Method for changing ingredients of plant secondary metabolites by using beta-ocimene
A technology for secondary metabolites, basilene, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, horticultural methods, applications, etc., can solve problems such as changing the composition of secondary metabolites in plants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0012] Example 1: Alteration of secondary metabolite components of Echinacea purpurea with β-ocimene
[0013] 1. Processing of plant material
[0014] 1. Put two Echinacea purpurea plants that have grown for 30 days into two desiccators that have been cleaned and air-dried;
[0015] 2. Add β-ocimene to one of the desiccators so that the final concentration of β-ocimene in the desiccator is 10 μmol / L, and quickly cover the lid as the treatment group; add nothing to the other desiccator as the treatment group. Blank control;
[0016] 3. Seal the two desiccators, and then put them into a plant growth room with a temperature of 20-25°C, a light of 8000-10000 Lux, and a relative humidity of 60-75%, and treat them for 3 days.
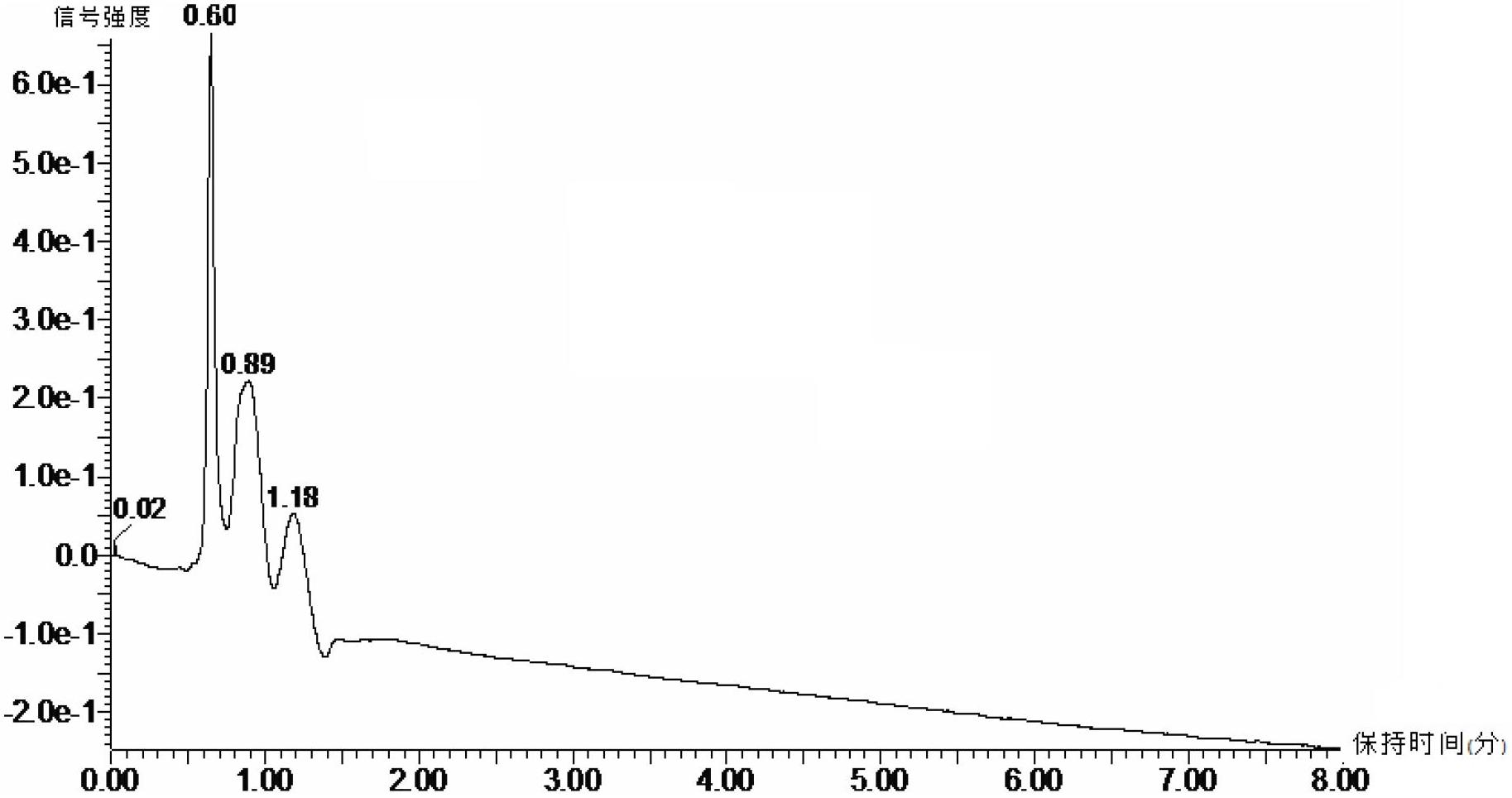
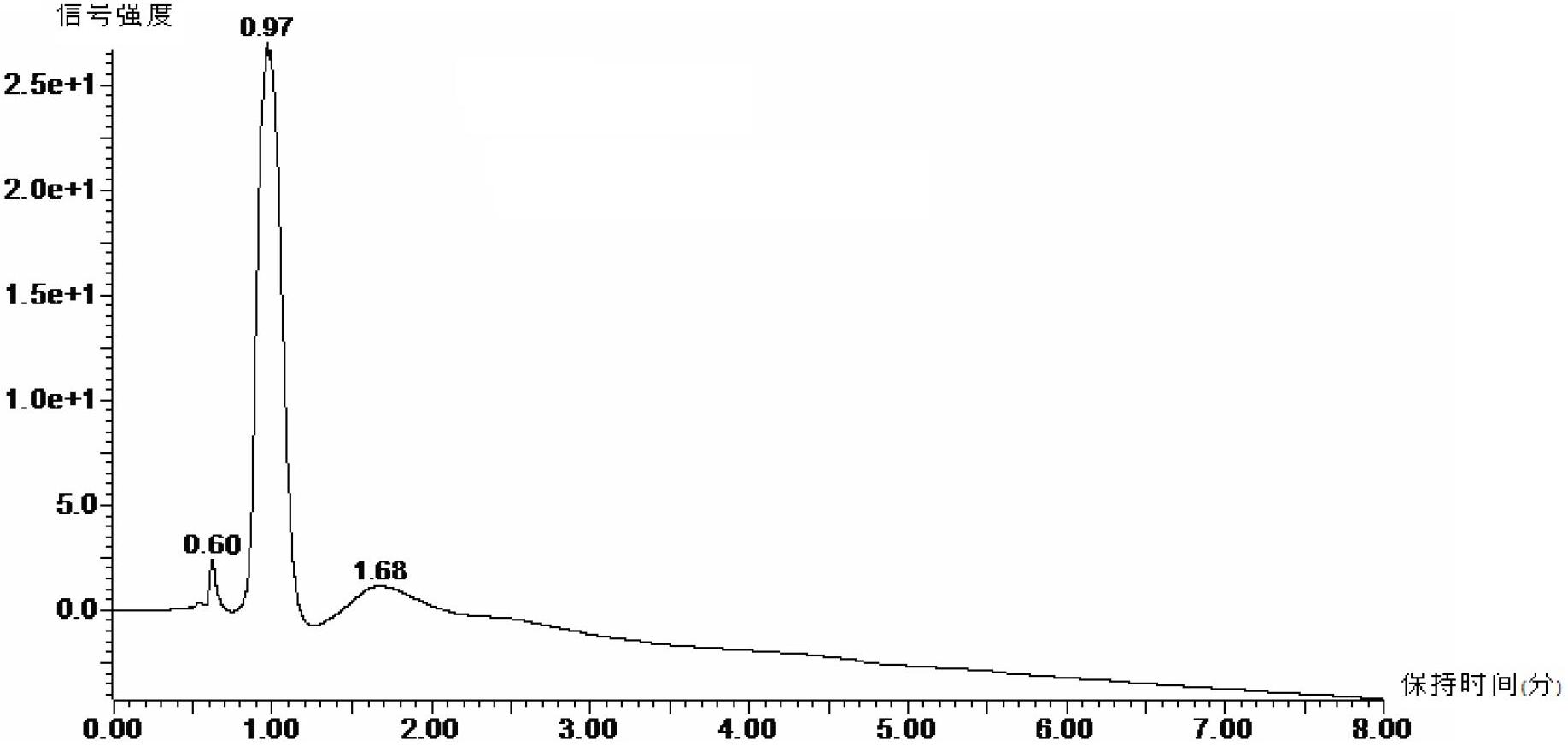
[0017] 2. Extraction of secondary metabolites in Echinacea purpurea (using conventional solvent extraction technology)
[0018] 1. Wash the two cultured Echinacea purpurea (including the roots), place them in a mortar respectively, add twice the weight of ...
example 2
[0023] Example 2: β-Ocimene Alters the Composition of Volatiles in Tomato Plants
[0024] 1) Treatment of plant material:
[0025] 1. Put two 25-day-old tomato seedlings into two clean and air-dried desiccators respectively;
[0026] 2. Add β-ocimene to one of the desiccators, and quickly cover the lid so that the final concentration of β-ocimene in the desiccator is 5 μmol / L, as the treatment group; add nothing to the other desiccator, as the treatment group. Blank control;
[0027] 3. Seal the two desiccators, then put them into a plant growth room with a temperature of 20-25°C, a light of 8000-10000 Lux, and a relative humidity of 60-75%, and treat for 24 hours.
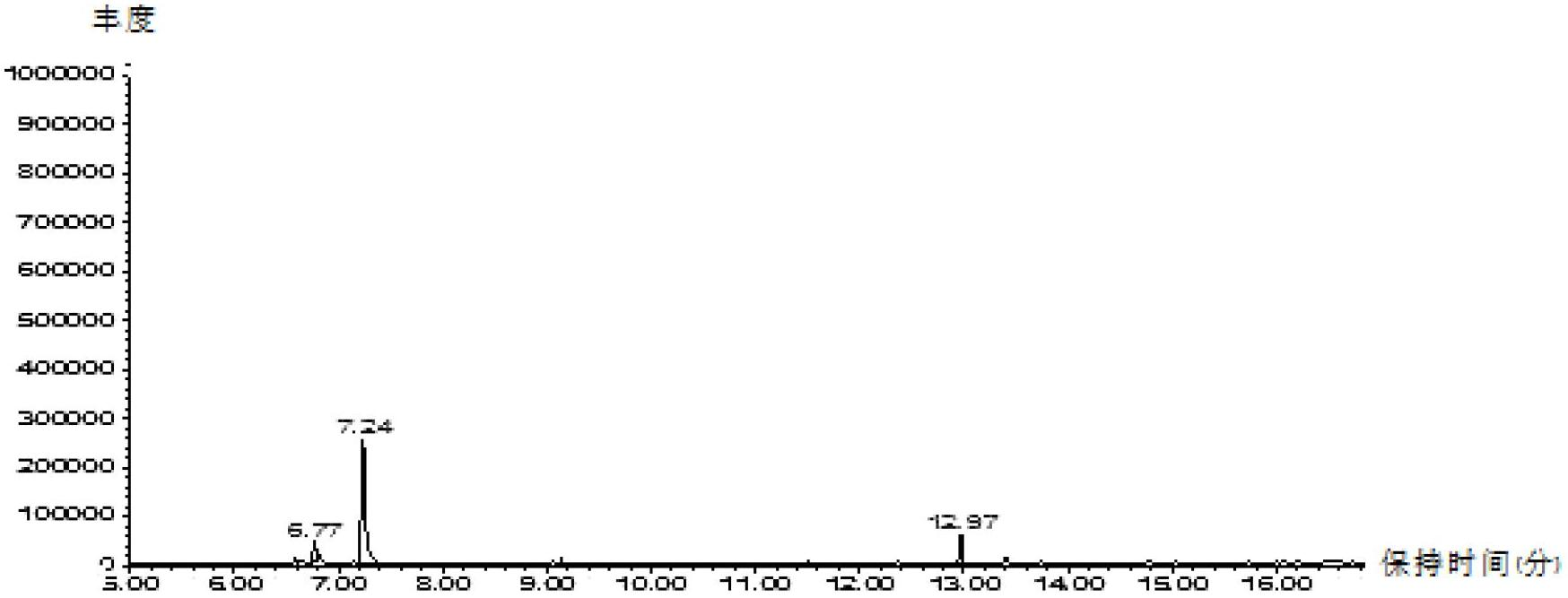
[0028] 2) Take the tomato seedlings of the control group and the treatment group out of the desiccator, transfer them to the volatile matter collector respectively, and collect the volatile products of tomato seedlings with two different treatments.
[0029] 3) Determination of volatiles by gas chromatography (...
example 3
[0031] Example 3: glucosinolate content in rapeseed treated with β-ocimene
[0032] 1) Rapeseed treatment: 10 plants of Brassica napus GX-27 were planted in each of two 5-square-meter artificial climate chambers, and β-ocimene was added to one chamber to a final concentration of 5 μmol / L as a treatment group; the other One chamber without β-ocimene was used as a control group. The conditions of the artificial climate chamber are: the temperature is 20-25°C, the light is 10000-20000Lux, and the relative humidity is 50-65%.
[0033] 2) Determination of total glucosinolate content: After the rapeseeds were harvested by individual plants, the glucosinolate content in the rapeseed was measured by near-infrared spectroscopy. was 103.24 μmol / g, and the difference between the two reached an extremely significant level, as shown in Table 1 below. It indicated that β-ocimene treatment could increase the content of secondary metabolite glucosinolate in rapeseed.
[0034] Table 1
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com