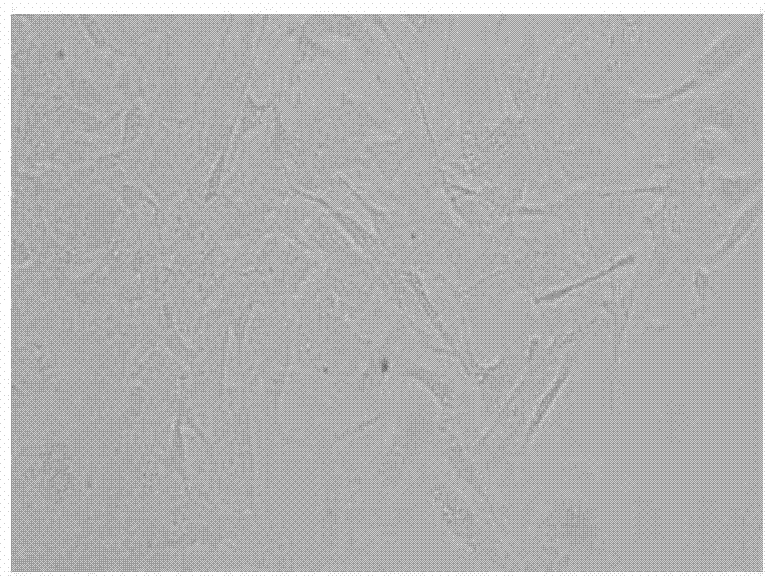
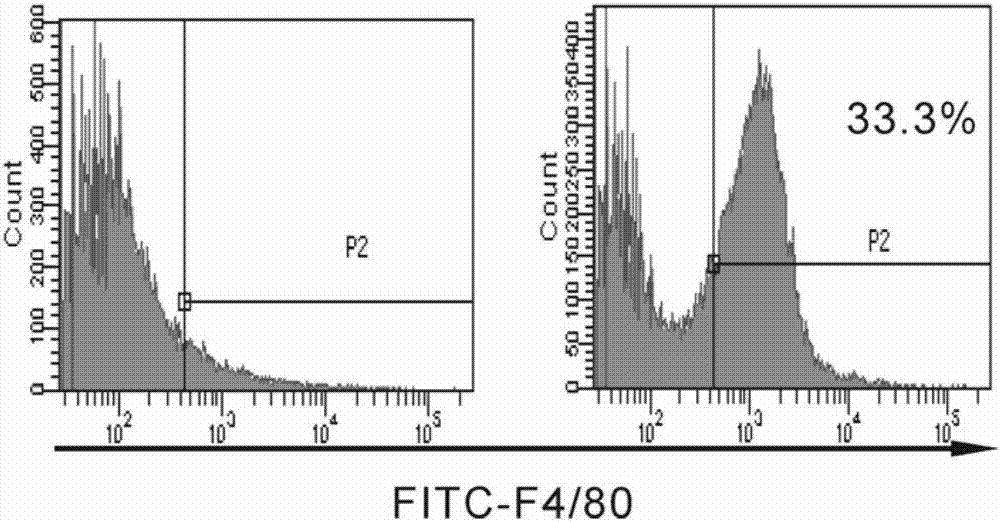
In vitro induction culture method for bone marrow-derived macrophages
A bone marrow-derived, macrophage technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of short survival time, poor macrophage homogeneity, and low yield, and achieve the effect of improving purity, shortening the time required for differentiation and maturation, and improving purity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 Preparation of bone marrow-derived cell mixture
[0029] Take 6-8 week old mice, let them die by taking off their necks, and immerse them in 70% ethanol by volume. Use tweezers to pick up the abdominal epithelium, cut a small opening horizontally under the mouse abdomen with scissors, clamp the two ends of the opening and separate them in different directions to expose the mouse legs, pull out the mouse femur and tibia by hand, and make the small The mouse femur was separated from the mouse body and tibia at the joint, leaving both ends intact. Use alcohol-soaked gauze to remove the remaining tissue and cartilage at the articular junction of the femur.
[0030] Rinse the removed femur in 70% alcohol for 2 to 3 times, and then rinse in PBS buffer; prepare 5 to 10ml of PBS in a centrifuge tube in advance, use a 1mL syringe to draw the PBS buffer in the centrifuge tube and insert it into the femur The cartilage at the two ends of the femur was quickly flushed o...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 Treatment of Cell Suspension
[0034] The bone marrow-derived cell mixture was gently pipetted several times to prepare a mononuclear cell suspension. Pipette the cell suspension through a 75 μm filter (multiple experiments have proved that a 40 μm filter can also be achieved), transfer it into a 10ml centrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 1000-1500rmp / min for no more than 10min. Remove the supernatant, and gently pipette the resuspended cell suspension with PRMI1640 complete medium containing M-CSF (20ng / ml) to prepare a mononuclear cell suspension. Bone marrow source used in "Ishii M, Wen HT, Corsa CAS, Liu TJ, Coelho AL, Allen RM, et al. Epigenetic regulation of the alternatively activated macrophage phenotype. Blood. 2009;114(15):3244-54" The in vitro induction culture method of macrophages does not have this step; adding this step will greatly improve the purity of bone marrow-derived progenitor cells, and more importantly, it will also reduce the chance of ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 In vitro induction and culture of bone marrow-derived macrophages
[0036] Perform cell counting on the bone marrow-derived cells filtered in Example 2, determine the cell concentration, dilute the cell suspension and adjust the cell concentration to 1-2×10 6 pieces / ml. To plank, place 1 x 10 6 cells / ml of cell suspension was inoculated into 6 empty culture plates, 3ml / well. After incubating in a cell culture incubator at 37° C. and 5% for 30 hours, the supernatant was discarded, and new PRMI1640 complete medium containing M-CSF (20 ng / ml) was added. The step of aspirating and discarding the supernatant is very critical. The significance of this step is to purify macrophage progenitor cells and improve the purity of induced differentiation macrophages. The obtained single cell suspension is directly induced and cultured in vitro without the critical step of aspiration and discarding the supernatant. Some dead cells or non-macrophage progenitor cells are not...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com