Semi-automatic digital method of non-standard map
A non-standard, semi-automatic technology, applied in image data processing, image communication, image enhancement, etc., can solve the problems of lack of accurate and efficient vectorization methods, inappropriate use of non-standard vector maps, increasing the difficulty of digitization, etc. Working cycle, high image processing efficiency, and the effect of improving digitization accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
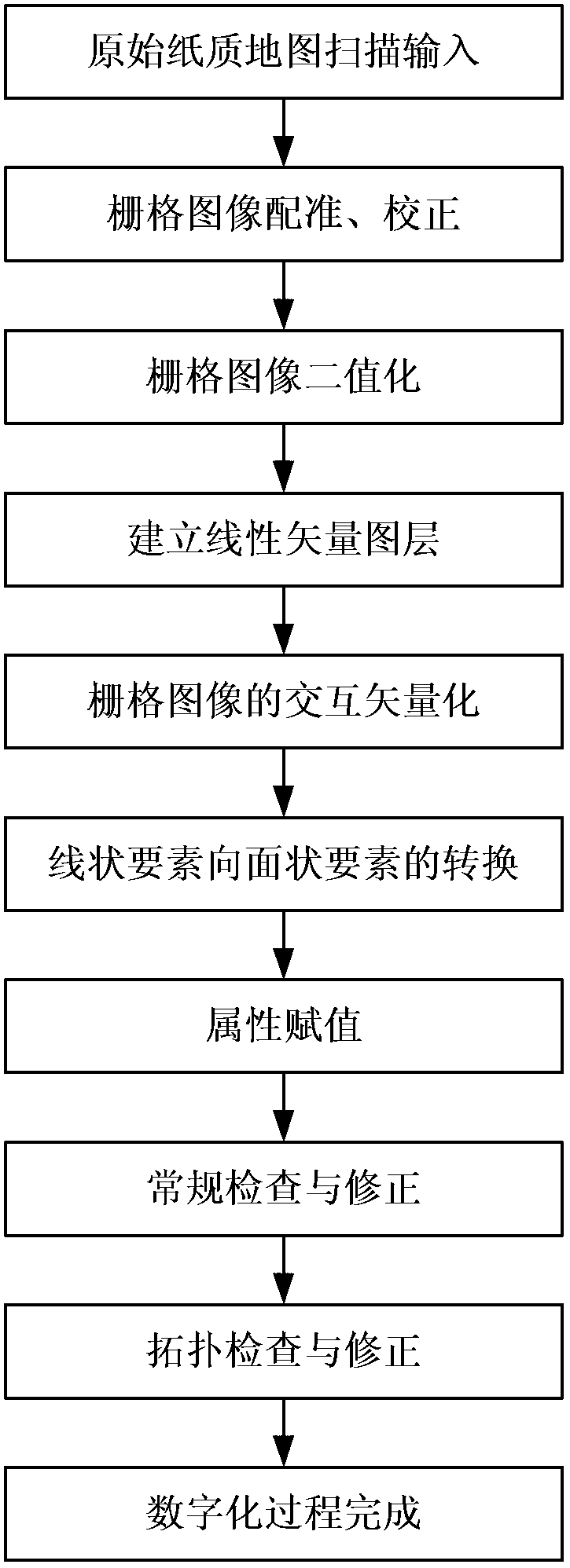
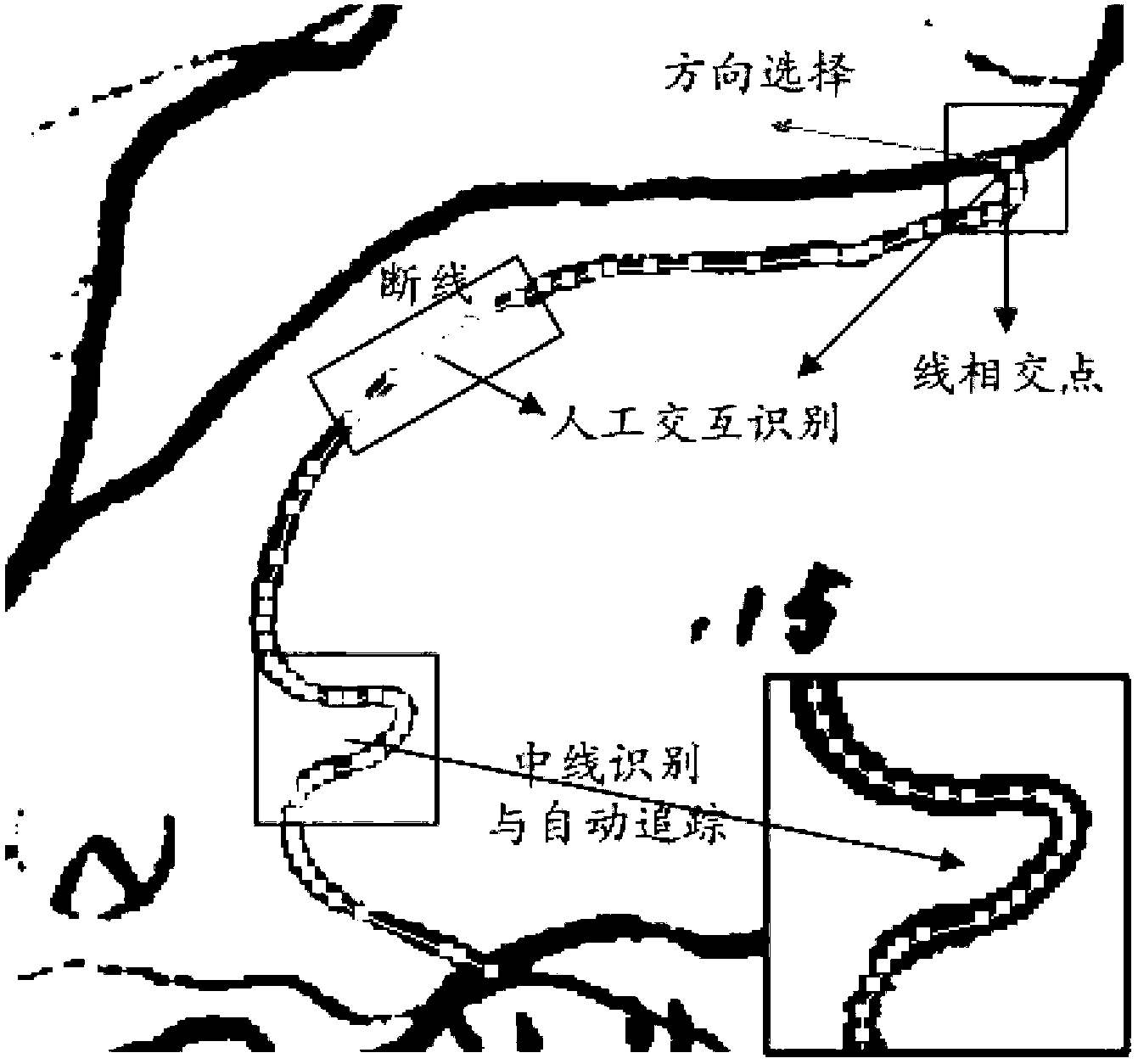
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] Adopt the most commonly used ArcMap 9.3 software platform in the embodiment of the present invention (some other geographic information system software platforms can also be realized), in conjunction with the 1: 50,000 soil map of each county (district) in Zhejiang province as the non-standard map of input Take an example to explain in detail. The 1:50,000 soil map in this example comes from the second soil census in Zhejiang Province. Since this soil census was carried out in units of counties (districts), the quality of soil maps among counties is uneven and the standards are different. one. Soil maps in most counties do not have kilometer grids or latitude and longitude grids, and the registration of soil maps can only refer to topographic feature points, which affects the registration accuracy of soil maps to a certain extent. Restricted by technical conditions, workload and time at that time, the 1:50,000 soil maps of each county (district) were hand-painted, with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com