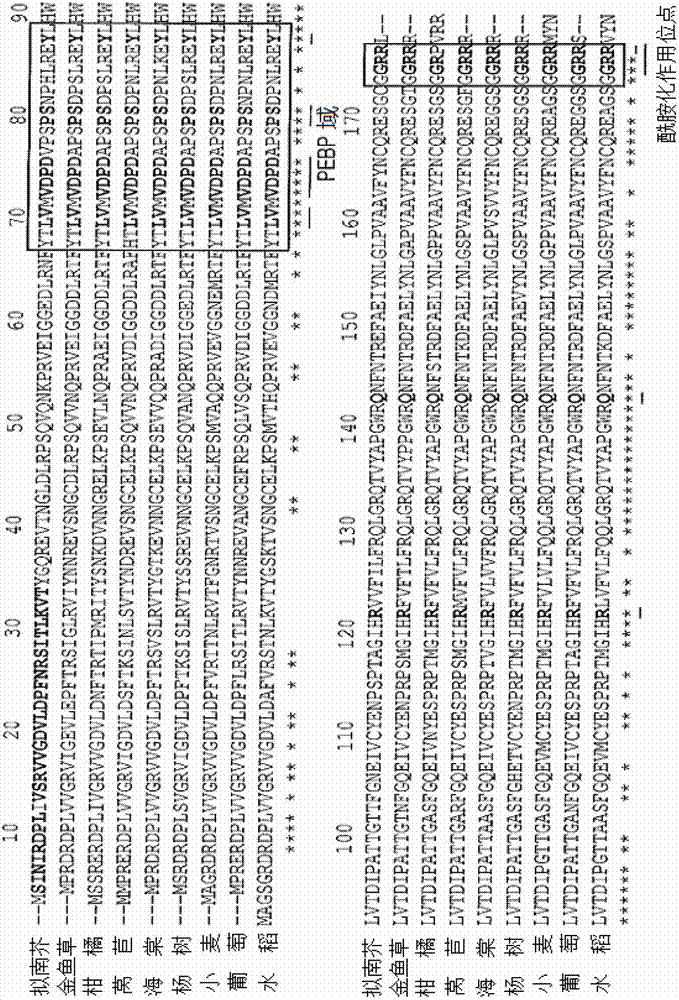
Molecular engineering of a floral inducer for crop improvement
A plant and seed technology, applied in the direction of genetic engineering, the use of vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, plant peptides, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing fruit and/or seed production and improving flowering ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0118] Coding FT G172A 、FT R173A and FT R174A Arabidopsis FT derivatives by using the corresponding primer pair A and D ( figure 2 ) and PCR with the plasmid PVX / FT carrying the wild-type FT gene as a template for amplification 12 . The PCR reaction system contained: 5 μL of 10× reaction buffer (Promega), 0.2 mM dNTPs (dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP), 15 pmole of each primer, 1.25 units of pfu DNA polymerase (Promega) and 50 ng of template DNA. The resulting PCR product was purified with the QIAGEN Quick PCR Purification Kit, followed by double digestion with C / al and Eagl, and then cloned into the C / al / Eagl site of a PVX-based gene expression vector 12 .
[0119] All other FT derivatives were obtained by overlap extension PCR ( figure 2 ). Design 2 mutagenic primers B and C for each sample involved ( figure 2 ), which contain specific mutations and are partially complementary to each other. Perform two separate PCR reactions (5 μL of 10...
Embodiment 2
[0121] Modification of FT gene
[0122] In order to modify the 5' (that is, any nucleotide in the first 100 nucleotides) or 3' (that is, any nucleotide in the last 100 nucleotides) end of the FT gene, chemically synthesized specific primers ( 30-110 nucleotides), the specific primer has a substitution for a codon selected for an amino acid with three nucleotides encoding alanine. Of course, using this methodology, other amino acid substitutions can be utilized and the resulting mutants tested in the same manner as described below. As described in Example 1, mutagenic primers were used in PCRs and optionally primers A or D ( figure 2 A) in order to introduce specific modifications into the FT gene.
[0123] To introduce nucleotide changes into the middle portion of the FT gene (i.e., nucleotides 101-429), two partially complementary primers B and C ( figure 2 ). Nucleotide changes were introduced into both primers to substitute codons for selecting amino acids for mutatio...
Embodiment 3
[0125] Expression of Modified Genes in Plants
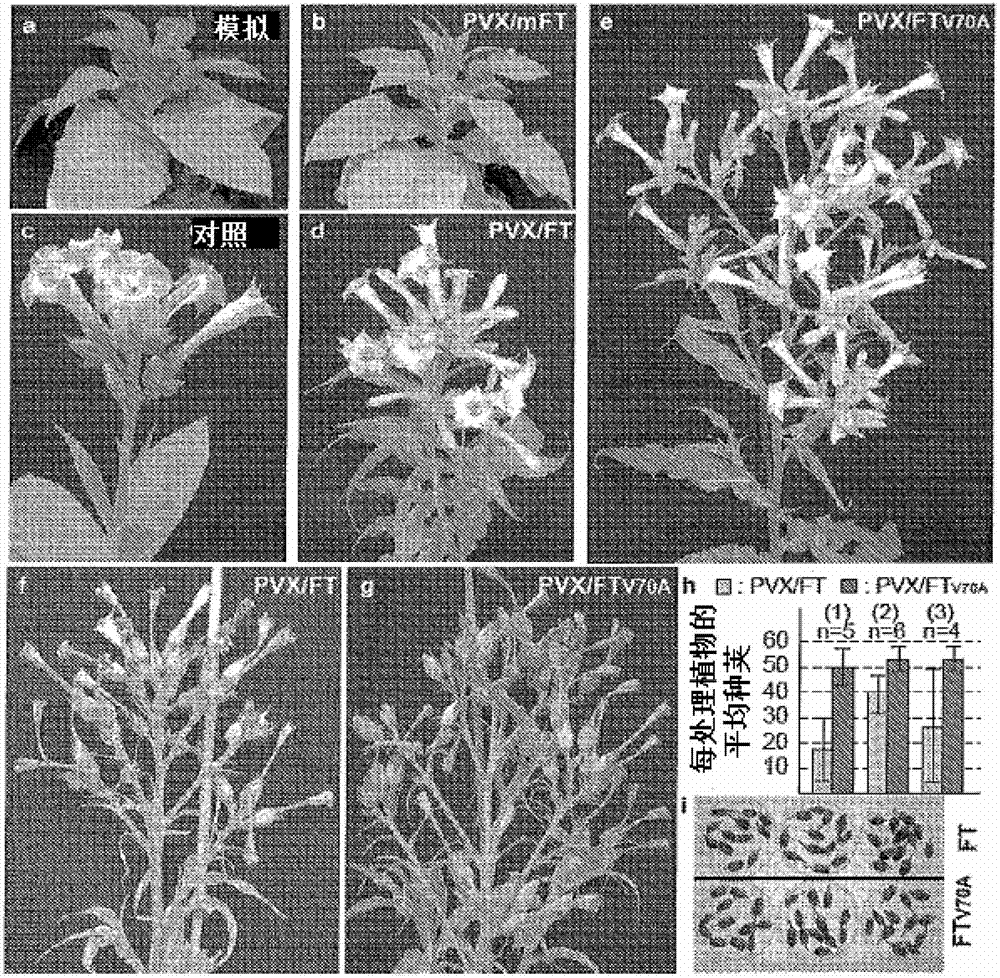
[0126] RNA transcripts from each recombinant PVX vector are generated by in vitro run-off transcription 12. Typical in vitro full-length transcription reaction (50 μL containing 5 μL of 10× buffer (Biolabs), 40 units of RNasin (Promega), 2 mM each of ATP, CTP, UTP, and GTP, 0.5 mM m 7 GpppG (Biolabs), 2.5 μg of Spel-linearised carrier DNA and 200 units of T7 RNA polymerase) were incubated at 37° C. for 1 hr. The RNA transcripts were further treated with 1 unit of RNase-free DNase at 37°C for 30 min, and then mechanically inoculated at the 5-6 leaf stage of the plants. Young short-day (SD) tobacco Maryland Mammoth (MM) plants were grown in an insect-free greenhouse at 25°C with continuous light providing a long-day (LD, 16-hr) photoperiod. 12 Viral ectopic overexpression of wild-type and modified FT genes was analyzed at the RNA and protein levels as previously described, and viral delivery of wild-type and modified FT genes wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com