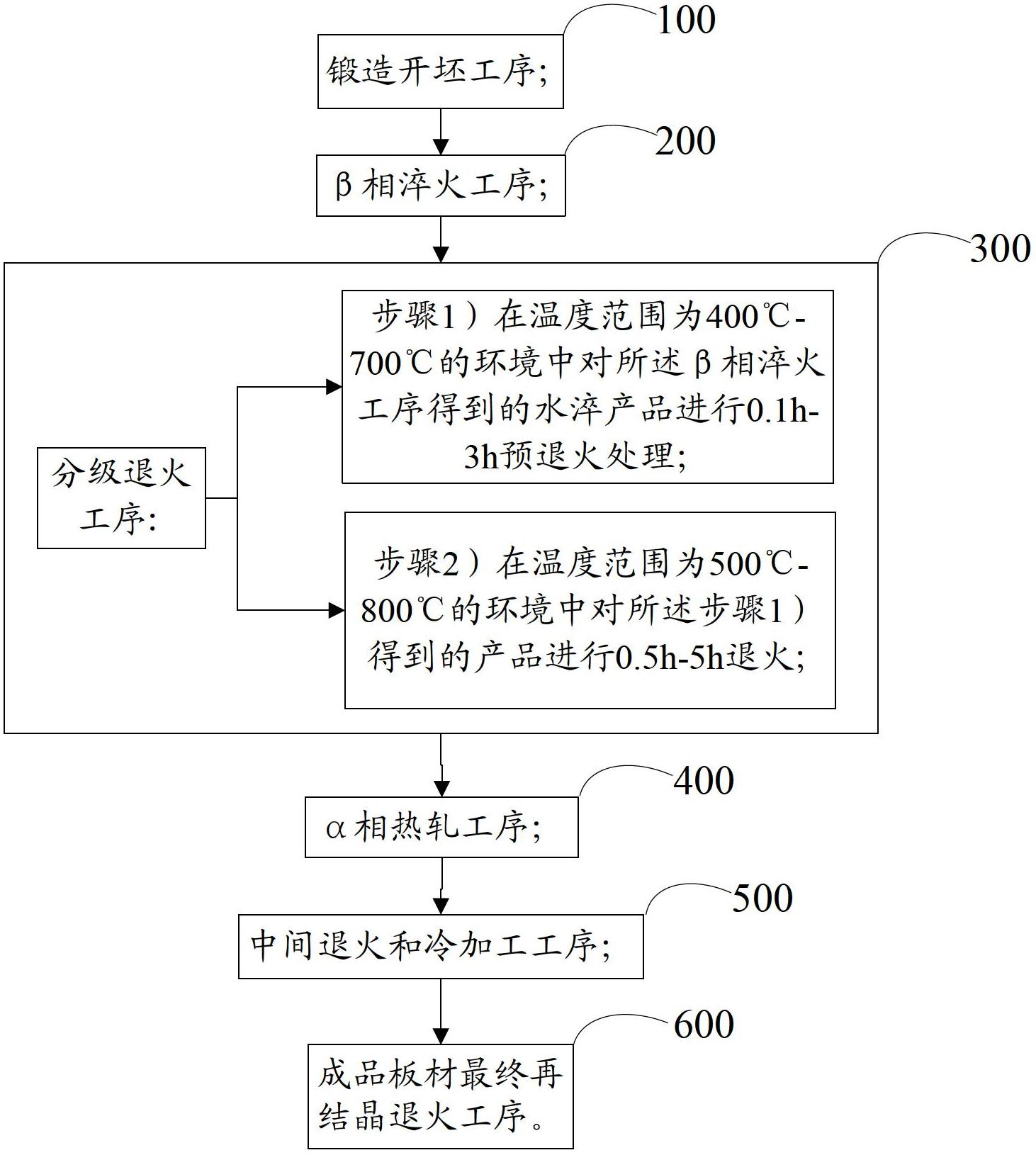
Machining process for zirconium alloy
A processing technology, zirconium alloy technology, applied in the field of alloys, can solve the problems of reduced corrosion resistance, poor plastic processing ability of zirconium alloys, large second phase particle size, etc., to improve plastic processing ability, improve plastic deformation ability, save Effects of Time and Energy Consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
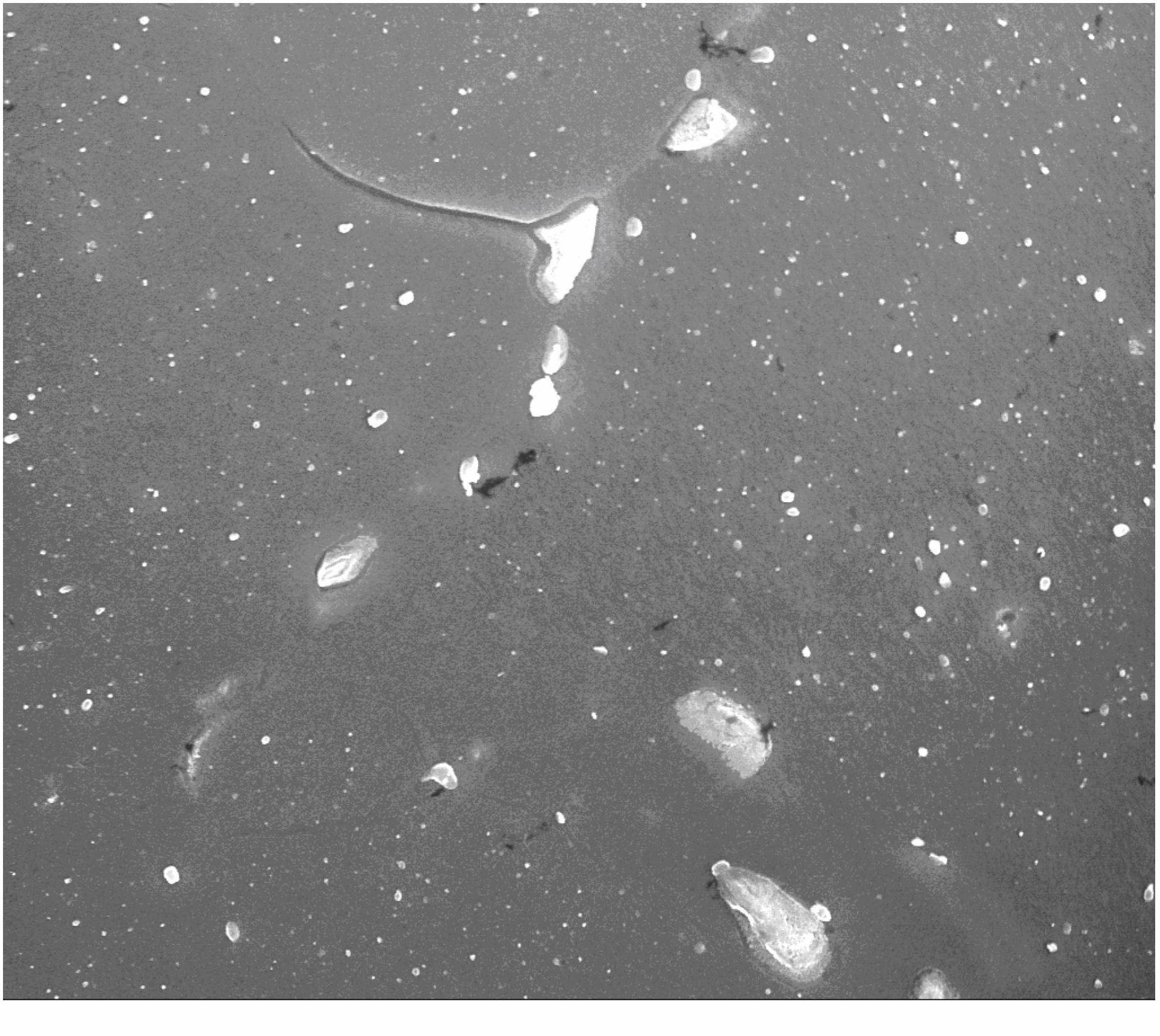
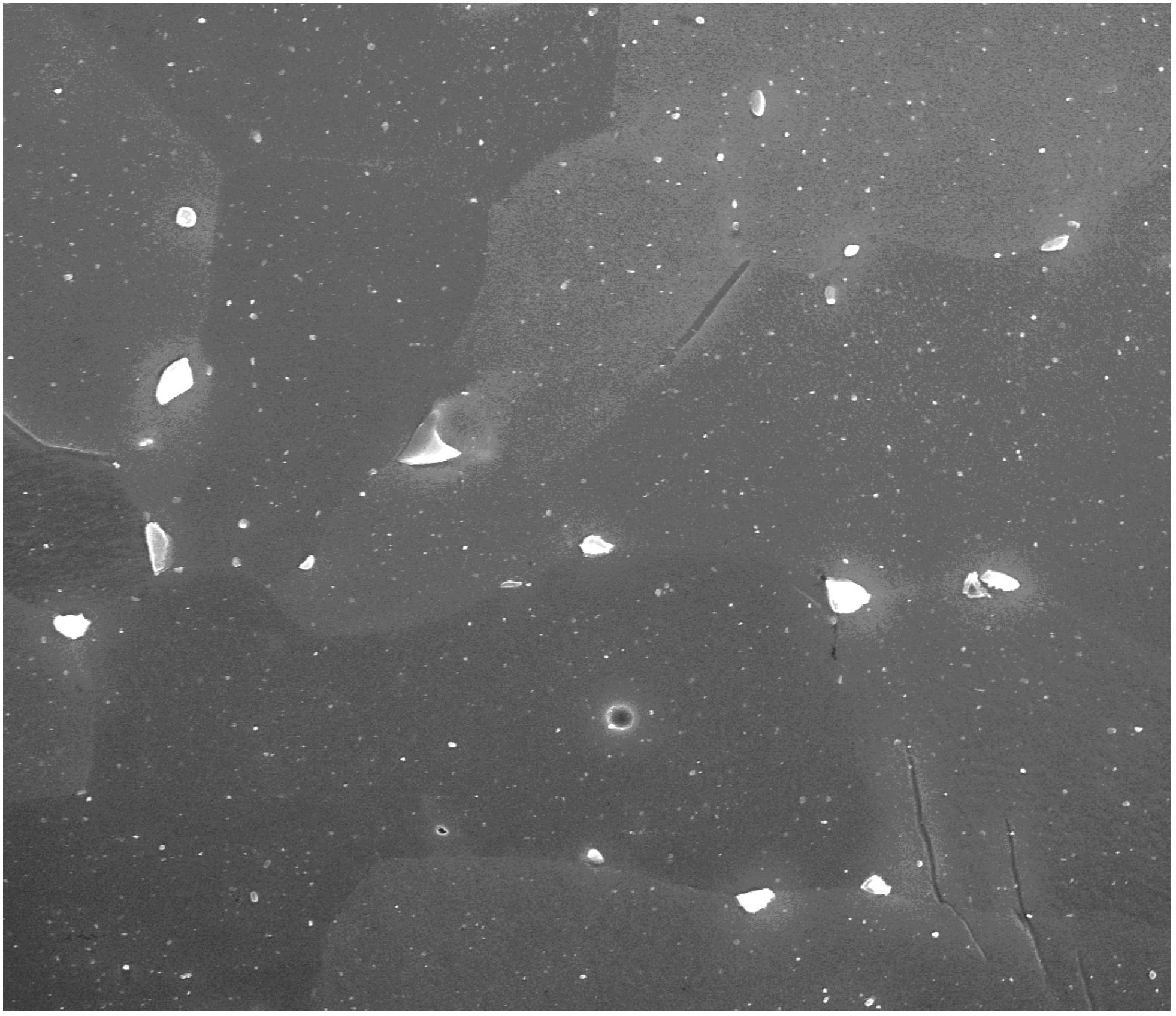
[0054] Taking a zirconium alloy with a weight percentage of 1% of the Sn element and a 0.3% weight percentage of the Nb element as an example, it is processed by the existing processing technology under the conditions of a vacuum degree of 2.27E-3Pa and an acceleration voltage of 20.00KV. The scanning electron microscope image obtained is figure 2 As shown, among them, the larger bright spot is the precipitated phase produced at the grain boundary, which is prone to cracks and is harmful to the subsequent processing performance. Obviously, the particle size and distribution of the second phase are not uniform, and the size is large; The same zirconium alloy is processed by the process provided by the embodiment of the present invention. In the step annealing process, the pre-annealing step is carried out at 500°C for 0.5h, and the annealing and heat preservation step is carried out at 650°C for 2h. After the processing is completed , the scanning electron microscope image of ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Taking a zirconium alloy with a weight percentage of Sn element (1%) and a weight percentage of Nb element (0.3%) as an example, it is processed by the existing processing technology, and the scanning electron microscope image obtained under the conditions is as follows figure 2 As shown, among them, the larger bright spot is the precipitated phase produced at the grain boundary, which is prone to cracks and is harmful to the subsequent processing performance. Obviously, figure 2 The larger bright spot in the zirconium alloy is that the size and distribution of the second phase particles in the zirconium alloy are not uniform; the same zirconium alloy is processed by the method provided by the embodiment of the present invention, and the pre-annealing step in the step annealing process is 550 ℃ temperature for 1h, and the annealing and heat preservation step was carried out at 550℃ for 2h. The scanning electron microscope image obtained by using the same scanning equip...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Taking a zirconium alloy with a weight percent of Sn element of 0.8% and a weight percent of Nb element of 0.35% as an example, it is processed by the existing processing technology, and the scanning electron microscope image obtained under the conditions is as follows Figure 5 As shown, among them, the larger bright spot is the precipitated phase produced at the grain boundary, which is prone to cracks and is harmful to the subsequent processing performance. Obviously, Figure 5 The larger bright spot in the zirconium alloy is that the size and distribution of the second phase particles in the zirconium alloy are not uniform; the same zirconium alloy is processed by the method provided by the embodiment of the present invention, and the pre-annealing step in the step annealing process is 550 ℃ for 2 hours, and the annealing and heat preservation step was carried out at 650 ℃ for 2 hours. The scanning electron microscope image obtained by using the same scanning equipme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com