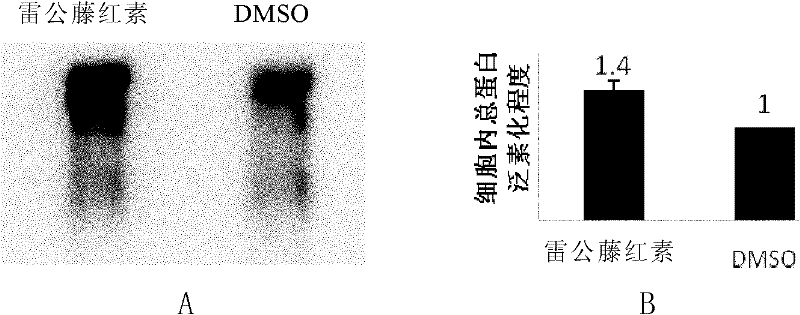
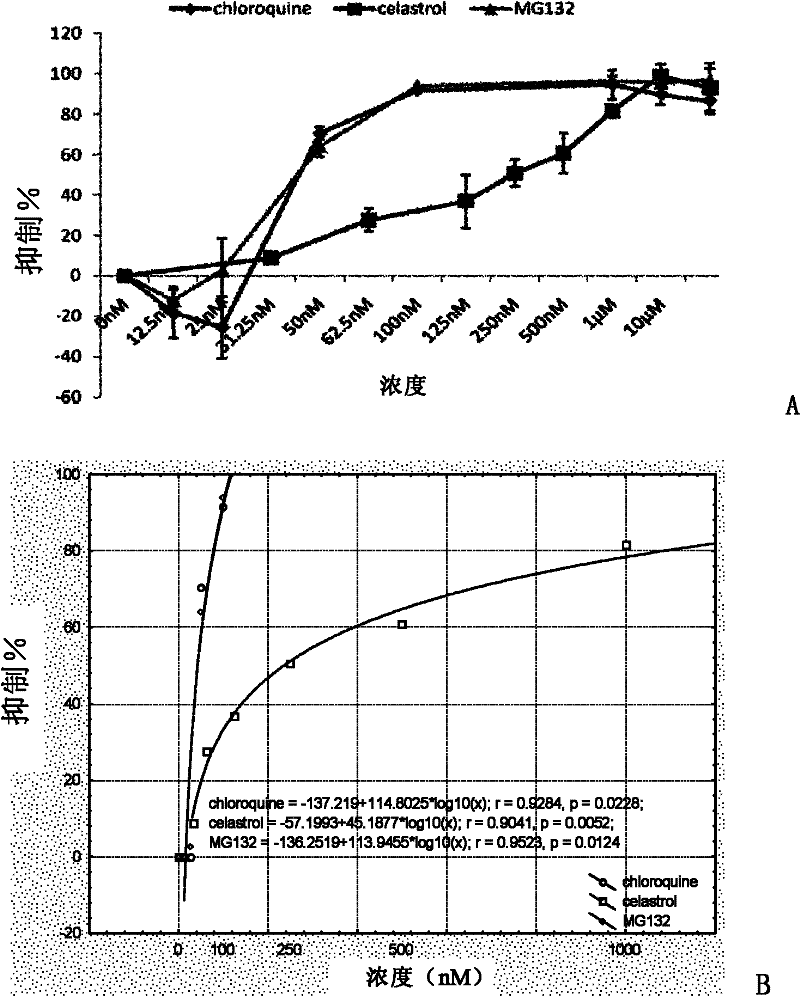
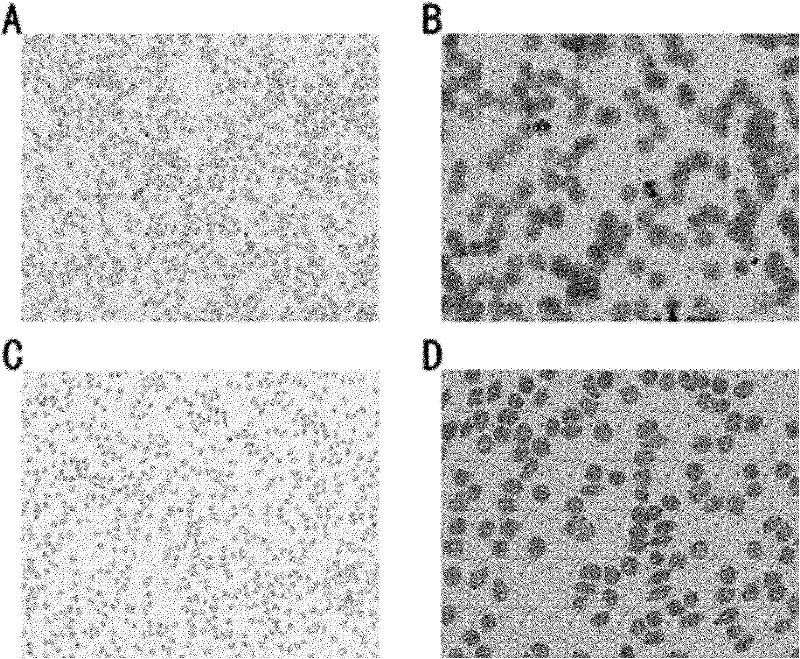
Antimalarial drug taking protein degradation pathway as target
A drug, proteasome technology, used in drug combinations, anti-infective drugs, pharmaceutical formulations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Embodiment 1: Plasmodium proteasome inhibition experiment
[0066] I. The experimental materials used in this embodiment include: RPMI 1640 medium (GibcoBRL company), rabbit serum (from rabbits, self-made), mouse anti-polyubiquitinylated protein monoclonal antibody (Enzo company), PVDF membrane (MILLIPORE company ), NC membrane (BIO-RAD company), SuperSignal chemiluminescence liquid (Thermo company). Plasmodium Hainan strain (FCC1 / HN) came from the Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention; human red blood cells (type O) came from Shanghai Ruijin Hospital; tripterygium came from aladdin company.
[0067] Other unmentioned experimental materials, instruments, reagents, etc. are various materials, instruments and reagents routinely used in this field.
[0068] II. the experimental method of the present embodiment is as follows:
[0069] (1) Plasmodium culture
[0070]Plasmodium culture conditions are RPMI 1640 medium, add 22mM H...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Embodiment 2: tripterine inhibits the proliferation of Plasmodium
[0136]Commonly used antimalarial drug screening methods include in vitro microtest (WHO microtest, also known as WHO schizont maturation assay) recommended by WHO, isotopic microtest (isotopic microtest), lactate dehydrogenase method (parasite lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH), double-site enzyme-linked lactate dehydrogenase immunodetection assay (DELI), histidine-rich protein II (HRP2) and fluorescence assay method (fluorescence assay, FA) and so on. Among them, in vitro micromethod and isotope microtest method are antimalarial drug screening and sensitivity detection methods recommended by WHO. The present invention uses these two methods respectively to detect the screening platform for the influence of the compound to be tested on the proliferation of Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. In vitro micromethod [see Rieckmann, K.H., etc., Drug Sensitivity of Plasmodium-Falciparum-Invitro Microtechnique.Lancet,...
Embodiment 3
[0139] Embodiment 3: animal experiments
[0140] Plasmodium P.berghei NK65 strain and wild-type mouse BALB / c (from Shanghai Experimental Animal Center) were used in this experiment.
[0141] Inoculate 10 times per week intraperitoneally 6 The way parasites infect blood cells maintain passage of Plasmodium parasites in mice.
[0142] In vivo anti-malarial experimental steps are as follows:
[0143] The mice were randomly divided into 5 groups, and 10 groups were inoculated intraperitoneally 6 Plasmodium infection was carried out in the manner of carrying worms infecting blood cells, and at the same time, group drug treatment was started. The method of administration is tail vein injection. 5 groups of dosages are respectively negative control (the PBS solution of DMSO), positive control (chloroquine of 50mg / kg dosage), experimental group (50mg / kg, 150mg / kg, tripterine of 500mg / kg dosage). Dose every 24 hours. On the 4th, 7th, and 15th days, rat blood was collected, smeare...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com