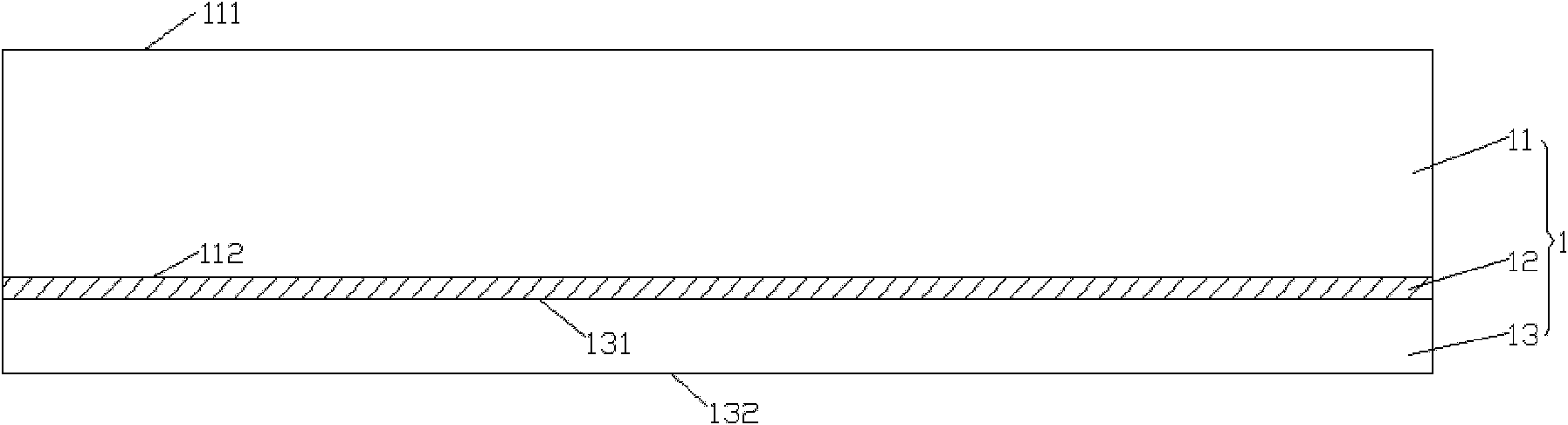
[0089] See Figure 9 , an LED heat dissipation substrate in this embodiment is obtained by etching an SOI wafer 1 as a base material. The structure of the SOI wafer 1 see figure 1 , is an etch stop layer 12 made of silicon dioxide between the upper layer 11 and the bottom layer 13 made of silicon. The thickness of the upper layer 11 is 300-500um; the thickness of the etching stop layer 12 is 1-2um, which is sufficient to resist the double-side etching operation; the thickness of the bottom layer 13 is 50-200um.
[0090] Such as Figure 9 As shown, the specific structure of the LED heat dissipation substrate is: an upper layer 11 of silicon material, which includes a silicon cup 4 formed by etching to the etching stop layer 12; an etching stop layer of silicon dioxide material located on the lower surface of the upper layer 11 12. A bottom layer 13 made of silicon, including at least ...
Embodiment 2
[0091] (Example 2, LED heat dissipation substrate, using SOI wafer as the base material)
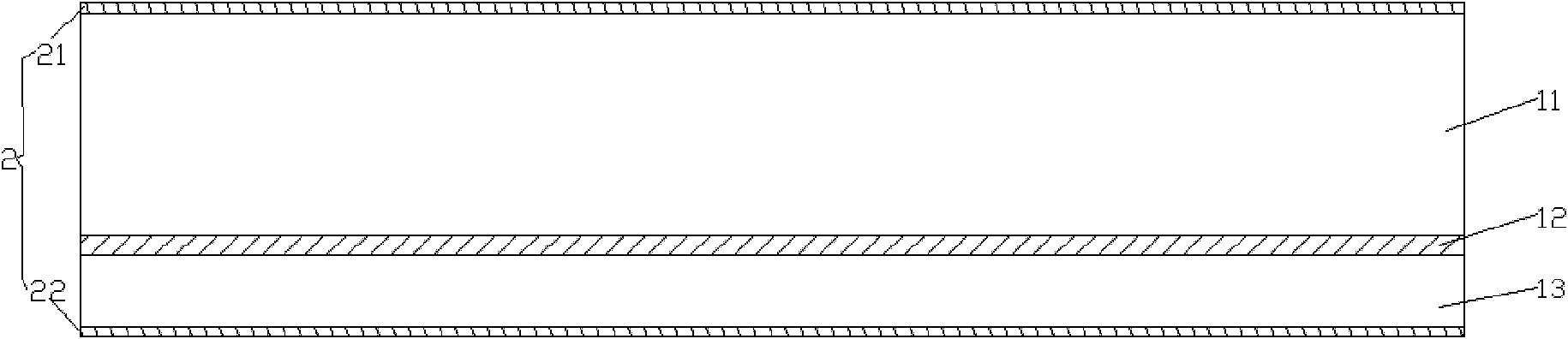
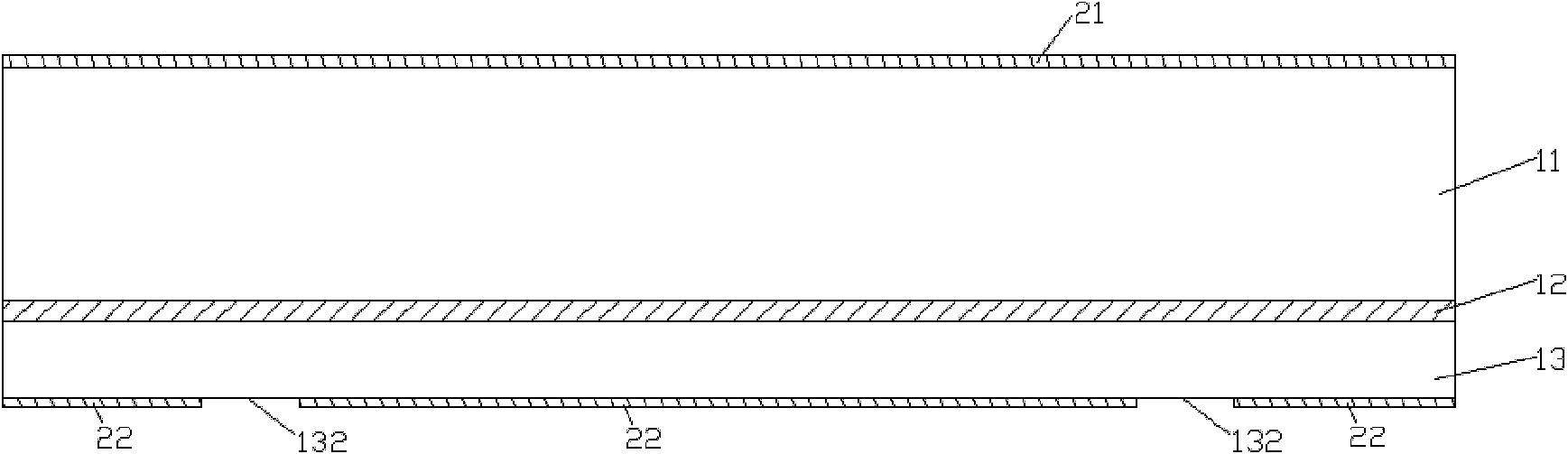
[0092] See Figure 10 On the basis of Embodiment 1, the LED heat dissipation substrate of this embodiment further includes an adhesive layer 6 made of Sn / Au alloy or silver paste on the bottom of the silicon cup 4 and the lower surface of the bottom layer 13 . Wherein the adhesive layer 6 at the bottom of the silicon cup 4 is used to bind the high-power LED chip 7; the adhesive layer 6 on the lower surface of the bottom layer 13 is used to connect with other circuit boards to form an effective mechanical binding and heat conduction path .
Embodiment 3
[0093] (Example 3, LED heat dissipation substrate, using a single crystal silicon wafer as the base material)
[0094] See Figure 21 , an LED heat dissipation substrate in this embodiment is obtained by etching a single crystal silicon wafer 20 as a base material. Specific structural parts of the monocrystalline silicon wafer 20 Figure 13 , including a first surface 201 and a second surface 202 .
[0095] Such as Figure 21 As shown, the specific structure of the LED heat dissipation substrate is: a silicon cup 4 formed by etching on the first surface 201; at least two guide holes 3 formed by etching on the second surface 202; the guide holes 3 are filled with metal conductors 5. The diameter of the upper end surface 31 of the guide hole 3 is ≥100um, which is used for welding the pins of high-power LED chips. The depth of the guide hole 3 is 50-200um. The guide hole 3 can be in various shapes, such as square, rectangle, trapezoid, etc. Moreover, the number of the guide ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com