Manufacturing method for semiconductor device
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., to achieve the effect of improving HCI effect, low cost, and improving interface quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
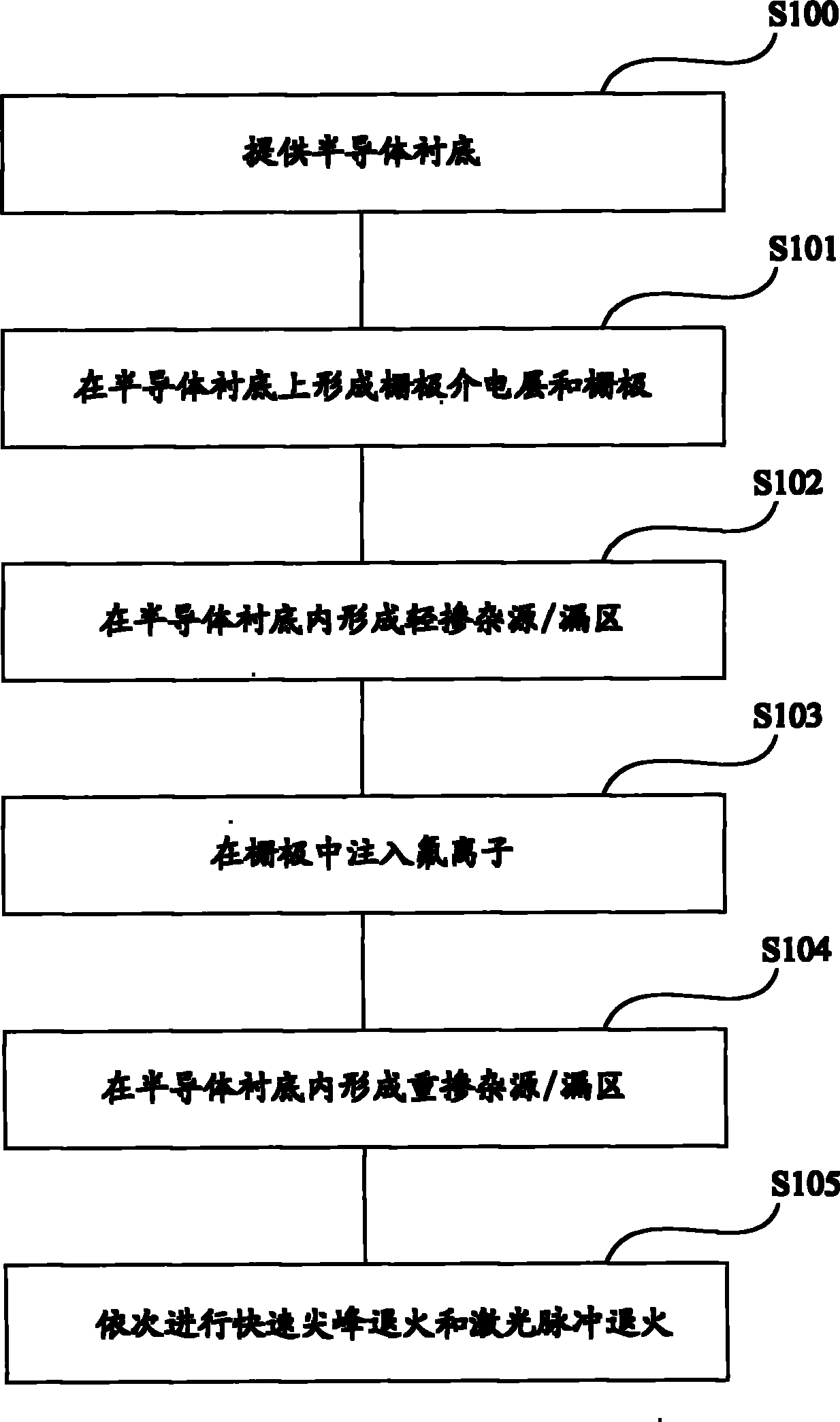
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0033] S100, providing a semiconductor substrate;
[0034] S101, forming a gate dielectric layer and a gate on the gate dielectric layer on the semiconductor substrate;
[0035] S102, performing lightly doped ion implantation in the semiconductor substrate on both sides of the gate to form lightly doped source / drain regions;
[0036] S103, implanting fluorine ions into the gate;
[0037] S104, performing heavily doped ion implantation in the semiconductor substrate on both sides of the gate to form heavily doped source / drain regions;
[0038] S105, performing rapid spike annealing and laser pulse annealing in sequence.
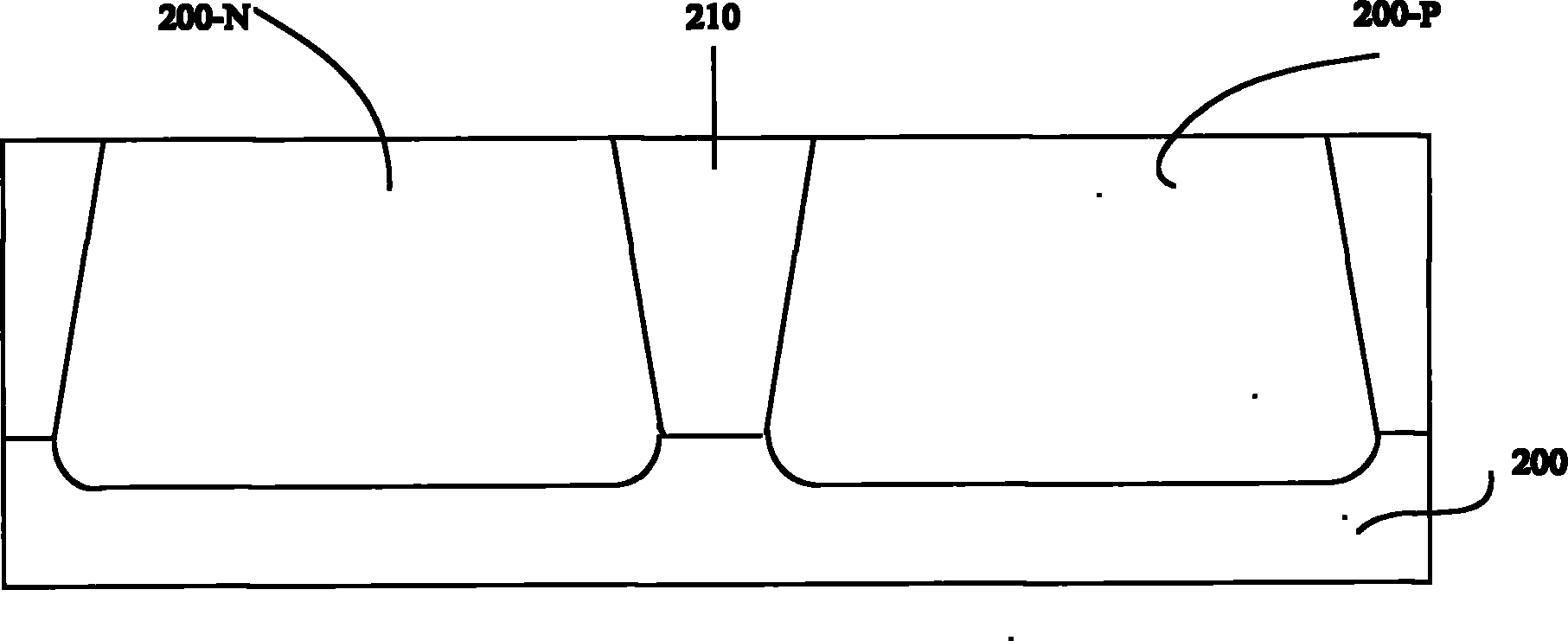
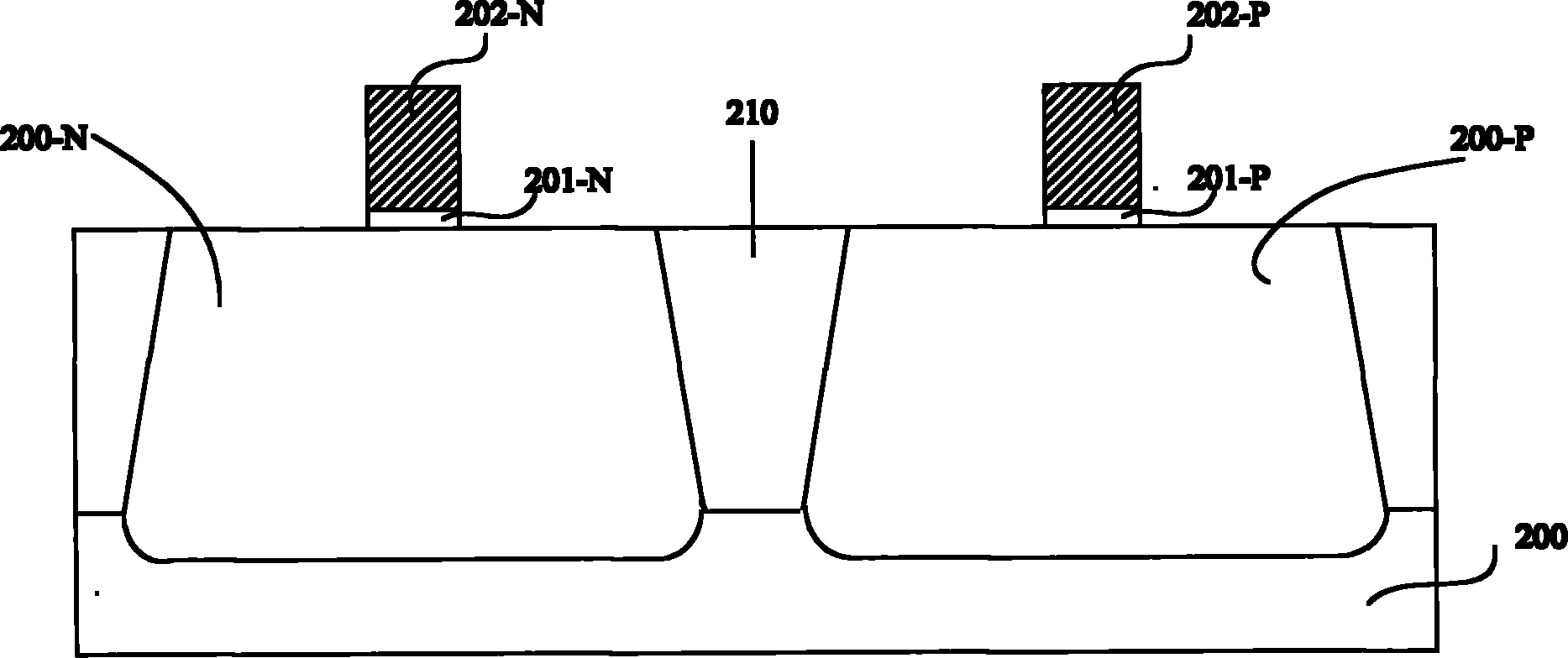
[0039] refer to figure 2 , first execute step S100 to provide a semiconductor substrate 200 . Wherein, the semiconductor substrate 200 includes: an N-type doped well 200 -N, a P-type doped well 200 -P and an isolation...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Such as Figure 10 As shown, the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0061]S300, providing a semiconductor substrate;
[0062] S301, forming a gate dielectric layer and a gate on the gate dielectric layer on the semiconductor substrate;
[0063] S302, performing lightly doped ion implantation in the semiconductor substrate on both sides of the gate to form lightly doped source / drain regions;
[0064] S303, performing heavily doped ion implantation in the semiconductor substrate on both sides of the gate to form heavily doped source / drain regions;
[0065] S304, implanting fluorine ions into the gate;
[0066] S305, performing rapid spike annealing and laser pulse annealing in sequence.
[0067] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 lies in the steps of "implanting heavily doped ions into the semiconductor substrate on both sides of the gate to form heavily doped source / drain regions" a...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Such as Figure 11 As shown, the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0071] S400, providing a semiconductor substrate;
[0072] S401, forming a gate dielectric layer and a gate on the gate dielectric layer on the semiconductor substrate;
[0073] S402, implanting fluorine ions into the gate;
[0074] S403, performing lightly doped ion implantation in the semiconductor substrate on both sides of the gate to form lightly doped source / drain regions;
[0075] S404, performing heavily doped ion implantation in the semiconductor substrate on both sides of the gate to form heavily doped source / drain regions;
[0076] S405, performing rapid spike annealing and laser pulse annealing in sequence.
[0077] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is only in the steps of "implanting lightly doped ions into the semiconductor substrate on both sides of the gate to form lightly doped source / drain region...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com