Method for removing glyphosate in water body by using montmorillonite
A technology of glyphosate and montmorillonite, which is applied in the field of water pollution treatment, can solve the problems of slow treatment rate and external energy, and achieve the effects of rapid reaction, low cost and high adsorption efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
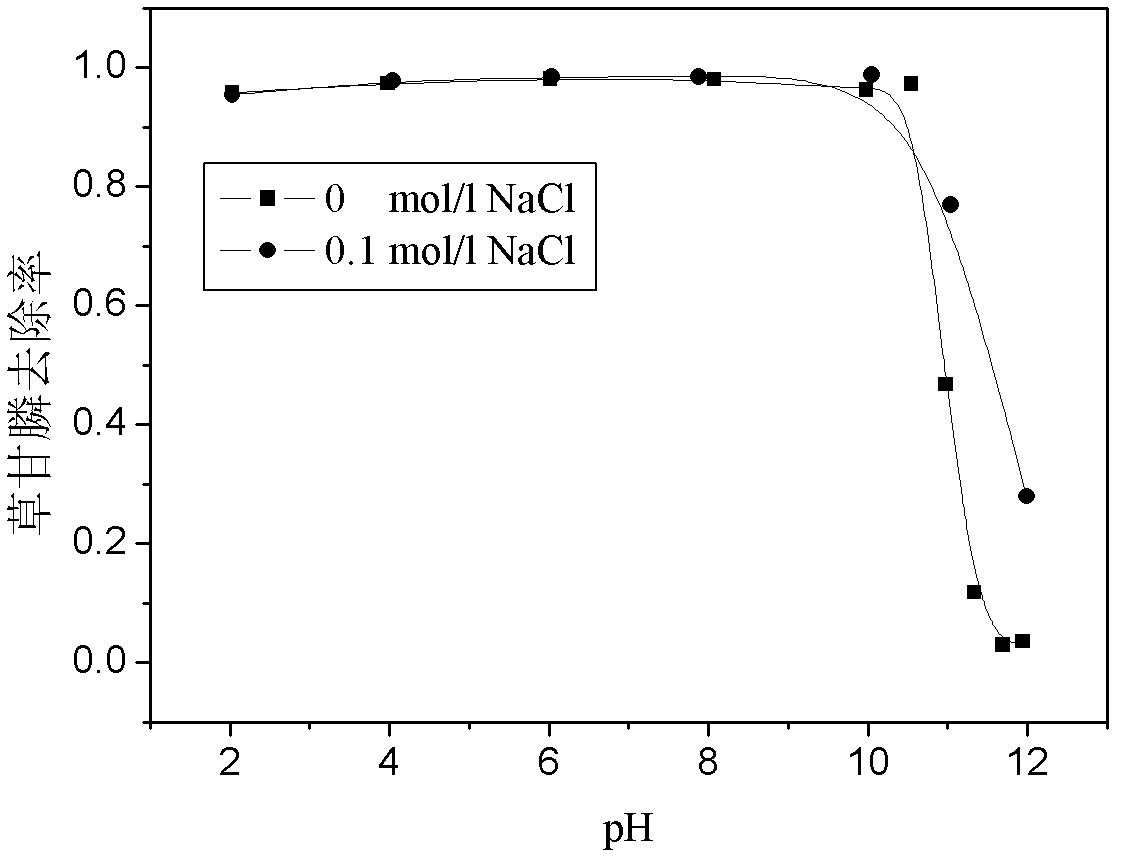
[0028] The montmorillonite is purchased from Inner Mongolia. It is a calcium-based montmorillonite with a purity of 95%, a cation exchange capacity (CEC) of 115-139mmo1 / 100g, and a grinding particle size of ≤100 mesh. Dosing at a dose of 2 g / L into an aqueous solution containing 350 mg / L glyphosate and pH 2.95, adding FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O to 0.6 g / L, shake at 100 r / min at 25°C for 2 hours. The results showed that the removal rate of glyphosate in this state was 96.67%. Under the same conditions, the initial pH of the solution was adjusted with 0.1 mol / L HCl and NaOH so that the initial pH was 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, respectively, and the corresponding removal rates were 95.76%, 97.32%, 98.05%, 98.05% %, 96.29%, 3.51%.
[0029] It can be seen that within the initial pH of 2~10, the pH basically has little effect on the removal rate of glyphosate in water, but if the initial pH reaches 12, this method will almost lose its effect on glyphosate, and the removal rate will drop sharply to ...
Embodiment 2
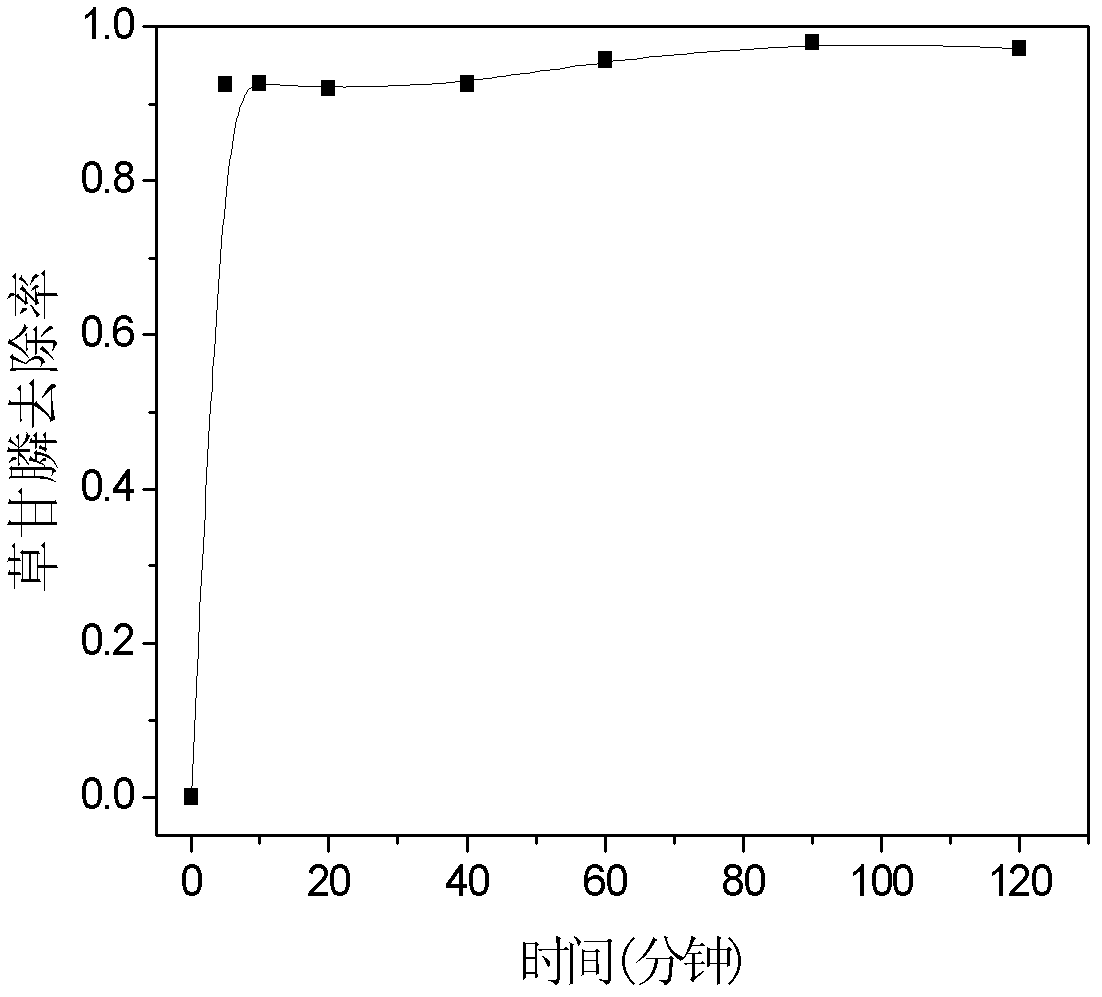
[0031] The montmorillonite was purchased in Inner Mongolia. It is a calcium-based montmorillonite with a purity of 95%, a CEC of 115-139mmo1 / 100g, and a grinding particle size of ≤100 mesh. Dosing at a dose of 2 g / L into an aqueous solution containing 350 mg / L glyphosate, pH 2.95 (natural pH), adding FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O to 0.6 g / L, shake at 100 r / min at 25°C for 5 minutes. The results showed that the removal rate of glyphosate in this state was 92.51%. Under the same conditions, the oscillation time was changed to 10, 20, 40, 60, 90, and 120 min, and the corresponding removal rates were 92.62%, 91.96%, 92.60%, 95.72%, 98.02%, and 97.24%, respectively.
[0032] It can be seen that the reaction reaches equilibrium within 5 minutes, which is very fast and easy to apply in actual wastewater engineering.
Embodiment 3
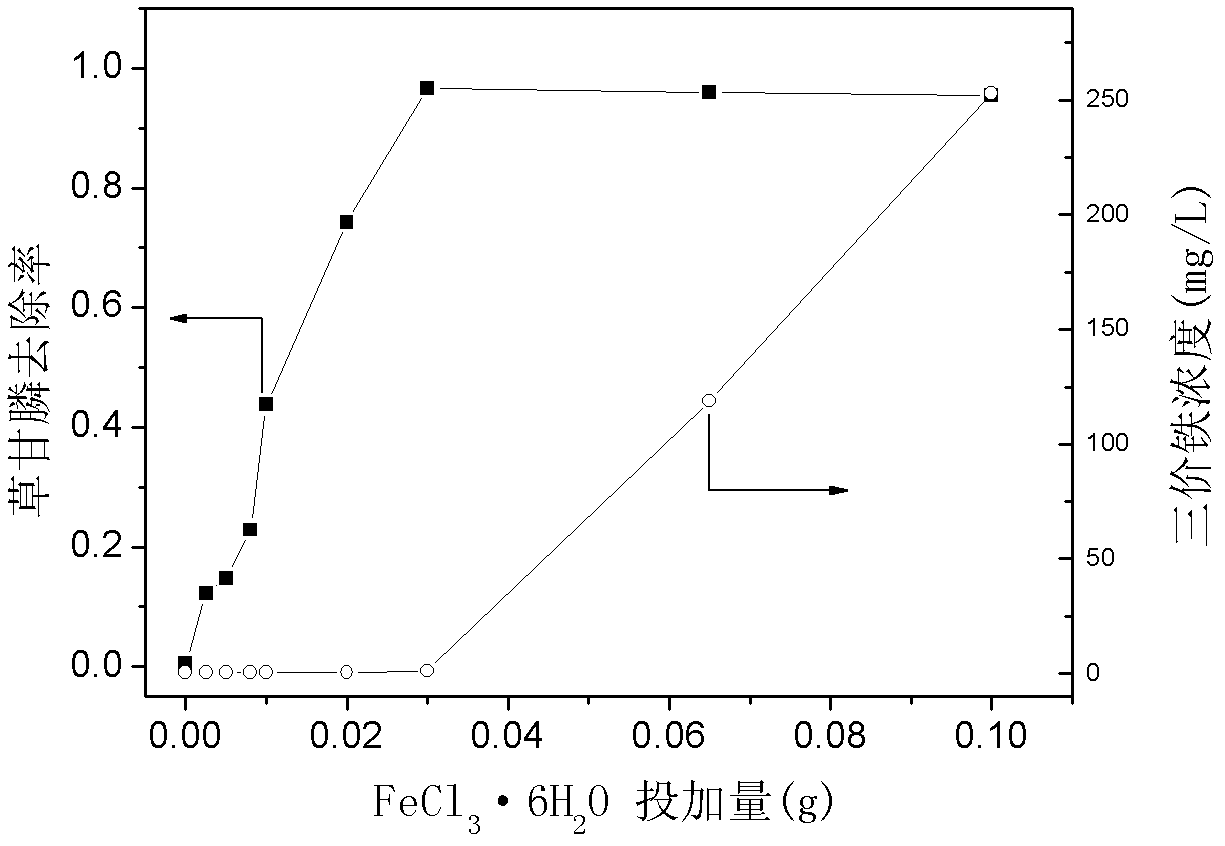
[0034] The montmorillonite was purchased in Inner Mongolia. It is a calcium-based montmorillonite with a purity of 95%, a CEC of 115-139mmo1 / 100g, and a grinding particle size of ≤100 mesh. Dosing at a dose of 2 g / L into an aqueous solution containing 350 mg / L glyphosate and pH 2.95, adding FeCl 3 ·6H 2 From 0 to 0.6 g / L, shake at 100 r / min at 25°C for 2 hours. The results showed that the removal rate of glyphosate in this state was 96.67%. Under the same conditions, the added FeCl 3 ·6H 2 The O content was adjusted to 0.05, 0.10, 0.16, 0.20, 0.40, 1.30, and 2 g / L, and the corresponding removal rates were 12.26%, 14.74%, 22.82%, 43.78%, 74.28%, 95.94%, and 95.47%, respectively.
[0035] It can be seen that FeCl 3 ·6H 2 The amount of O added is a controlling factor, FeCl 3 ·6H 2 The amount of O added has a linear relationship with the removal amount of glyphosate, which is determined by the removal mechanism, and FeCl can be adjusted in the application 3 ·6H 2 The amo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com