Hib polysaccharide purifying technology
A polysaccharide and process technology, applied in the field of Hib polysaccharide purification process, can solve the problems of many steps, difficult to remove nucleic acid, large difference in stability between batches, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing protein impurities, easy enrichment and harvesting, and saving usage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
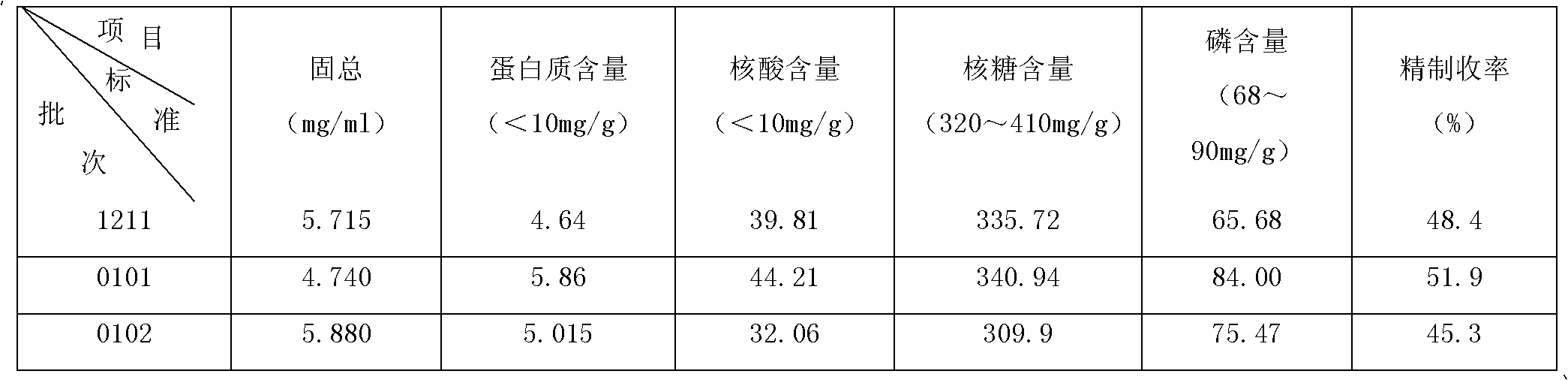
[0031] Hib polysaccharide purification process, which includes the following eight steps: collecting polysaccharide complex precipitates, centrifuging to collect rough sugar precipitates, washing rough sugar precipitates, drying raw sugar, dissolving raw sugar, phenol extraction, phenol removal, and refining refined sugar:
[0032] S1: Collect the polysaccharide complex precipitate:
[0033] S11: Centrifuge the sterilized culture solution, remove bacteria by centrifugation, and collect the supernatant;
[0034] S12: Add 10% cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution to the collected supernatant until the final concentration is 2‰, stir and mix evenly, let stand at 5°C for 5 hours, and then collect by centrifugation Precipitation of polysaccharide complexes;
[0035] S2: Centrifuge to collect crude sugar precipitate:
[0036] S21: Use an appropriate amount of 0.7M NaCl to depolymerize the polysaccharide complex, then add 95% ethanol to a final concentration of 25% (v / v), let sta...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Hib polysaccharide purification process, which includes the following eight steps: collecting polysaccharide complex precipitates, centrifuging to collect rough sugar precipitates, washing rough sugar precipitates, drying raw sugar, dissolving raw sugar, phenol extraction, phenol removal, and refining refined sugar:
[0054] S1: Collect the polysaccharide complex precipitate:
[0055] S11: Centrifuge the sterilized culture solution, remove bacteria by centrifugation, and collect the supernatant;
[0056] S12: Add 5% cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution to the collected supernatant until the final concentration is 1‰, stir and mix evenly, let stand at 8°C for 6 hours, and then collect by centrifugation Precipitation of polysaccharide complexes;
[0057] S2: Centrifuge to collect crude sugar precipitate:
[0058] S21: Use an appropriate amount of 0.4M NaCl to depolymerize the polysaccharide complex, then add 95% ethanol to a final concentration of 30% (v / v), let stan...
Embodiment 3
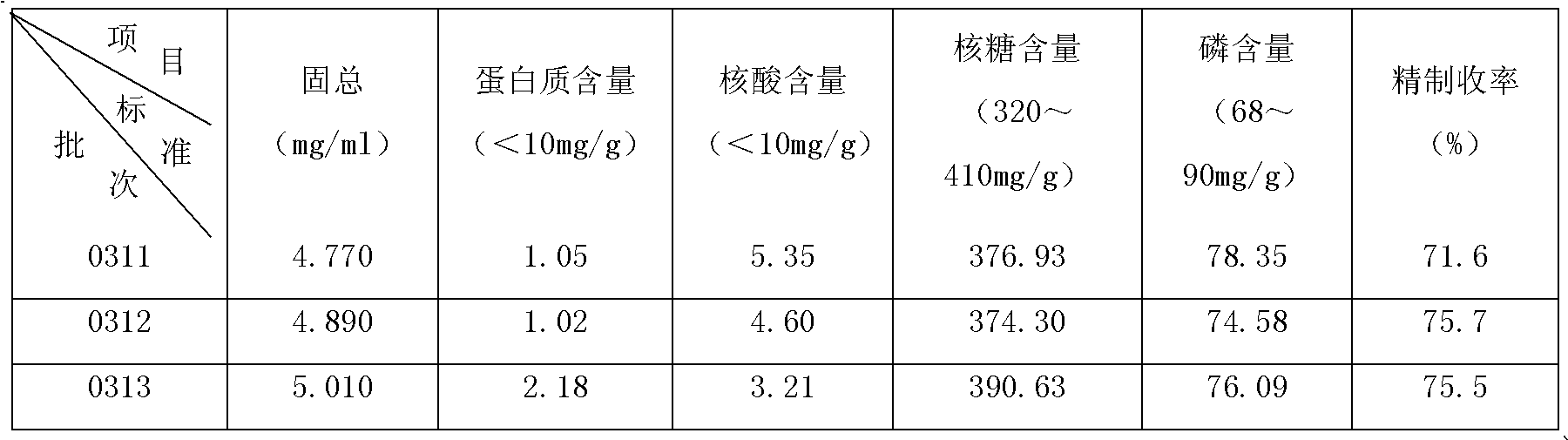
[0069] Hib polysaccharide purification process, which includes the following eight steps: collecting polysaccharide complex precipitates, centrifuging to collect rough sugar precipitates, washing rough sugar precipitates, drying raw sugar, dissolving raw sugar, phenol extraction, phenol removal, and refining refined sugar:
[0070] S1: Collect the polysaccharide complex precipitate:
[0071] S11: Centrifuge the sterilized culture solution, remove bacteria by centrifugation, and collect the supernatant;
[0072] S12: Add 15% cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution to the collected supernatant until the final concentration is 3‰, stir and mix evenly, let stand at 2°C for 4 hours, and then collect by centrifugation Precipitation of polysaccharide complexes;
[0073] S2: Centrifuge to collect crude sugar precipitate:
[0074] S21: Use an appropriate amount of 1.0M NaCl to depolymerize the polysaccharide complex, then add 95% ethanol to a final concentration of 20% (v / v), let sta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com