Method for etching edges of solar battery
A solar cell, edge technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve the problems of over-etching, high equipment cost, difficult control, etc., to achieve parallel resistance and fill factor improvement, leakage current The effect of reduced, high parallel resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0010] In order to make the present invention more comprehensible, a preferred embodiment is described in detail below with accompanying drawings.
[0011] The invention provides a solar cell edge etching method, the steps of which are:
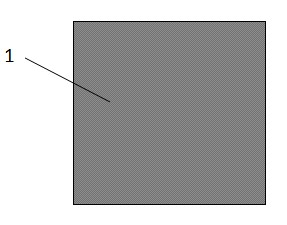
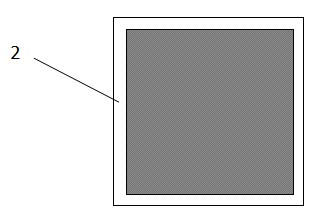
[0012] Step 1, providing a diffused silicon wafer, Figure 1A Shown is a diffused silicon wafer 1 whose surface is covered with dark phosphosilicate glass. Perform a plasma etching on it to remove the phosphosilicate glass around the silicon wafer. Figure 1B Shown is the silicon wafer 2 after plasma etching, and the phosphosilicate glass with a width of 1-2 mm has been etched away around it, exposing the silicon body.
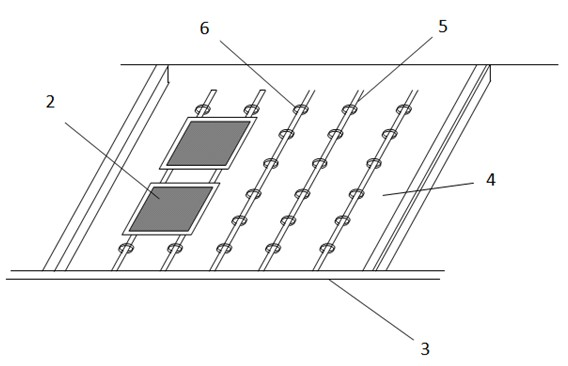
[0013] Step 2, performing wet etching on the silicon wafer after plasma etching according to a conventional process. figure 2 Shown is a typical wet etching tank, the tank body 3 is a part of the wet etching machine, containing etching solution 4, its composition is a mixed solution of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com