Method for rapidly detecting edible oil added with illegal cooking oil
A technology for waste oil and edible oil, applied in material excitation analysis, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve problems such as poor reproducibility of results, poor universality, and failure to meet the requirements of waste oil detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The method that the present invention adopts is as follows:
[0029] 1. The instrument used: F-4600 Shimadzu fluorescence spectrophotometer;
[0030] 2. Instrument test conditions:
[0031] 3D fluorescence scanning mode;
[0032] Excitation start wavelength: 200.0nm
[0033] Excitation stop wavelength: 700.0nm
[0034] Emission start wavelength: 210.0nm
[0035] Emission stop wavelength: 710.0nm
[0036] Sampling interval: 5.0nm
[0037] Scan rate: 2400nm / min
[0038] Slit width: 10.0nm
[0039] 3. Preparation of waste oil:
[0040] After collecting swill from restaurants, restaurants, hot pot restaurants, small restaurants and other dining places, first filter it to remove impurities such as vegetable leaves and sediment; then wash it twice with an equal amount of tap water, let it stand for stratification, discard the water layer, and Oil layer to remove salt; finally, put the oil layer in a stainless steel pot and heat and stir for 40 minutes, the temperatur...
Embodiment 2
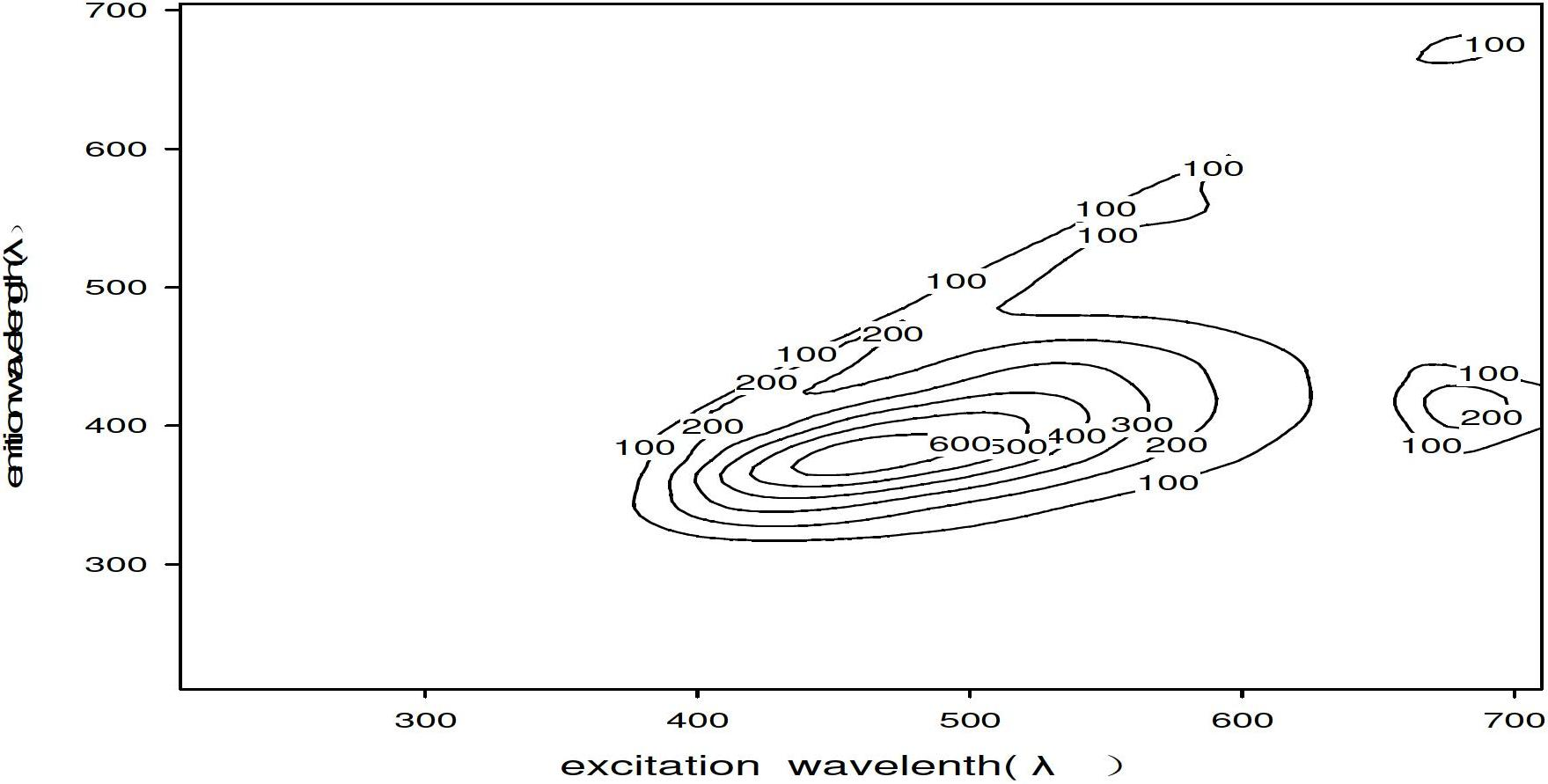
[0048] Scan the ethanol layer in the obtained No. 3 test tube (70% waste oil) with a fluorometer in a three-dimensional fluorescence mode. The test conditions are as shown in 2 in Example 1, and the rest are the same as in Example 1.
[0049] Such as figure 2 As shown, the highest fluorescence intensity of 70% waste oil reaches 800 in this embodiment.
Embodiment 3
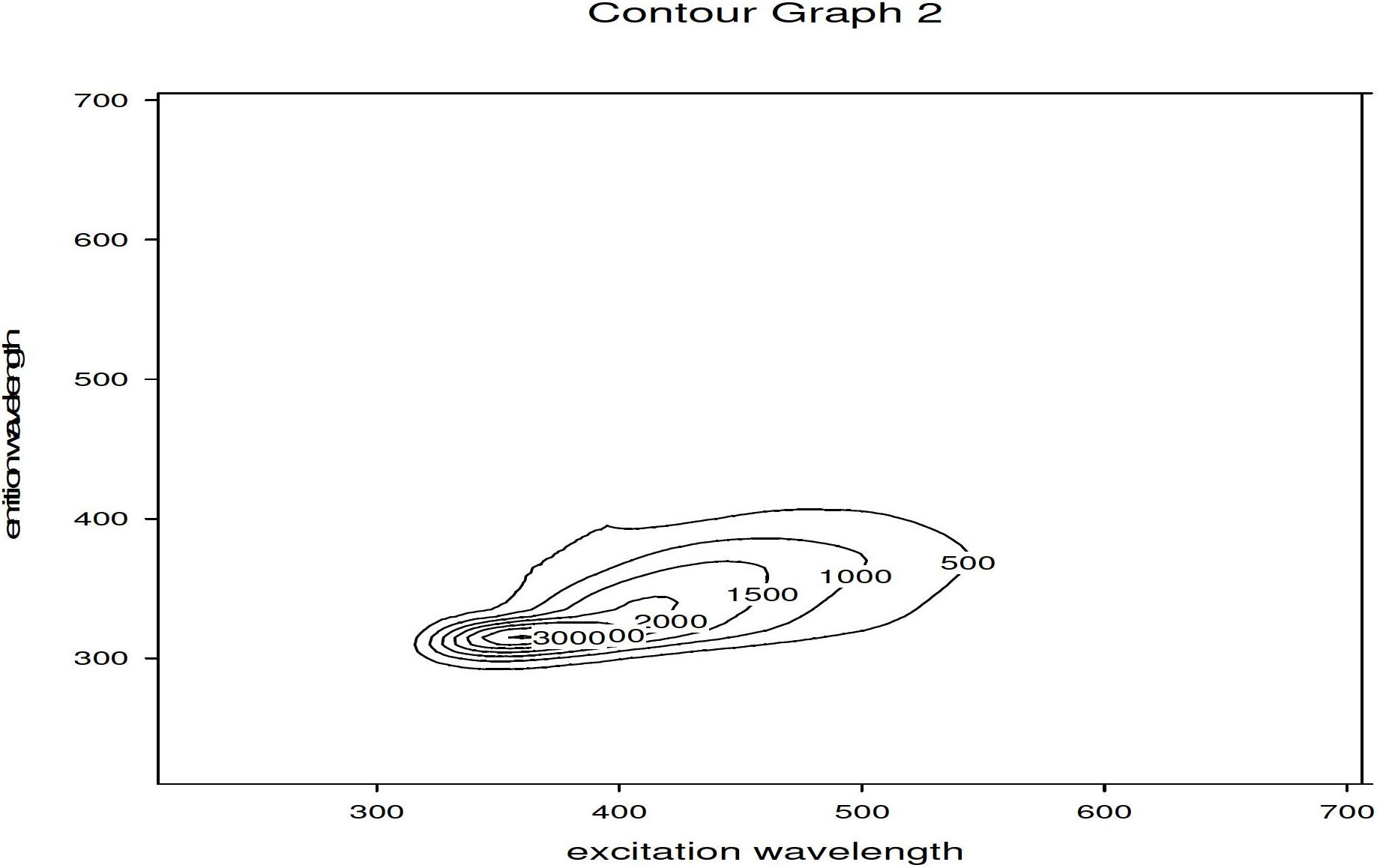
[0051] Scan the ethanol layer in the obtained No. 9 test tube (10% waste oil) with a fluorometer in a three-dimensional fluorescence mode. The test conditions are as shown in 2 in Example 1, and the rest are the same as in Example 1.
[0052] Such as image 3 As shown, the highest fluorescence intensity of 10% waste oil reaches 3000 in this embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com