Method for removing phosphorus by utilizing waste cement
A cement and wastewater technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of susceptibility to temperature, poor stability, etc. Good phosphorus removal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] A kind of method utilizing waste cement to remove phosphorus, its step is:
[0021] A: Weigh cement powder in different amounts (0.2g, 0.3g, 0.4g, 0.6g, 0.8g, 1.0g, 1.2g, 1.5g, 2.0g) into a 250mL conical flask;
[0022] B: Add 100mL of waste water with a phosphorus concentration of 25mg / L to each Erlenmeyer flask, seal the Erlenmeyer flask and place it in a constant temperature oscillator, and set the temperature at 25±1°C;
[0023] C: After shaking for 24±1h, centrifuge to measure the concentration of TP in the supernatant.
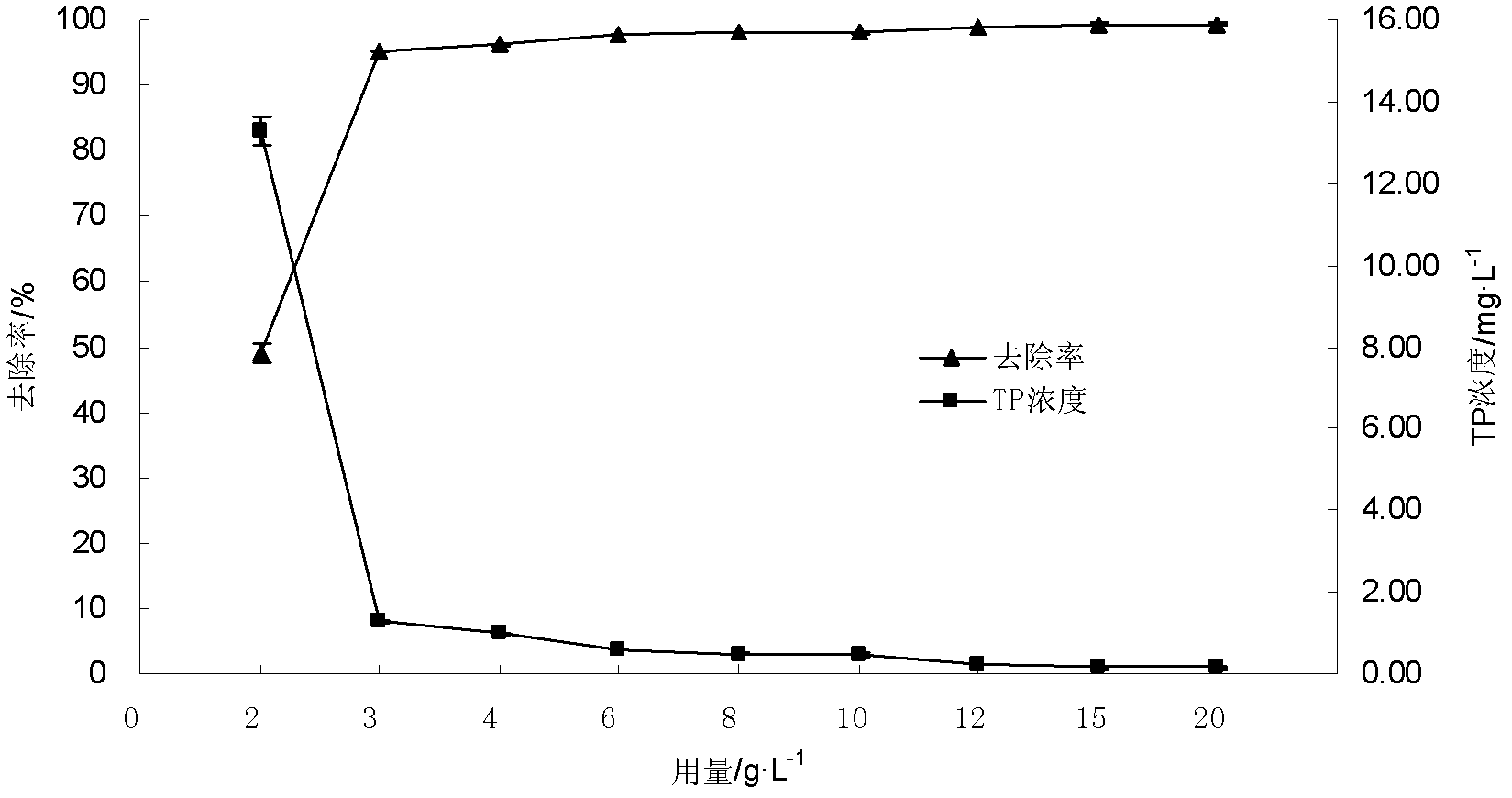
[0024] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that with the increase of the amount of cement powder, the concentration of phosphorus (TP) in the solution decreases gradually, and the removal rate increases gradually. When the dosage increased from 2g / L to 3g / L, the phosphorus (TP) removal rate rose rapidly from 49.06% to 95.13%; when the dosage continued to increase, the phosphorus (TP) removal rate tended to be stable. The amount of cement powder i...
Embodiment 2
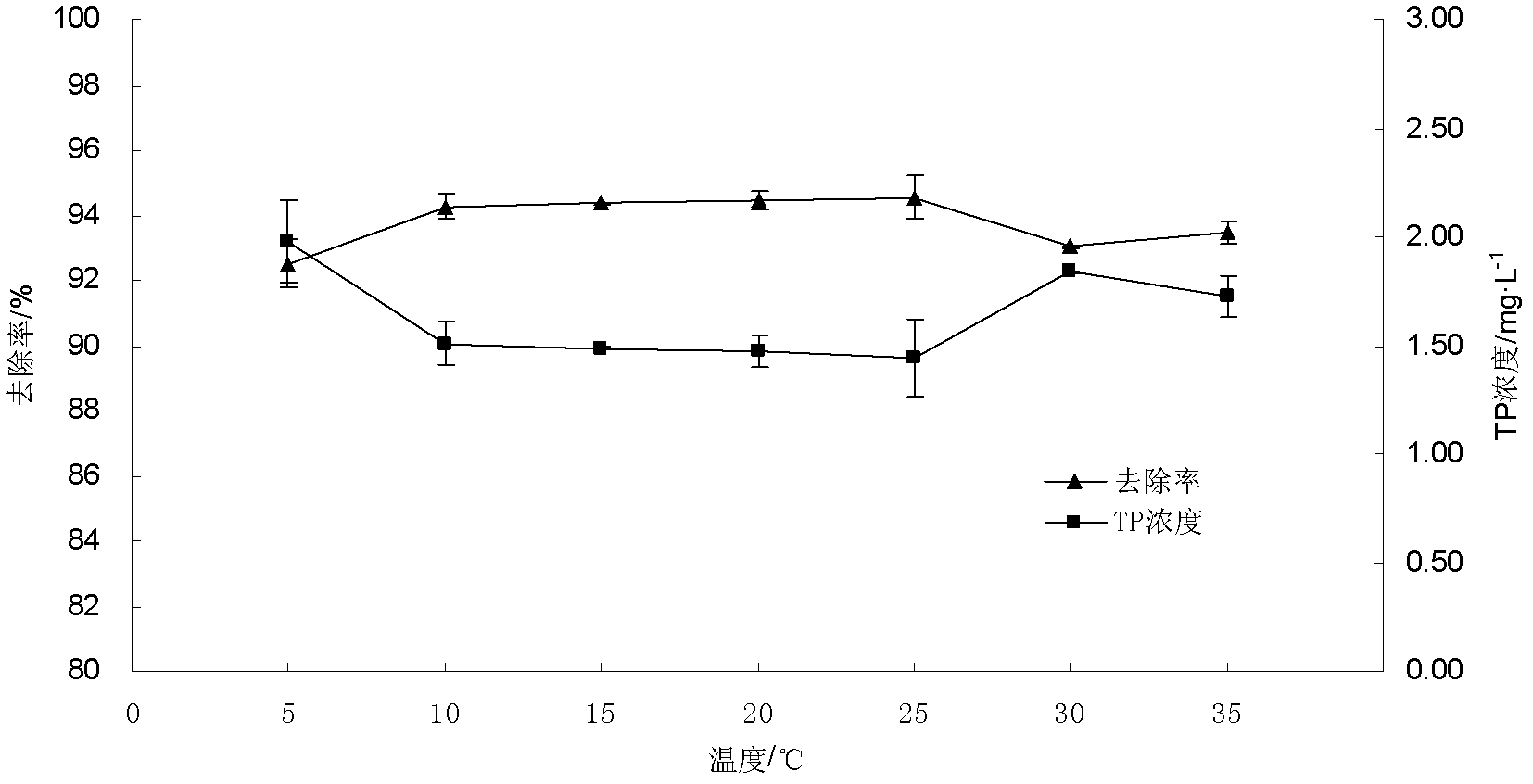
[0026] The difference from Example 1 is: 0.3g of cement powder was weighed into a 250mL conical flask, and 100mL of wastewater with a phosphorus concentration of 25mg / L was added. Set different temperatures (5°C or 10°C or 15°C or 20°C or 25°C or 30°C or 35°C), the effect of temperature on phosphorus removal in wastewater is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0027] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that temperature has a certain influence on the removal of phosphorus in water by cement powder. When the temperature is 5℃, the removal rate is the lowest, which is 92.51%. When the temperature ranged from 5°C to 25°C, the removal rate of TP increased from 92.51% to 94.54%. When the temperature continued to increase, the removal rate began to decrease. Therefore, it is considered that the optimum adsorption temperature is 22-26°C.
Embodiment 3
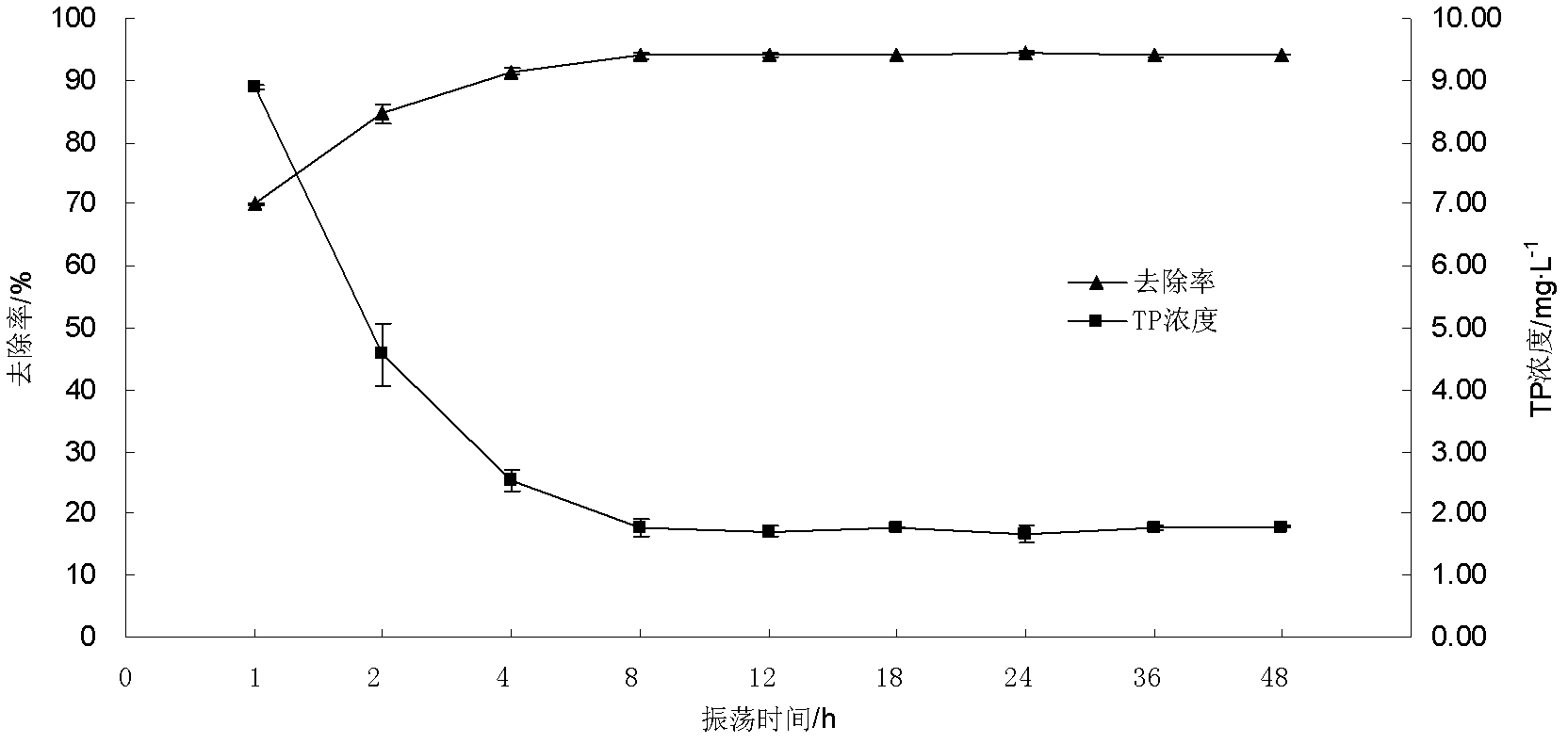
[0029] The difference from Example 1 is: Weigh 0.3 g of cement powder into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, and add 100 mL of a solution with a phosphorus concentration of about 25 mg / L. Set different shaking time (1h or 2h or 4h or 8h or 12h or 18h or 24h or 36h or 48h), centrifuge to measure the TP concentration in the supernatant. The effect of shaking time on phosphorus removal as image 3 shown.
[0030] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that with the extension of the oscillation time, the removal rate of TP gradually increases. When the time was extended from 1h to 8h, the removal rate increased significantly, from 69.98% to 94.02%; and from 8h to 48h, the removal rate did not change significantly, indicating that the adsorption of cement to phosphorus had basically reached saturation when the oscillation time was 8h state. Therefore, it is considered that the best oscillation time is 7-9h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com