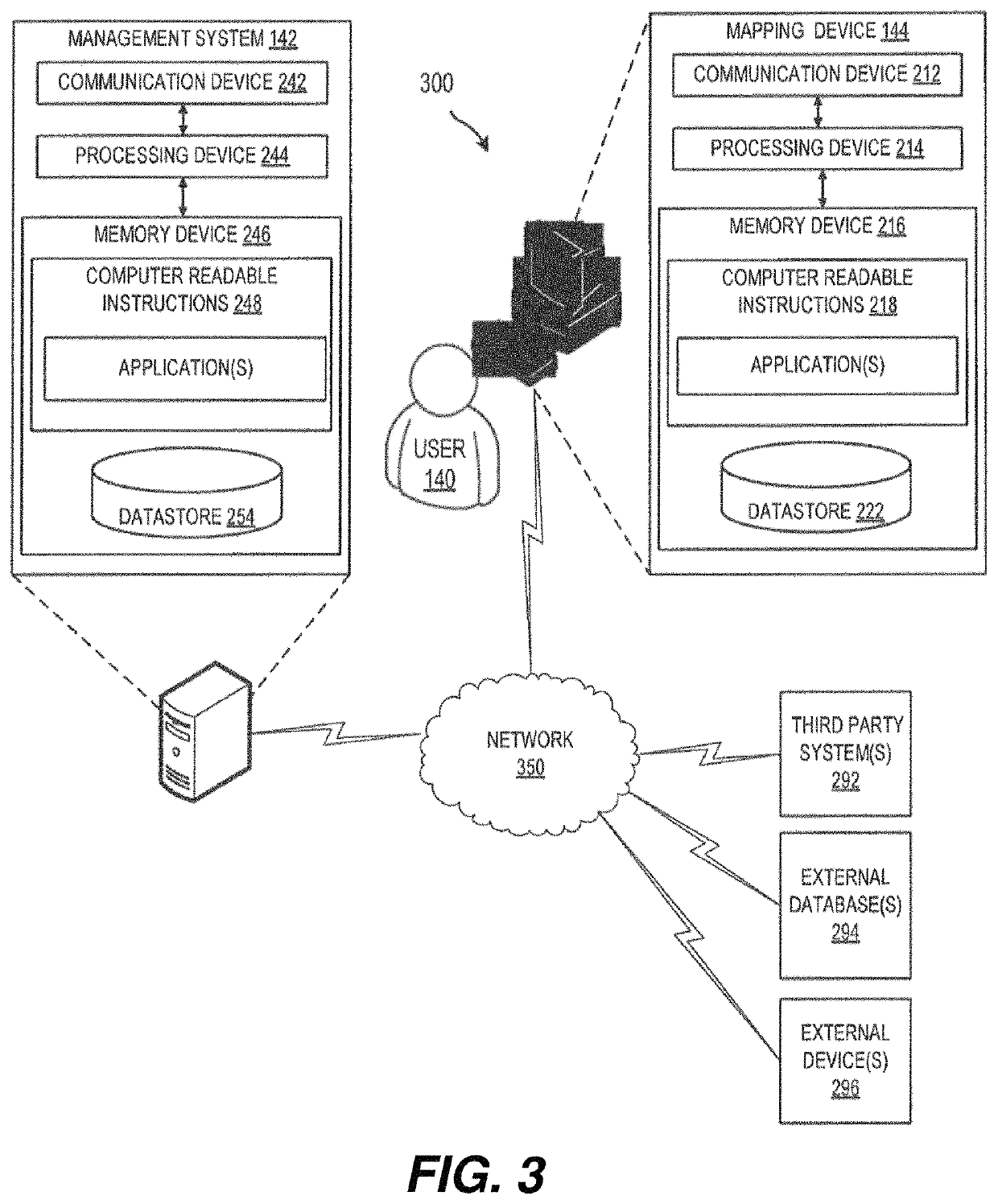
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Soil map" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
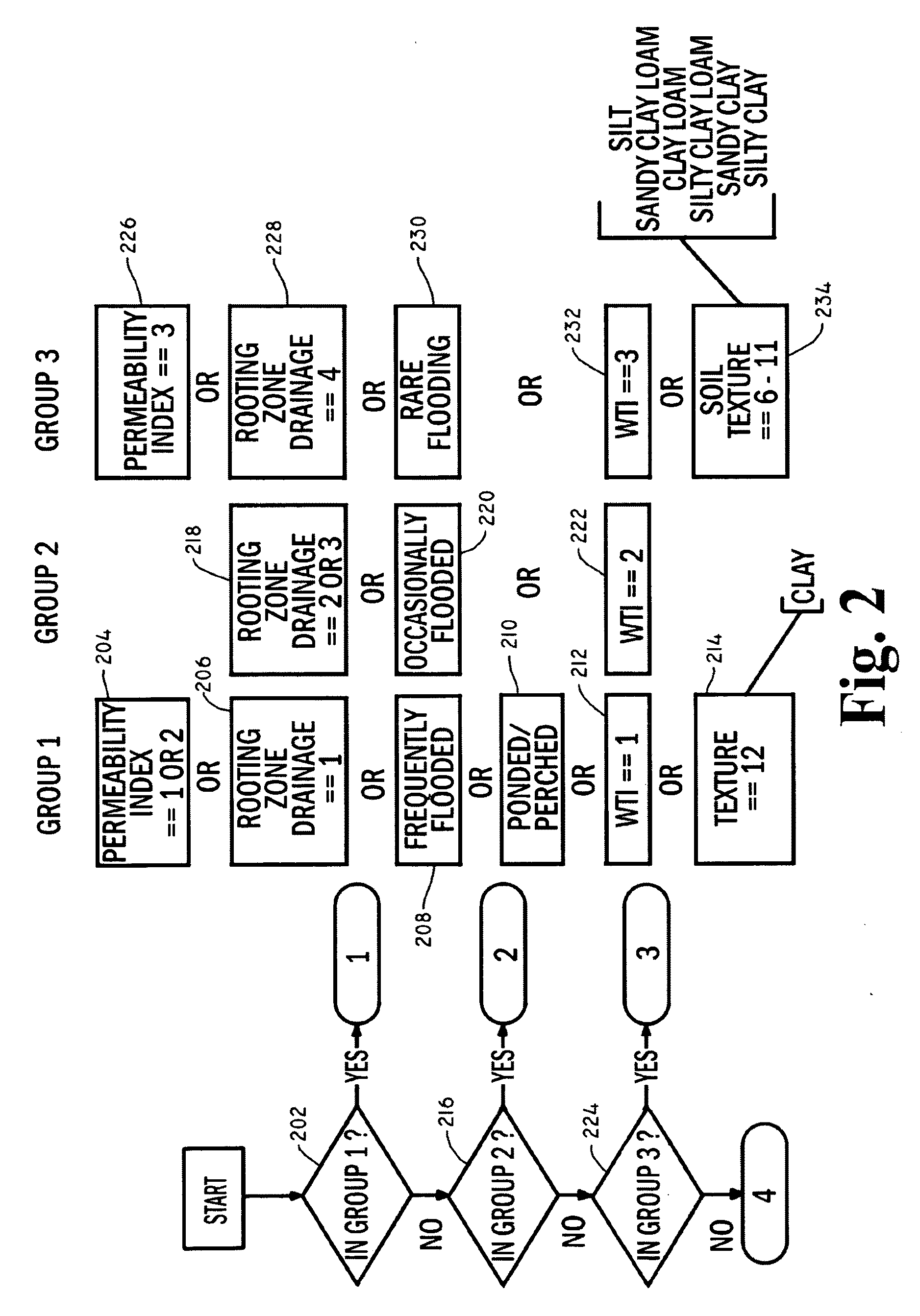
Soil map is a geographical representation showing diversity of soil types and/or soil properties (soil pH, textures, organic matter, depths of horizons etc.) in the area of interest. It is typically the end result of a soil survey inventory, i.e. soil survey. Soil maps are most commonly used for land evaluation, spatial planning, agricultural extension, environmental protection and similar projects. Traditional soil maps typically show only general distribution of soils, accompanied by the soil survey report. Many new soil maps are derived using digital soil mapping techniques. Such maps are typically richer in context and show higher spatial detail than traditional soil maps. Soil maps produced using (geo)statistical techniques also include an estimate of the model uncertainty.
Method for selecting crop varieties
InactiveUS20050150160A1Choosing one or more crop varieties is simplifiedSeed and root treatmentHorticulture methodsSoil typeGraphics
A process of recommending crop varieties based on management categories. The management categories are determined by utilizing indices, which measure the economic implication of physical and chemical properties of a specific soil type in a region. The management categories may then be indicated graphically by indicia overlaying digitized soil maps, each of the indicia grouping soil types within a management category. Each crop variety is characterized by how the crop variety performs in each of the management categories. Each of the crop varieties may then be assigned an indicium of the management category for which it is adapted.
Owner:NEW VISION COOP
Method for selecting crop varieties
InactiveUS20090164281A1Choosing one or more crop varieties is simplifiedSeed and root treatmentSowingSoil typeSoil map
Owner:NEW VISION COOP
GIS (geographic information system)-based distributed-type rice field nitrogen runoff loss load estimating method
The invention relates to a GIS (geographic information system)-based distributed-type rice field nitrogen runoff loss load estimating method. The method includes: 1), collecting basic information of a studied area, namely collecting daily rainfall, evaporation capacity, administrative area, land use map and soil map of the studied area; 2), investigating basic data of fertilizing and field moisture management; 3), generating a related space distribution grid map layer; 4), measuring and calculating dynamic changing rules of rice field surface water nitrogen concentration under different soil types, namely dynamically monitoring rice field surface water under different soil types and different fertilizing levels, and calculating fitting equation parameters of the rice field surface water; 5), calculating rice field nitrogen runoff loss load including a water quantity balance module, an initial concentration calculating module and a load output module. By the GIS-based distributed-type rice field nitrogen runoff loss load estimating method, temporal and spatial change of non-point-source-generated pollution discharging coefficient can be reflected, few basic data and parameters are needed, model building is easy, and running efficiency is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
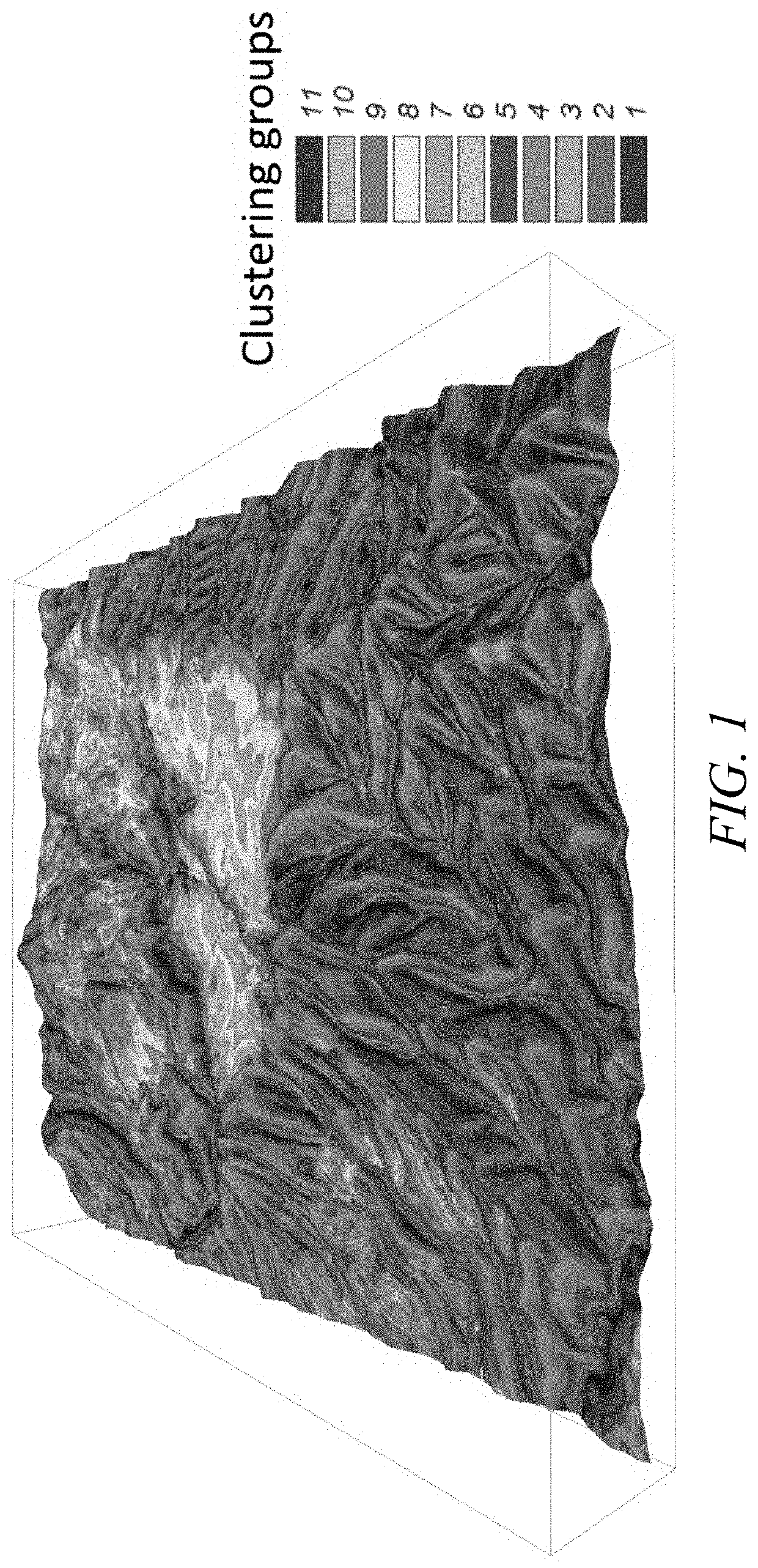
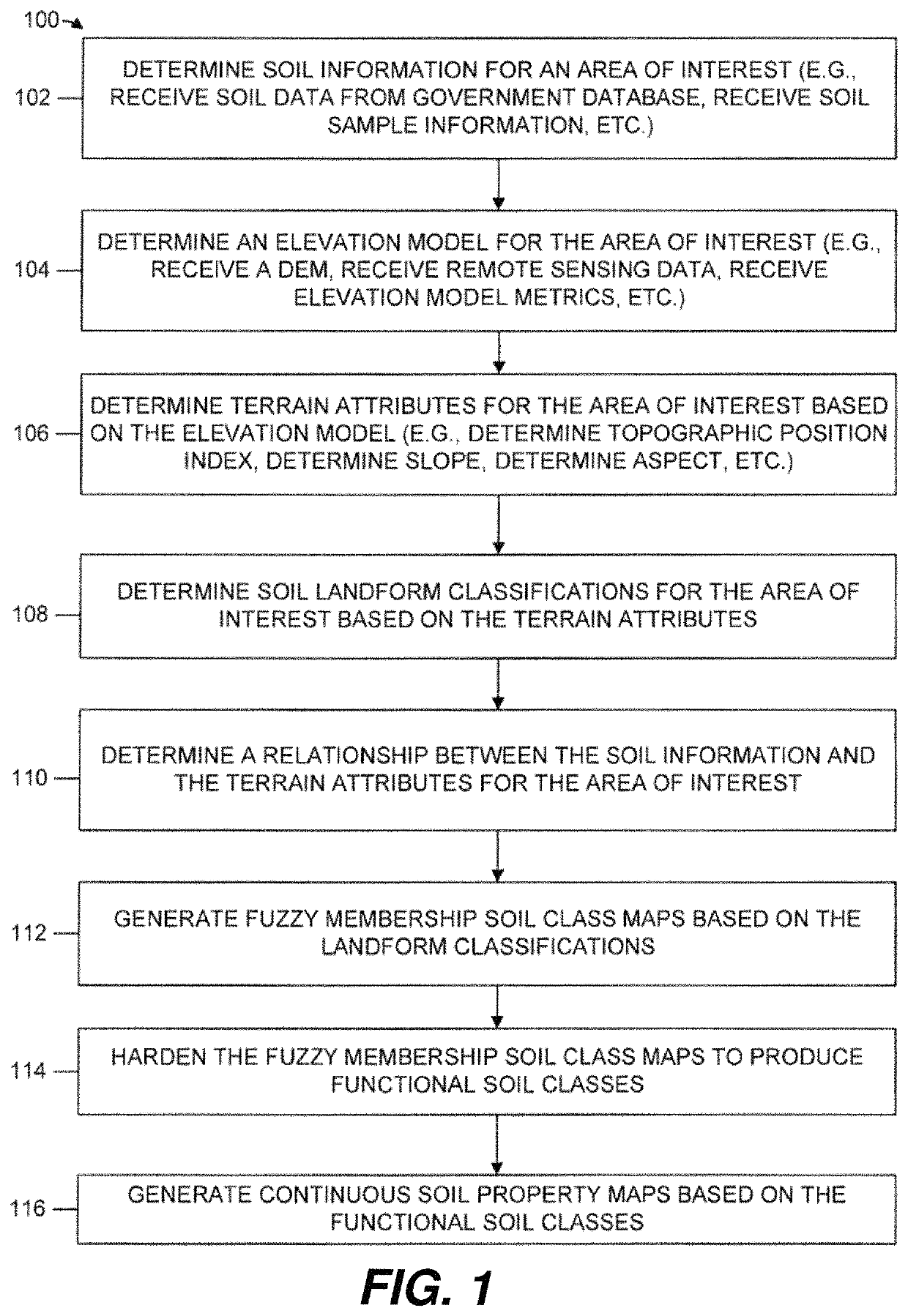
Functional soil maps
ActiveUS20160003792A1Improve land management practiceSimple technologyData processing applicationsEarth material testingTerrainSoil map
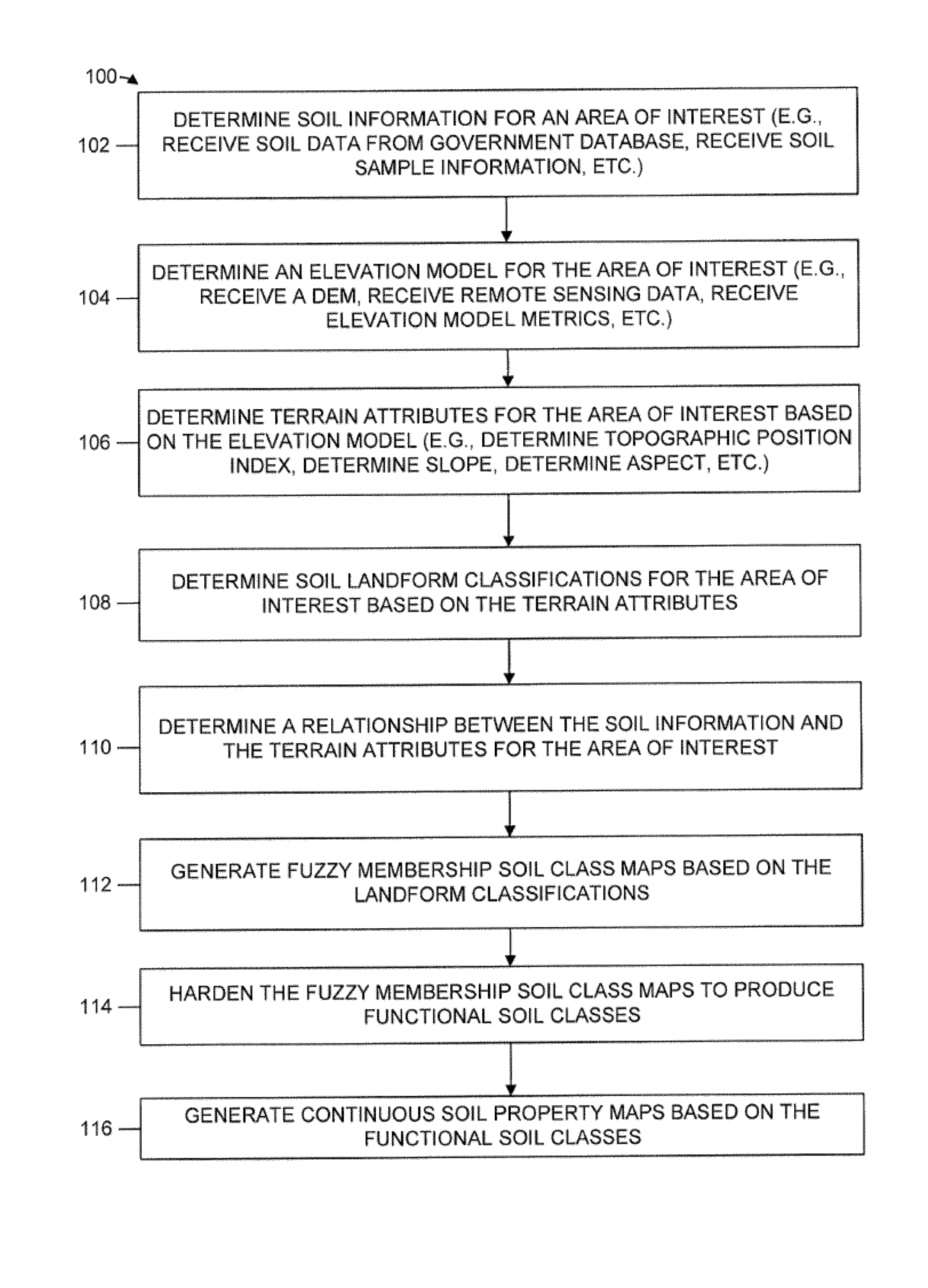
Embodiments of the present disclosure relate generally to system and methods for generating functional soil maps. The systems and methods are configured to determine soil information for an area of interest; determine an elevation model for the area of interest; determine terrain attributes for the area of interest based on the elevation model; determine a relationship between the soil information and the terrain attributes for the area of interest; and generate a functional soil map based at least in part on the relationship between the soil information and the terrain attributes for the area of interest. In an embodiment, the systems and methods can be used to improve management strategies for crops and other land management regions.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
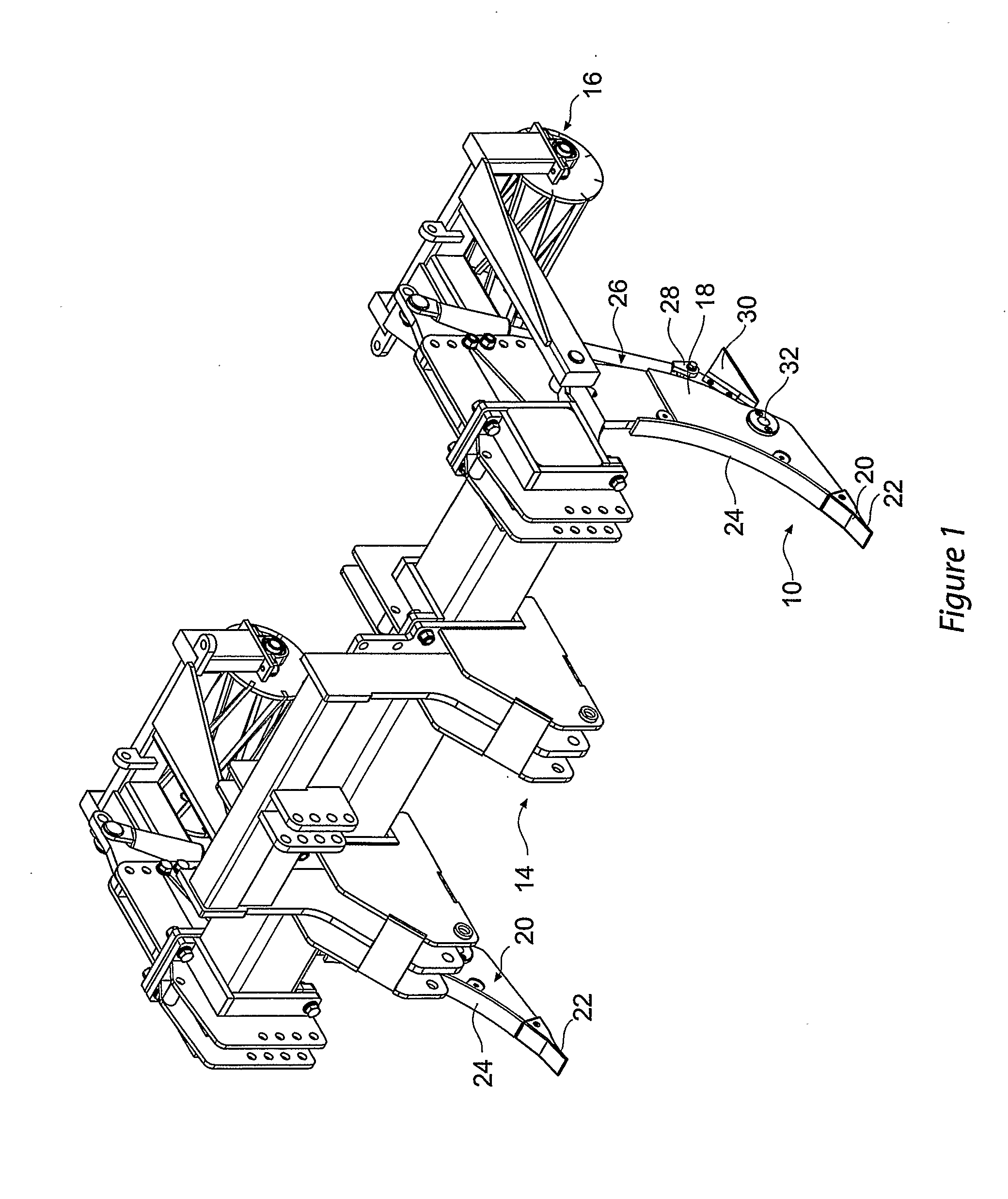
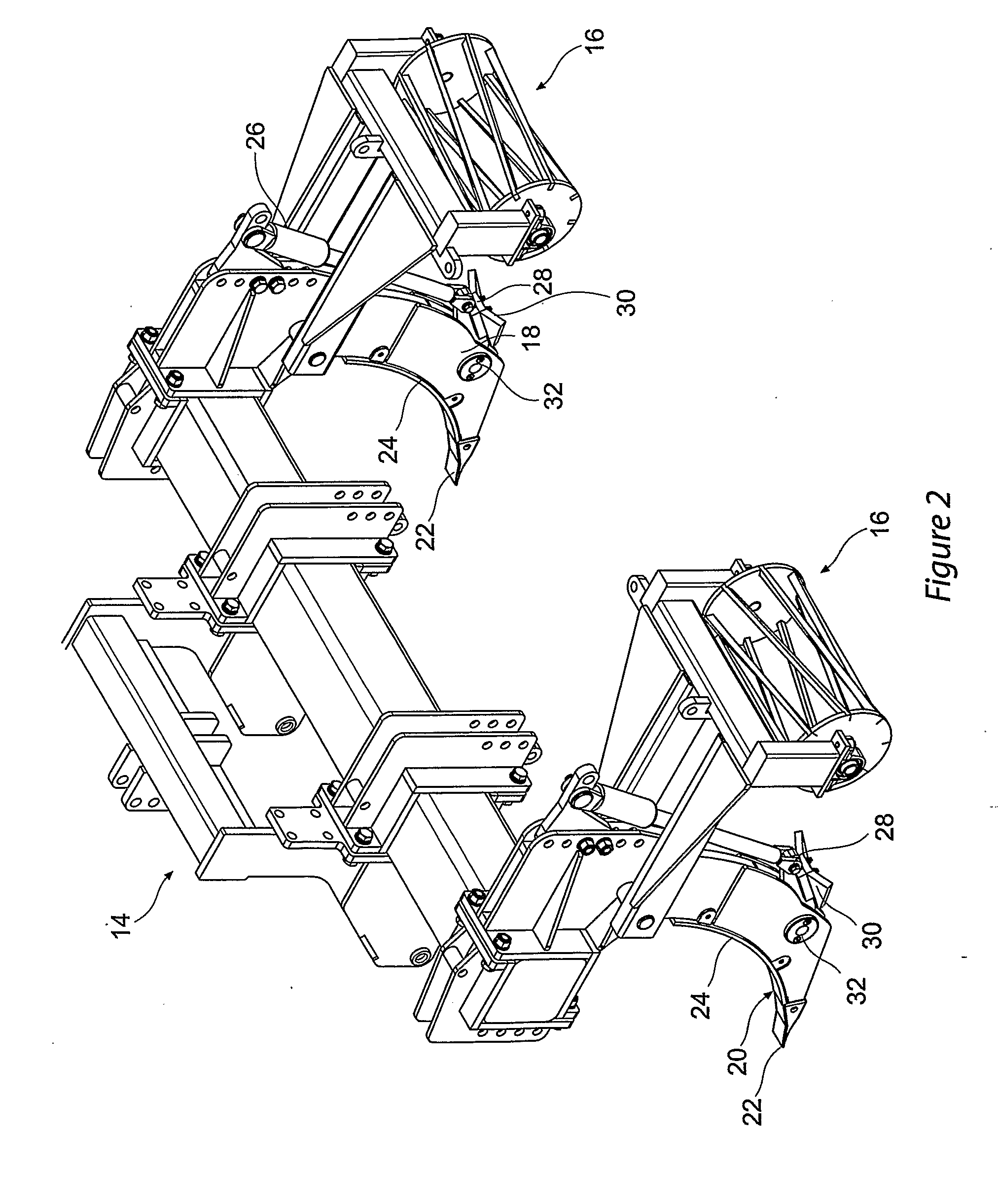
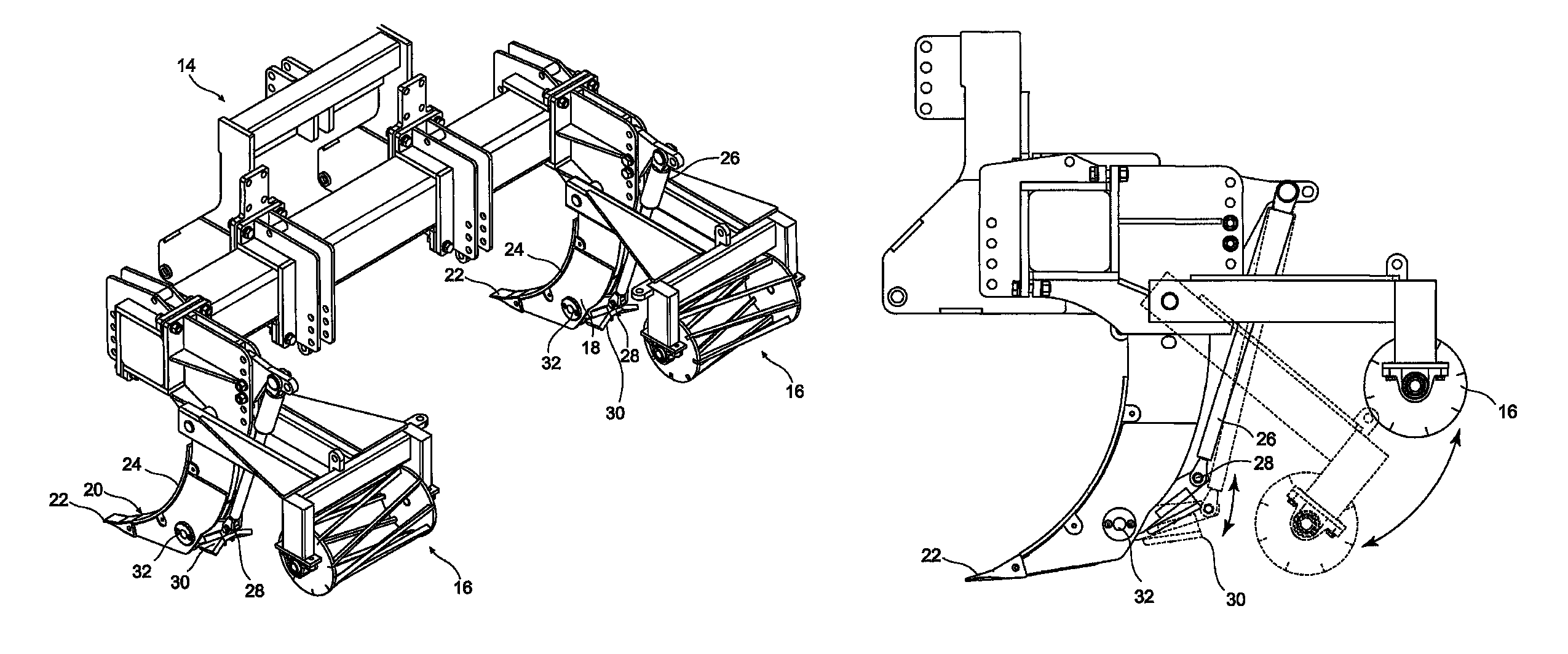
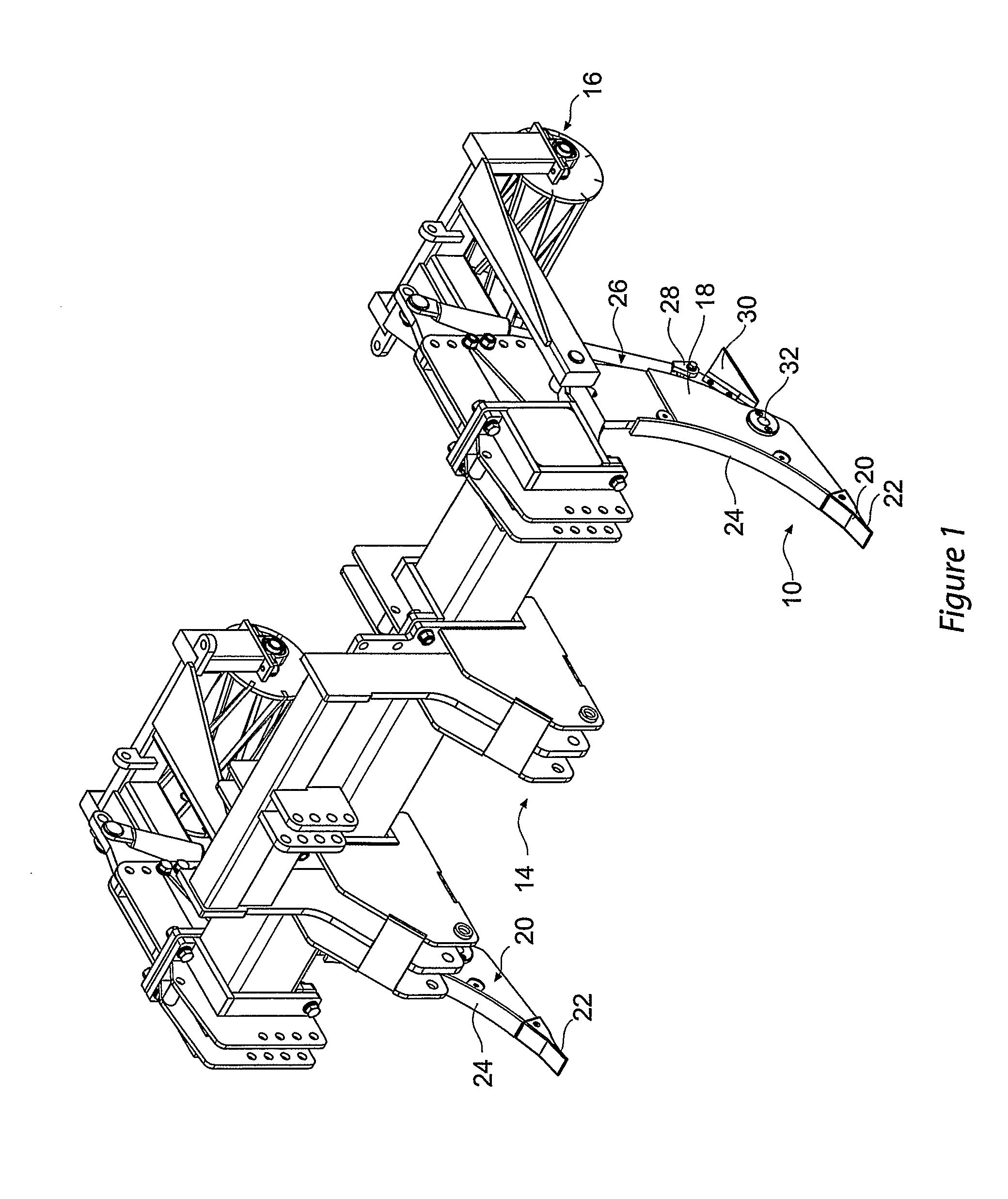
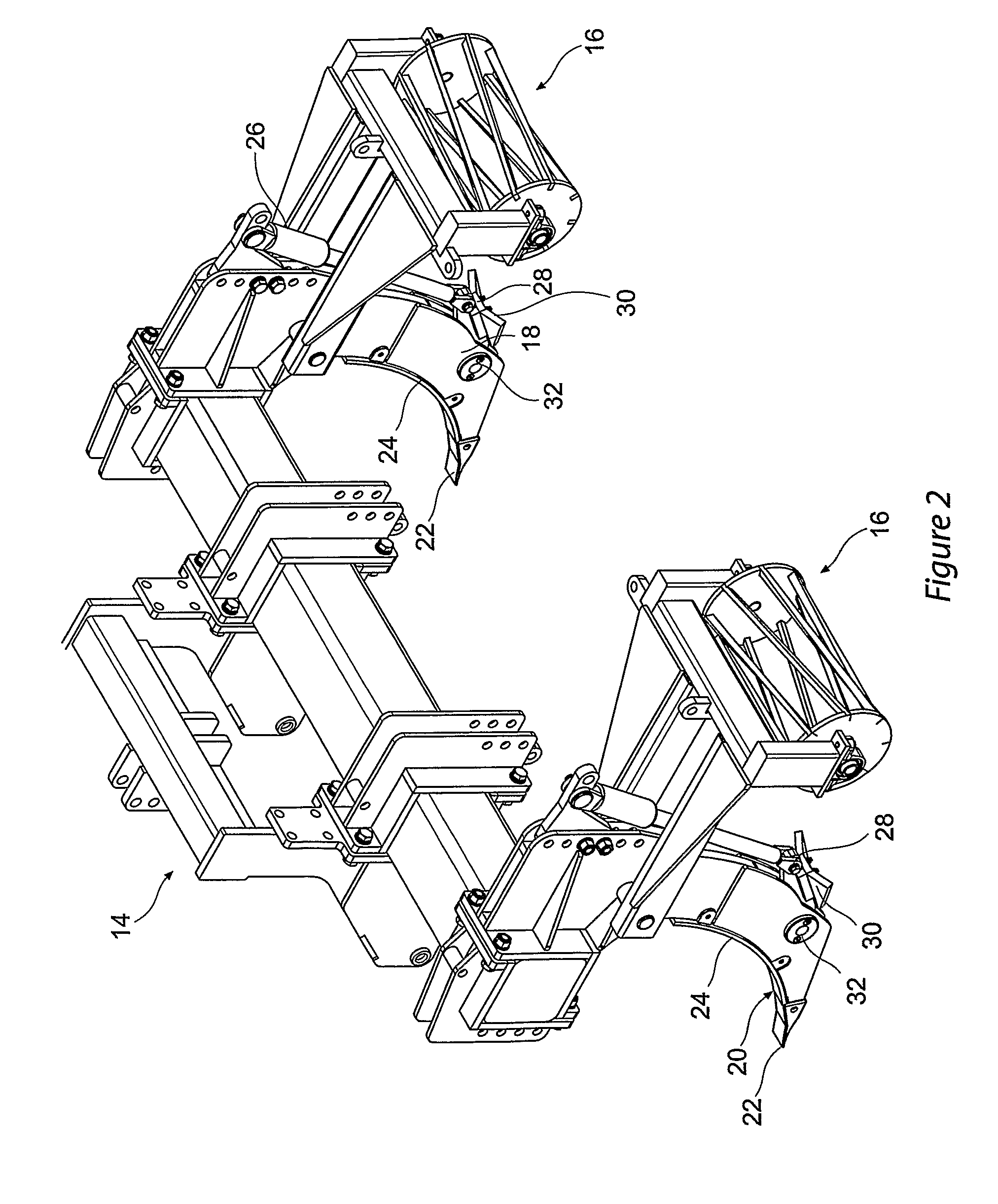
Cultivation system and a subsoil tool
ActiveUS20110010314A1Limit any undesirable incorporationFast infiltrationSpadesData processing applicationsSoil scienceHydraulic ram
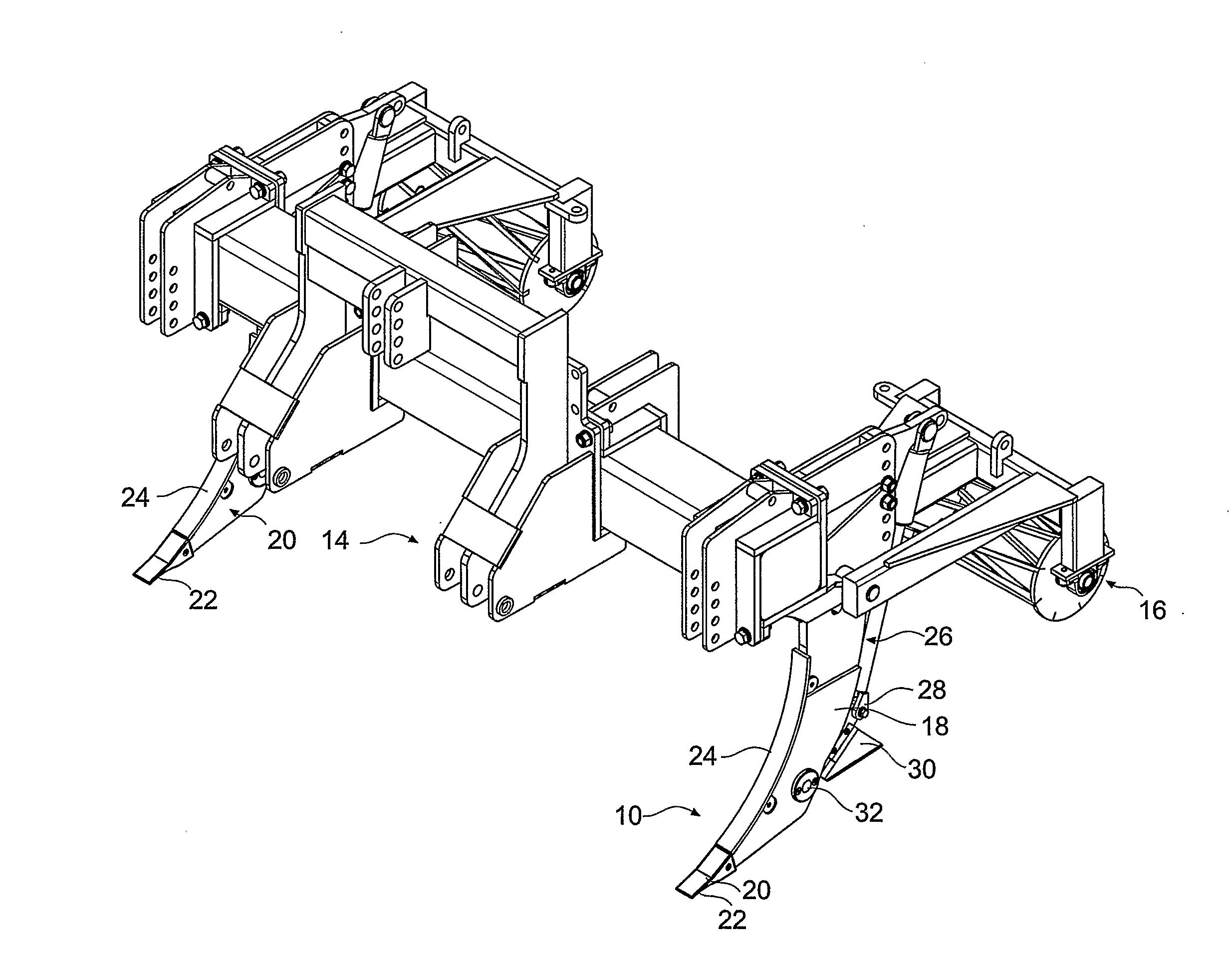
A method and system of tillage and tillage management that includes the steps of establishing a plurality of soil profiles over an area of soil to be cultivated, creating soil map database by combining these soil profiles to establish a treatment and cultivation regime, cultivating the ground in accordance regime and recording the cultivation in the soil map database. A subsoil tool for carrying out the method and system, with a shank (18) connected to a vehicle and to a ripper foot (20) terminating in a ripper tooth (22); a hydraulic ram (26) attached at a lower end to a first pivot connection (28) and at an upper end to an actuator means; the first pivot connection is attached to a rear end of a laterally extending wing member (30), a front end of the wing member being pivotally attached to the shank through a second pivot point (32) and the wing member is selected in accordance with soil profile at any position on a soil map database and is oscillated in response to actuation of the ram.
Owner:AGSOILWORKS TECH CO LLC
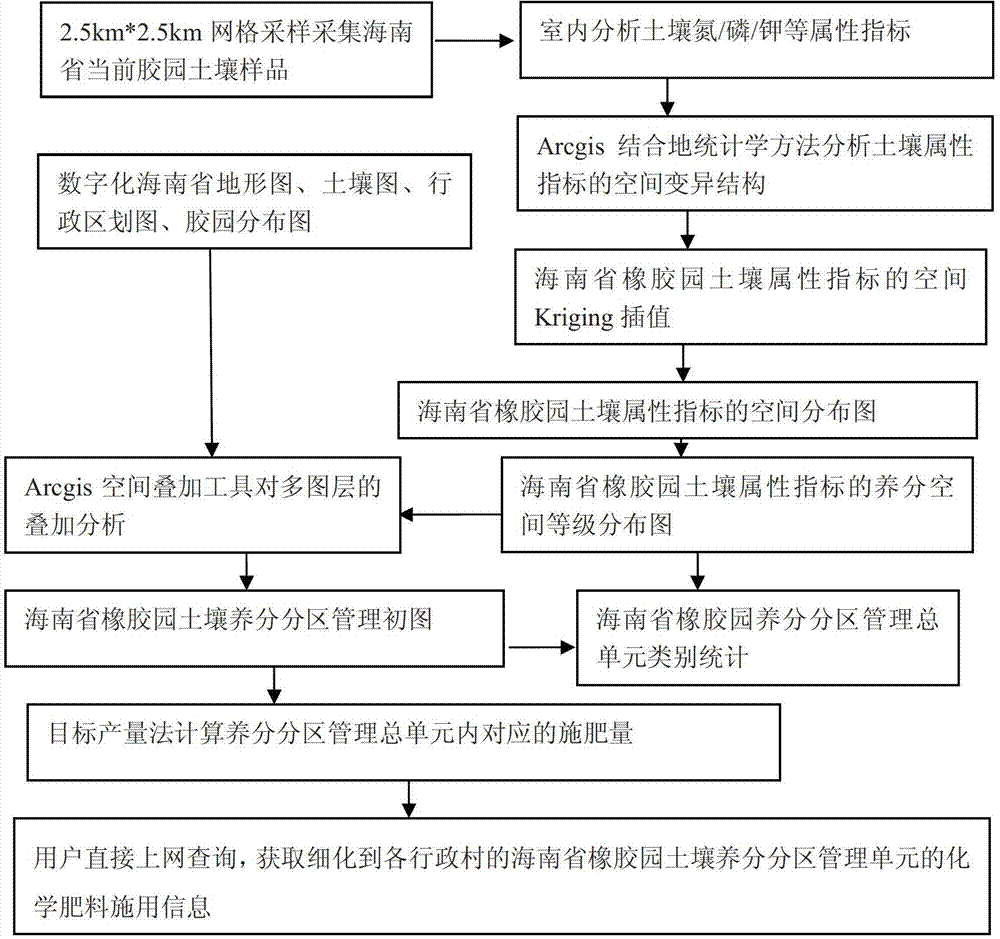
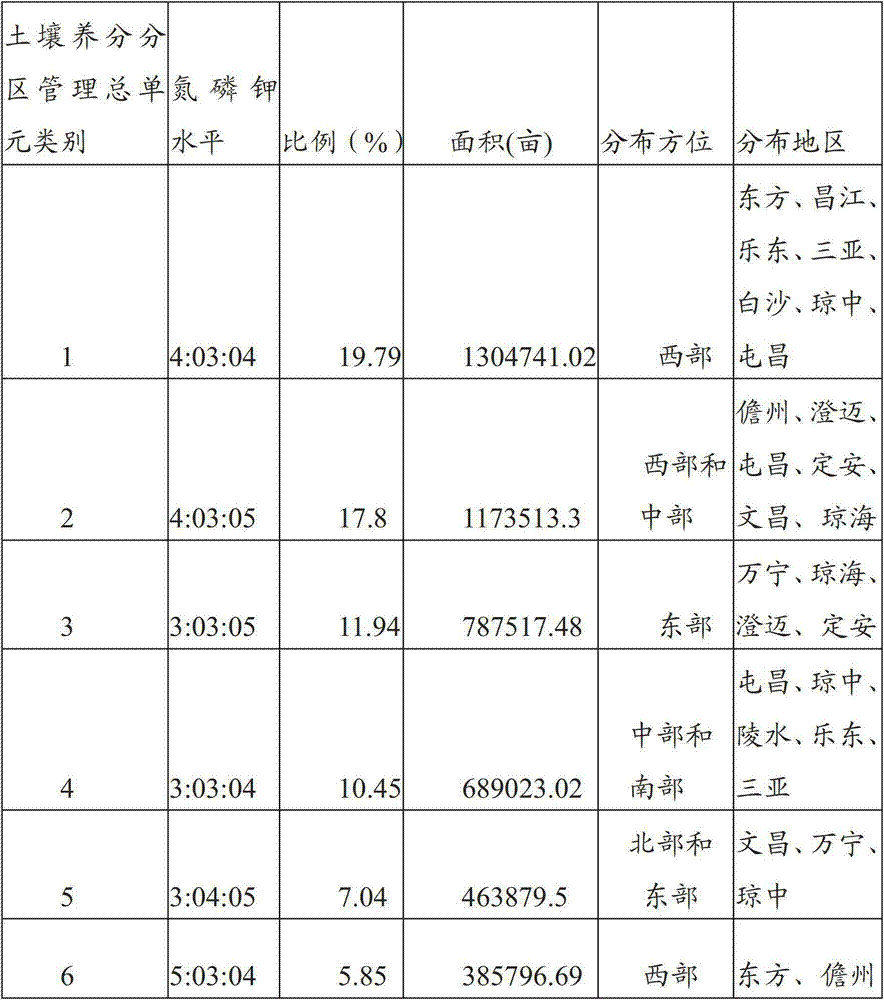
Partitioned management method of soil nutrients
InactiveCN103081624AEfficient managementFine ratioClimate change adaptationFertilising methodsSoil propertiesNormal growth
The invention provides a partitioned management method of soil nutrients. The partitioned management method comprises the steps of carrying out spatial overlay analysis on a topographic map, a soil map, an administrative map, a distribution map of set crops in a surveyed area and a spatial rank distribution map of nutrients in the digitized surveyed area by adopting a spatial overlay method to generate a primary partitioned management map of soil nutrients of the set crops in the surveyed area; carrying out merging operation on pattern spots in the primary partitioned management map of the soil nutrients in accordance with a preset rule and a main soil property similarity principle to obtain a total partitioned management unit of more than one variety of soil nutrients; and calculating the fertilizing amount of soil nutrients required for normal growth of each set plant in the total partitioned management unit of various varieties of soil nutrients according to a target output method. The partitioned management method can be used for quantitatively describing soil properties and space change situations in a targeted manner and has an important meaning in terms of improving the fertilizer utilization efficiency in a farmland, improving field management and especially implementing 'precision agriculture' in China.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Cultivation system and a subsoil tool
ActiveUS8626401B2Limit any undesirable incorporationFast infiltrationSpadesData processing applicationsSoil scienceHydraulic ram
A method and system of tillage and tillage management that includes the steps of establishing a plurality of soil profiles over an area of soil to be cultivated, creating soil map database by combining these soil profiles to establish a treatment and cultivation regime, cultivating the ground in accordance regime and recording the cultivation in the soil map database. A subsoil tool for carrying out the method and system, with a shank (18) connected to a vehicle and to a ripper foot (20) terminating in a ripper tooth (22); a hydraulic ram (26) attached at a lower end to a first pivot connection (28) and at an upper end to an actuator the first pivot connection is attached to a rear end of a laterally extending wing member (30), a front end of the wing member being pivotally attached to the shank through a second pivot point (32) and the wing member is selected in accordance with soil profile at any position on a soil map database and is oscillated in response to actuation of the ram.
Owner:AGSOILWORKS TECH CO LLC
Soil attribute parameter estimation method, fertilizer application program recommended method and fertilizer preparation program recommended apparatus
InactiveCN105432205ALow input costImprove accuracyData processing applicationsFertilising methodsEstimation methodsSoil map
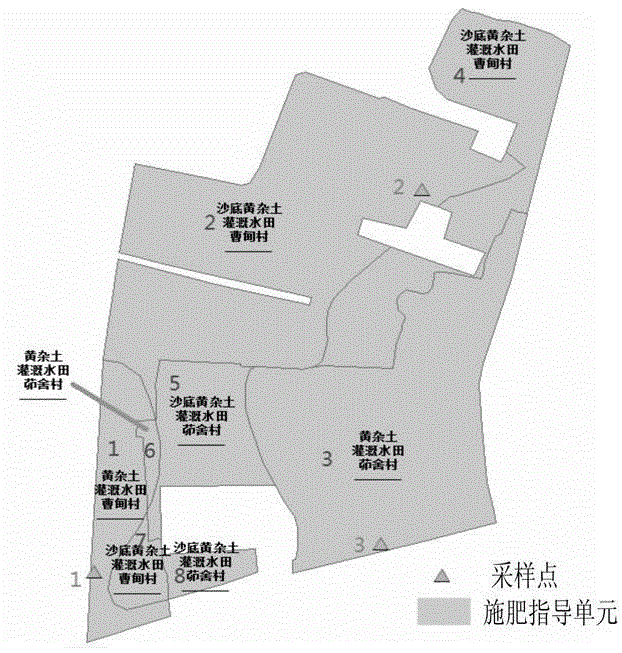
The present invention discloses a soil attribute parameter estimation method, a fertilizer application program recommended method and a fertilizer application program recommended apparatus. The estimation method is as follows: a block formed by superposition of a soil map, a land use actuality map, an administrative map and a sampled point bitmap is used for generating fertilization guide units; sampled fertilization guide units at the periphery of a target fertilization guide unit are identified, sampled fertilization guide units with first key fields same as a first key field of the target fertilization guide unit are selected as an estimation range; when the first key fields of the all the sampled fertilization guide units at the periphery of the target fertilization guide unit are not same as the first key field of the target fertilization guide unit, sampled fertilization guide units with second key fields same as a second key field of the target fertilization guide unit are selected as the estimation range; and soil attribute parameters of the sampled fertilization guide units in the estimation range are used for assignment of soil attribute parameters of the target fertilization guide unit.
Owner:扬州市土壤肥料站
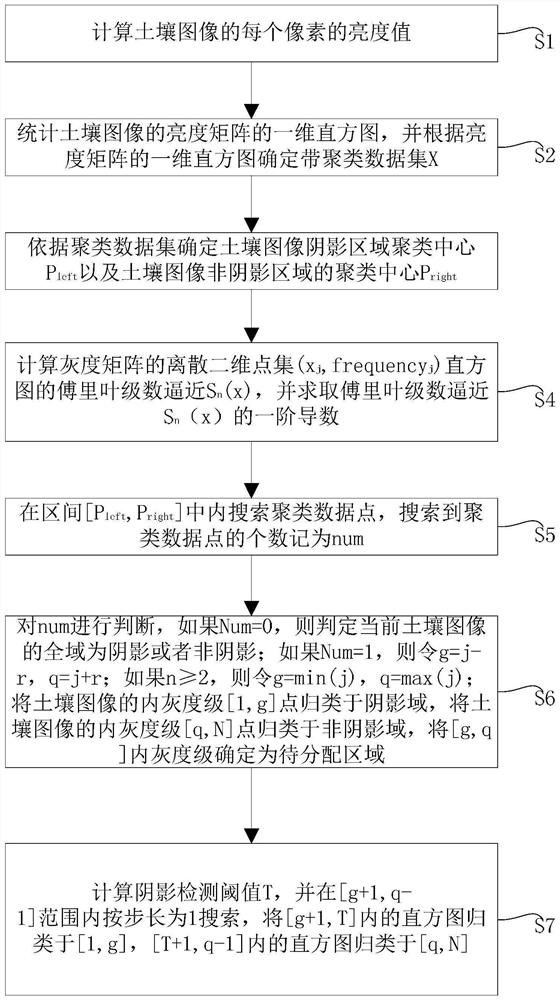
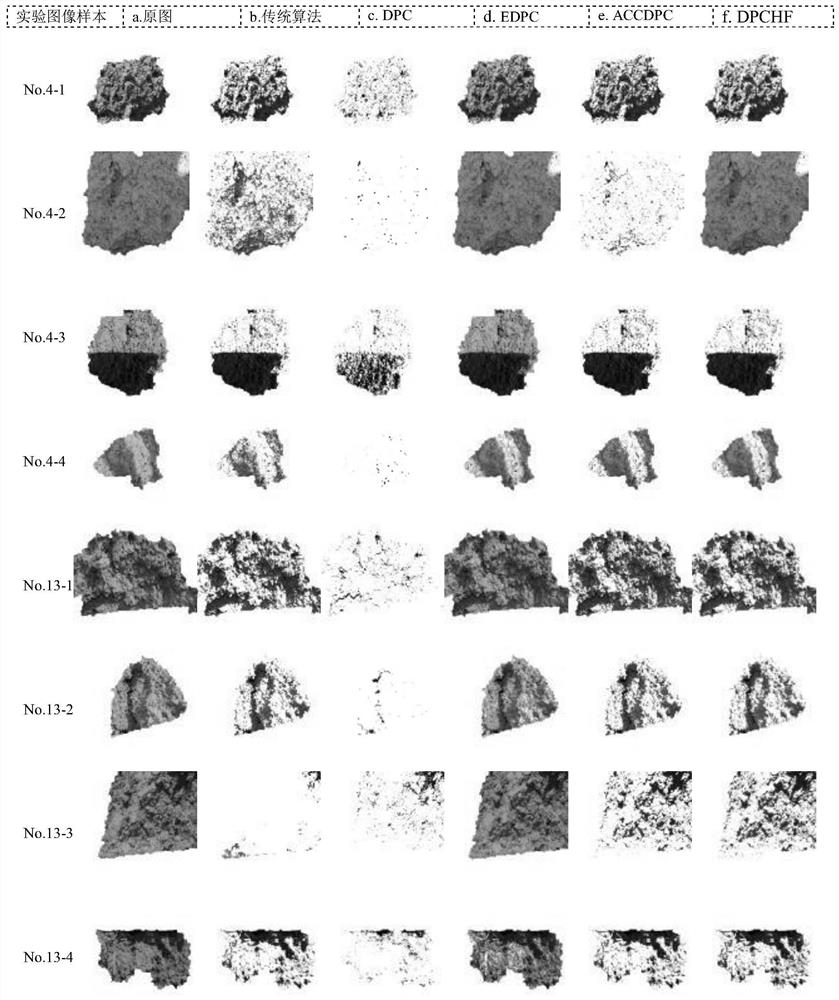
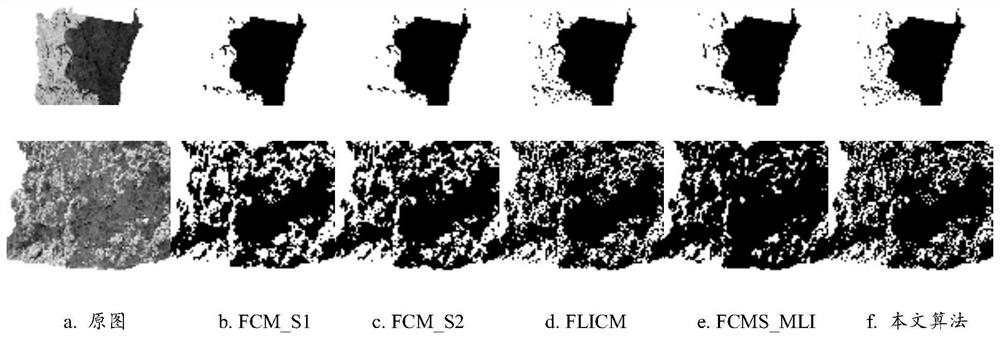
Density peak clustering soil image shadow detection method based on histogram fitting
PendingCN113808144AAvoiding Error Propagation FlawsHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisClustered dataCluster algorithm
The invention provides a density peak clustering soil image shadow detection methodbased on histogram fitting. The method is characterized in that the density of the clustering data set is reconstructed, then the clustering center is adaptively determined, the segmentation threshold value based on the data points between the non-shadow region and the shadow region is dynamically determined, and a final shadow detection result is obtained, so that the method can effectively avoid the error transmission defect of a clustering data distribution strategy in an original clustering algorithm, can effectively improve the precision of soil shadow detection, and guarantees the accuracy of subsequent soil image processing.
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
System and process for integrative computational soil mapping
ActiveUS20220067336A1Save monetary resourceShorten the timeScene recognitionSoil characteristicsSoil science
An integrative computational soil mapping system and process that reduces the required number of soil property measurements without jeopardizing the statistical precision of the resulting digital soil maps. The integrative computational soil mapping system and process saves monetary resources and time by reducing the number of soil property measurements required to produce digital soil maps and by offering soil sample locations which capture the maximum amount of representativeness of the soil characteristics in a determined area. In addition, the inventive system and process are integrative computational soil mapping that utilize algorithms based on state-of-the-art computational statistics and machine learning methods for the production of digital soil property maps and also provides soil sampling locations to collect new soil property measurements. These soil property measurements can be used to update and potentially improve previous versions of digital soil property maps, produced by the computational process.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS +1
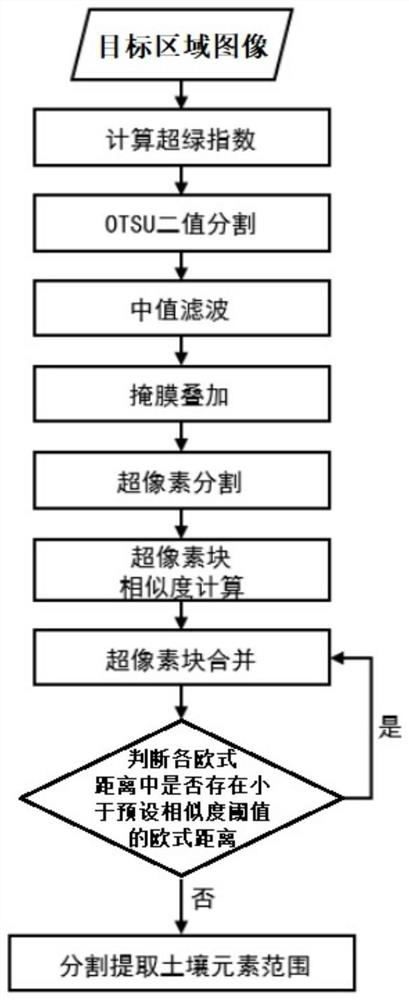
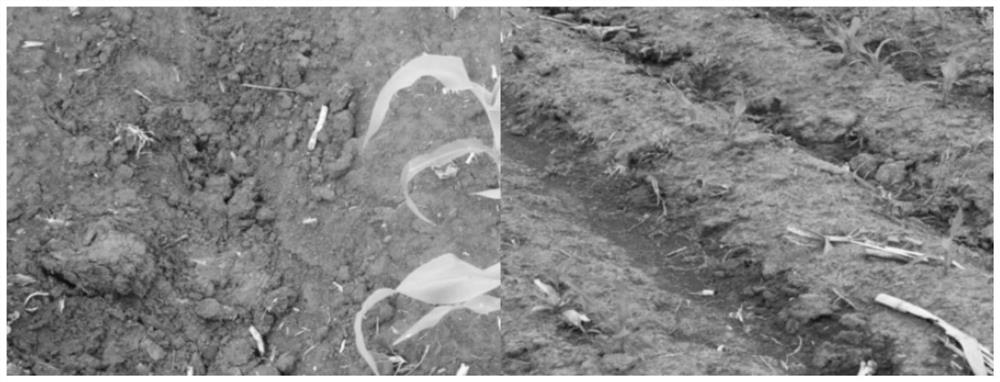
Soil image segmentation and extraction method based on super-green index and super-pixel
InactiveCN113205525ASegment extraction is fastAccurate extractionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionAutomatic segmentation
The invention relates to a soil image segmentation and extraction method based on a super-green index and a super-pixel, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly segmenting and removing the most common interference element green vegetation in a soil image through the super-green index; then, using a green vegetation area as a mask to be overlapped with an original image, reducing interference of non-soil elements on subsequent segmentation, and enhancing the stability of the whole algorithm; and finally, performing superpixel segmentation on the image after mask superposition, merging superpixel blocks based on the similarity corresponding to the Euclidean distance, and removing other interference elements in the soil image such as straws and small block shadows through segmentation. According to the whole design scheme, the soil elements in the soil image are automatically and quickly segmented and extracted, and the defects that time and labor are consumed when non-soil elements are removed from the soil image through a manual method are overcome. In addition, the method overcomes the defects that an existing automatic segmentation method can only extract part of soil areas in the image and is not accurate enough, and all soil element areas in the image can be extracted more accurately.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Functional soil maps
Embodiments of the present disclosure relate generally to system and methods for generating functional soil maps. The systems and methods are configured to determine soil information for an area of interest; determine an elevation model for the area of interest; determine terrain attributes for the area of interest based on the elevation model; determine a relationship between the soil information and the terrain attributes for the area of interest; and generate a functional soil map based at least in part on the relationship between the soil information and the terrain attributes for the area of interest. In an embodiment, the systems and methods can be used to improve management strategies for crops and other land management regions.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
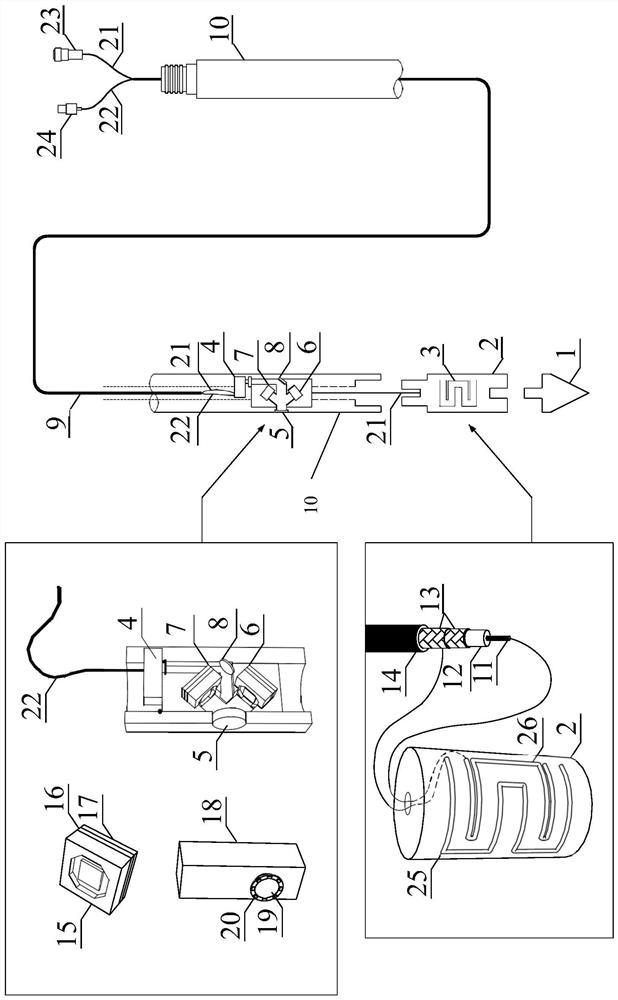
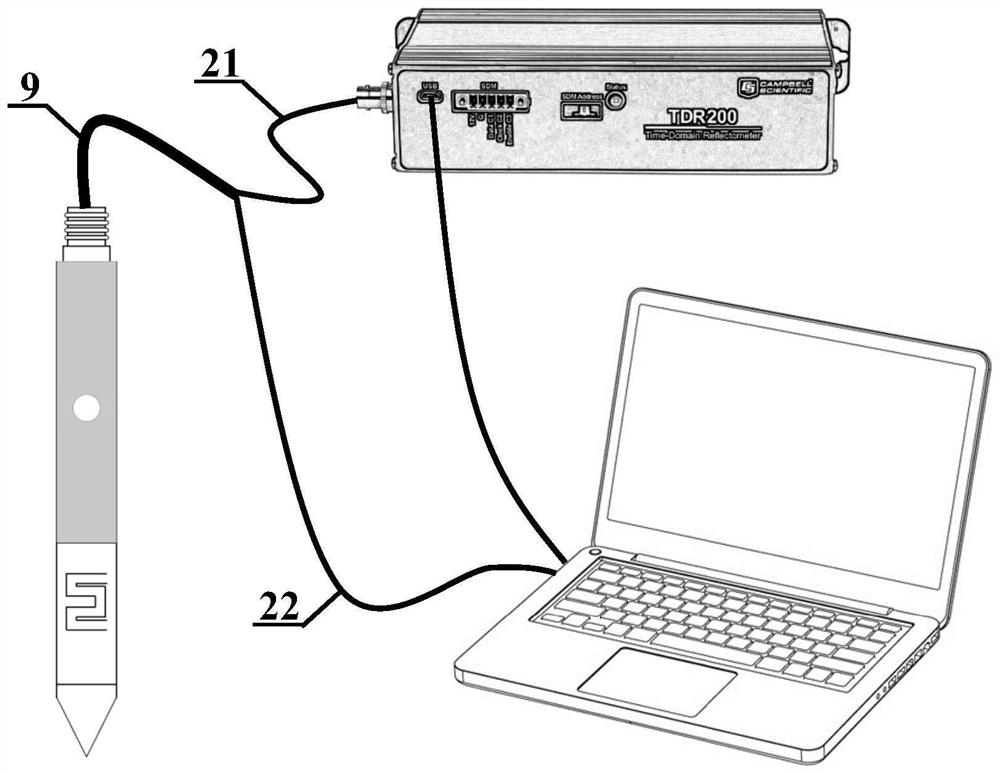
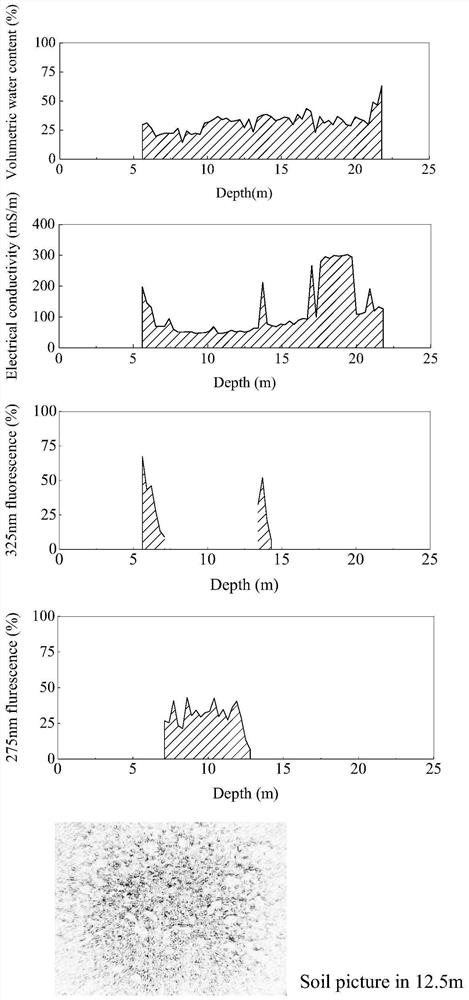
Pollution detection method of soil multi-pollutant identification probe based on multi-spectral and time-domain reflectance
ActiveCN113899406BEasy to carryLow working conditionsColor/spectral properties measurementsMaterial resistanceDielectricPoly ether ether ketone
The invention discloses a pollution detection method of a soil multi-pollutant identification probe based on multi-spectrum and time domain reflection. The polyether ether ketone insulating rod and the cone head are coaxially connected, and the gold-plated stainless steel probe is inlaid and fixed on the outer surface of the polyether ether ketone insulating rod; the polyether ether ketone insulating rod and the stainless steel probe rod are coaxially connected. The side wall is drilled, and the drilled hole is inlaid with an alumina glass lens. The stainless steel probe at the drilled hole is equipped with a multi-spectral detection module composed of an endoscopic image sensor, a 280nm wavelength UV LED, a 325nm wavelength UV LED and a flat mirror; detection Obtain soil dielectric constant, electrical conductivity and other indicators to characterize the content of ionic pollutants, 325nm fluorescence intensity, 280nm fluorescence intensity and soil pictures, characterize the content of humic acid, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and other pollutants and reflect soil types. The invention is easy to carry, quickly obtains content information of multiple pollutants, and is suitable for in-situ deep detection of solid waste landfill sites and other scenarios.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
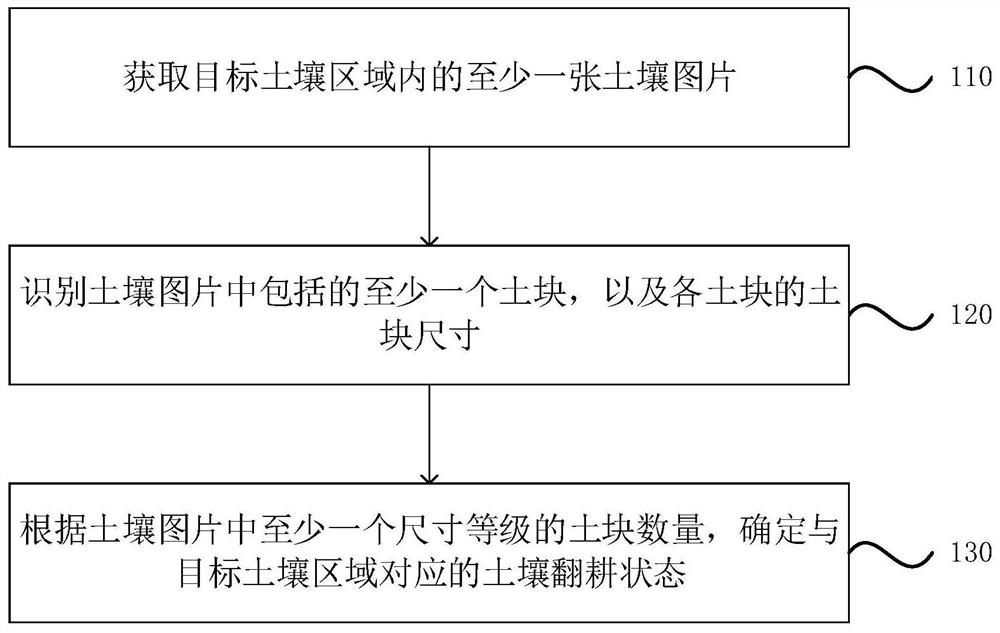
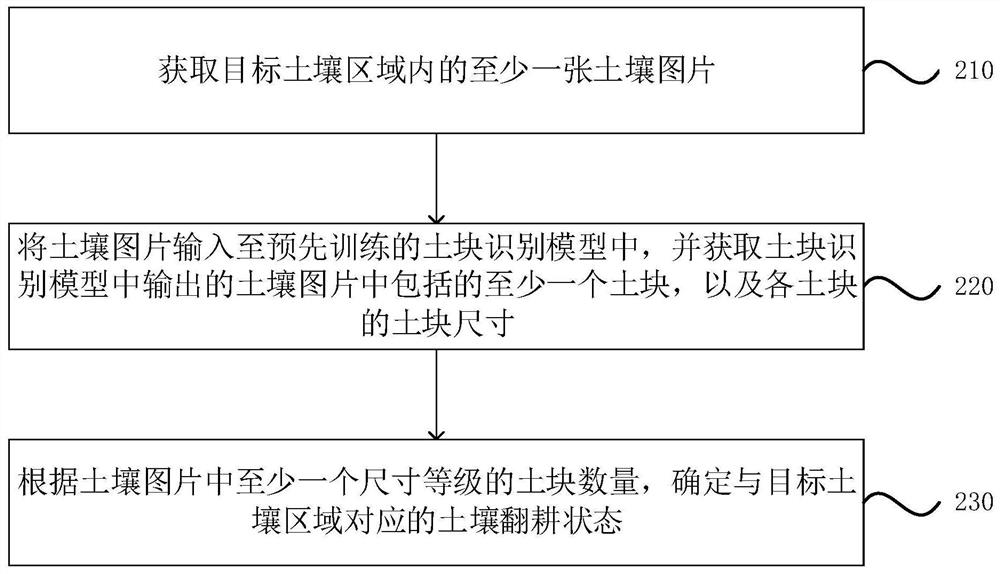
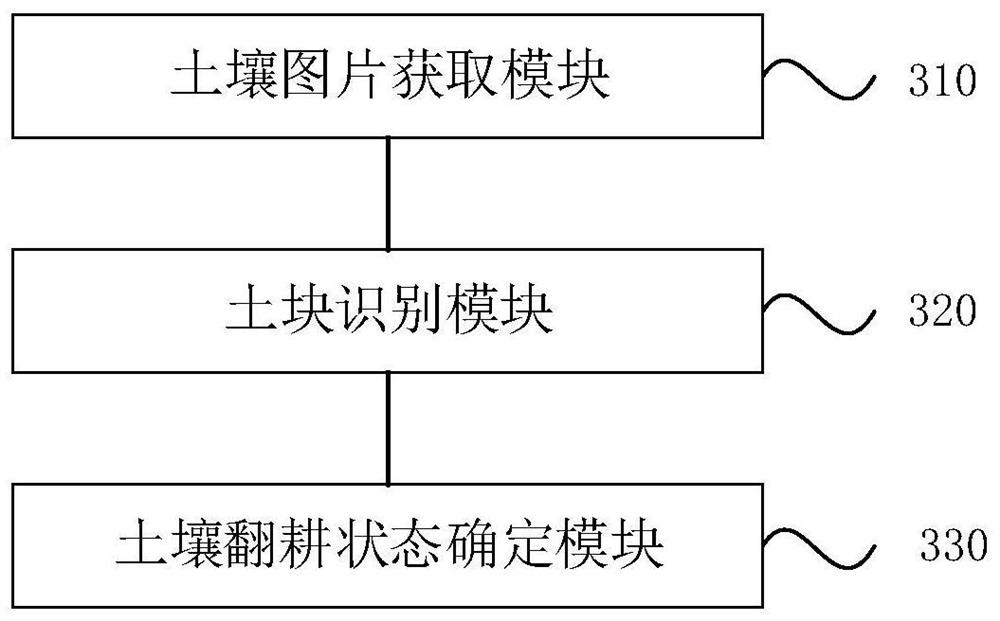
Soil ploughing state detection method, device and equipment and storage medium
PendingCN113807136AHigh degree of automationQuick displayData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionSoil mapSoil science
The invention discloses a soil ploughing state detection method and device, equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining at least one soil picture in a target soil area; identifying at least one soil block included in the soil picture and the soil block size of each soil block; and according to the number of the soil blocks of at least one size grade in the soil picture, determining the soil ploughing state corresponding to the target soil area. According to the technical scheme of the embodiment of the invention, the problem of low automation degree of a detection method of the soil ploughing state in the prior art is solved, the user can be quickly displayed or informed of the soil ploughing state, and the accuracy of ploughing state detection is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU XAIRCRAFT TECH CO LTD
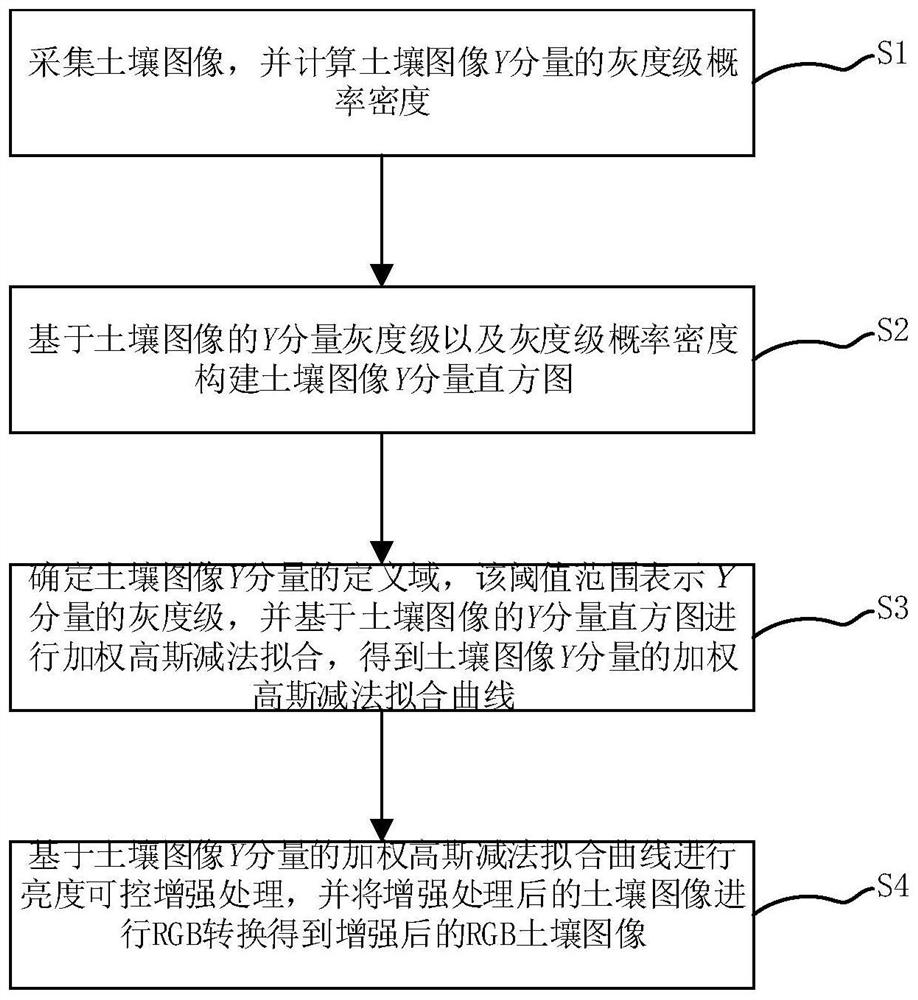
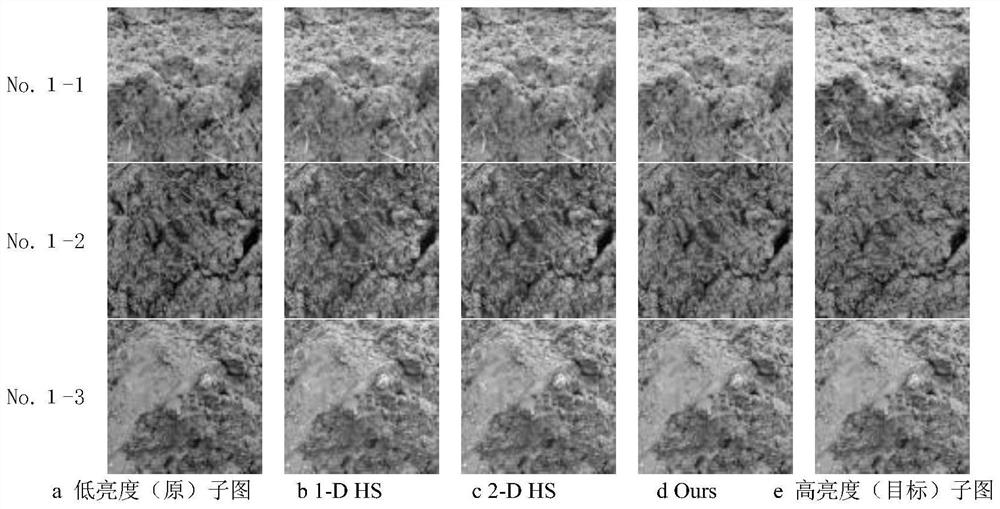
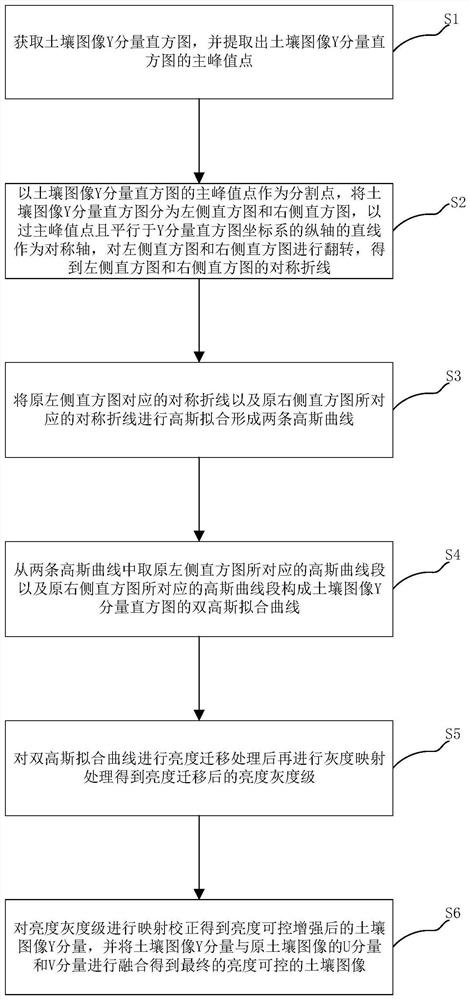
Soil image brightness controllable enhancement method based on weighted Gaussian subtraction fitting
PendingCN114764757AReduce the impact of recognitionImprove recognition accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisSoil typeMachine vision
The invention provides a soil image brightness controllable enhancement method based on weighted Gaussian subtraction fitting, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting a soil image, and calculating the gray scale probability density Porg (y) of a Y component of the soil image; s2, constructing a soil image Y component histogram based on the Y component gray level and the gray level probability density of the soil image; s3, determining the definition domain of the Y component of the soil image as [ya, yb], and performing weighted Gaussian subtraction fitting based on the Y component histogram of the soil image to obtain a weighted Gaussian subtraction fitting curve of the Y component of the soil image; s4, performing brightness controllable enhancement processing on the basis of the weighted Gaussian subtraction fitting curve of the soil image Y component, and performing RGB conversion on the enhanced soil image to obtain an enhanced RGB soil image; through brightness controllable enhancement, soil images collected under inconsistent natural illumination conditions are adjusted, so that the soil images are very similar to real soil images collected under certain specific illumination conditions, and the method is used for machine vision soil type identification, thereby reducing the influence of different natural illumination conditions on soil image identification, and improving the subsequent soil type identification precision.
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +2
A sampling device based on soil research of chrysanthemum chrysanthemum
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
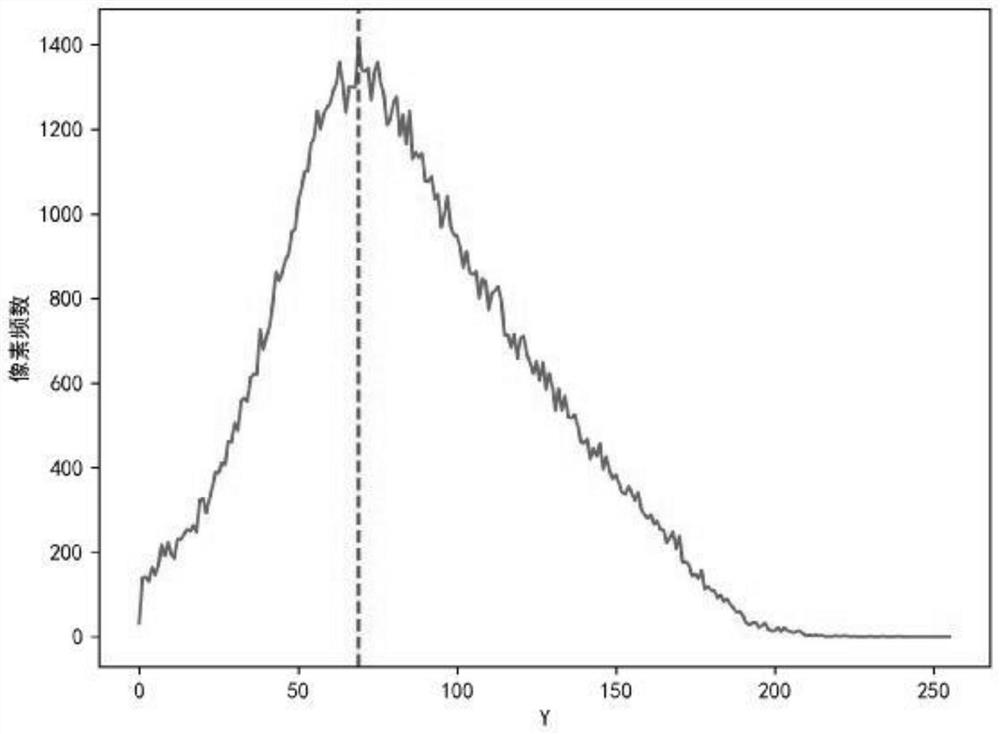
Soil image brightness controllable enhancement method based on double Gaussian fitting
PendingCN114757858ABrightness controllableQuality assuranceImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Gray level
The invention provides a soil image brightness controllable enhancement method based on double Gaussian fitting, and the method comprises the following steps: taking a main peak point of a soil image Y component histogram as a segmentation point, and dividing the soil image Y component histogram into a left histogram and a right histogram, turning over the left histogram and the right histogram by taking a straight line which passes through the main peak point and is parallel to the longitudinal axis of the Y-component histogram coordinate system as a symmetric axis to obtain symmetric broken lines of the left histogram and the right histogram; performing Gaussian fitting on the original left histogram, the symmetric broken line corresponding to the original left histogram and the symmetric broken line corresponding to the original right histogram to form two Gaussian curves; a Gaussian curve segment corresponding to the original left histogram and a Gaussian curve segment corresponding to the original right histogram are taken from the two Gaussian curves to form a double-Gaussian fitting curve of the soil image Y component histogram; carrying out brightness migration processing on the double-Gaussian fitting curve, and then carrying out gray mapping processing to obtain a brightness gray level after brightness migration; and performing mapping correction on the brightness gray level to obtain a Y component of the soil image after brightness controllable enhancement, and fusing the Y component of the soil image with the U component and the V component of the original soil image to obtain a final brightness controllable soil image.
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +2
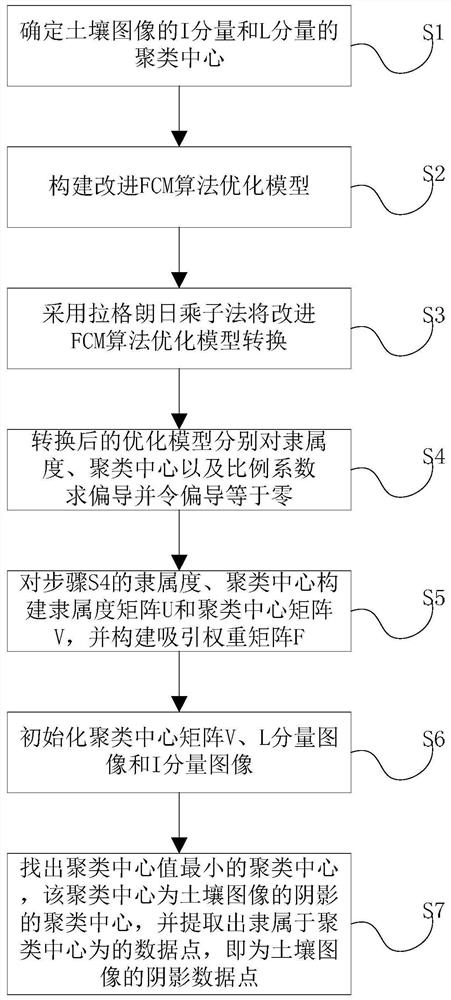
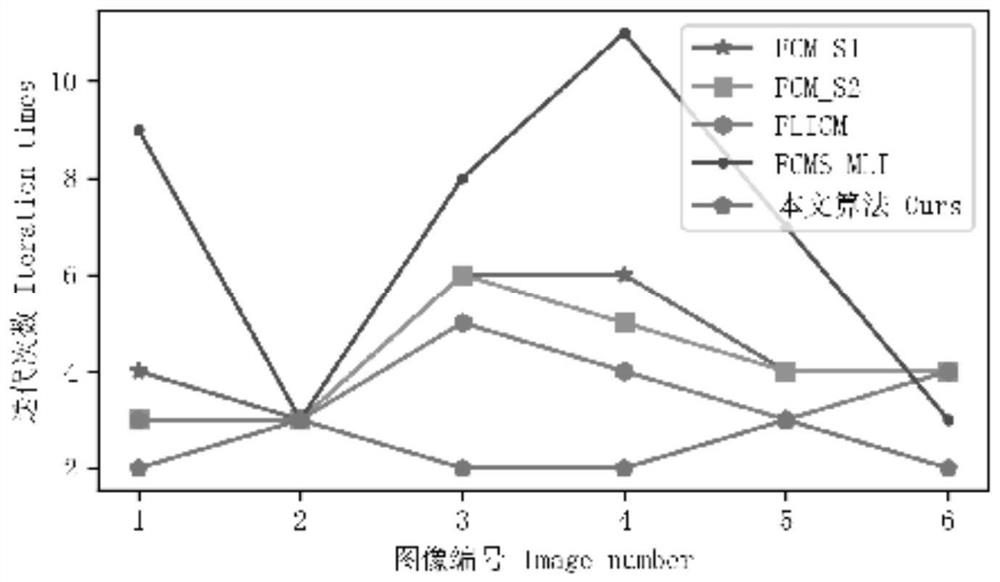
An Adaptive Soil Image Shadow Detection Method Based on FCM Algorithm
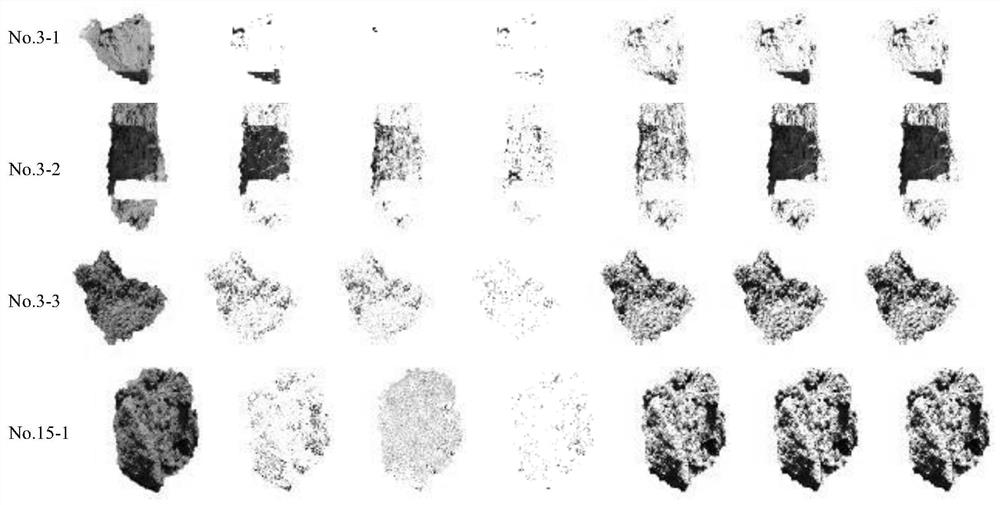
ActiveCN111754501BAccurate detectionGuaranteed detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisSoil scienceSoil map
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Soil humidity monitoring method and system based on unmanned aerial vehicle and readable storage medium
InactiveCN112487956ADifferential monitoringAchieve integrationImage enhancementImage analysisSoil scienceUncrewed vehicle
The invention relates to a soil humidity monitoring method and system based on an unmanned aerial vehicle, and a readable storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: collecting a soil image ina target region, carrying out the preprocessing of the soil image, and obtaining soil image information; establishing a soil humidity prediction model, and extracting a soil image gray value to obtain a soil dielectric property; analyzing the soil water content according to the soil dielectric property to obtain result information; displaying the result information according to a preset mode. Theradar echo signals are different according to different dielectric properties of soil with different water contents, the relationship between the scattering coefficient and the soil water content canbe established, the water content in the soil is further analyzed, and the calculation result is relatively accurate.
Owner:广东竞合基业科技服务有限公司
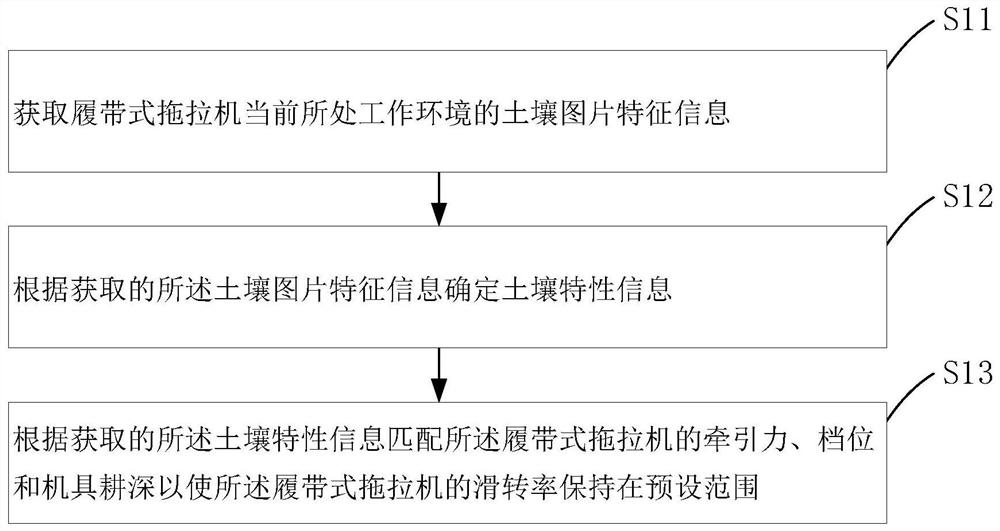
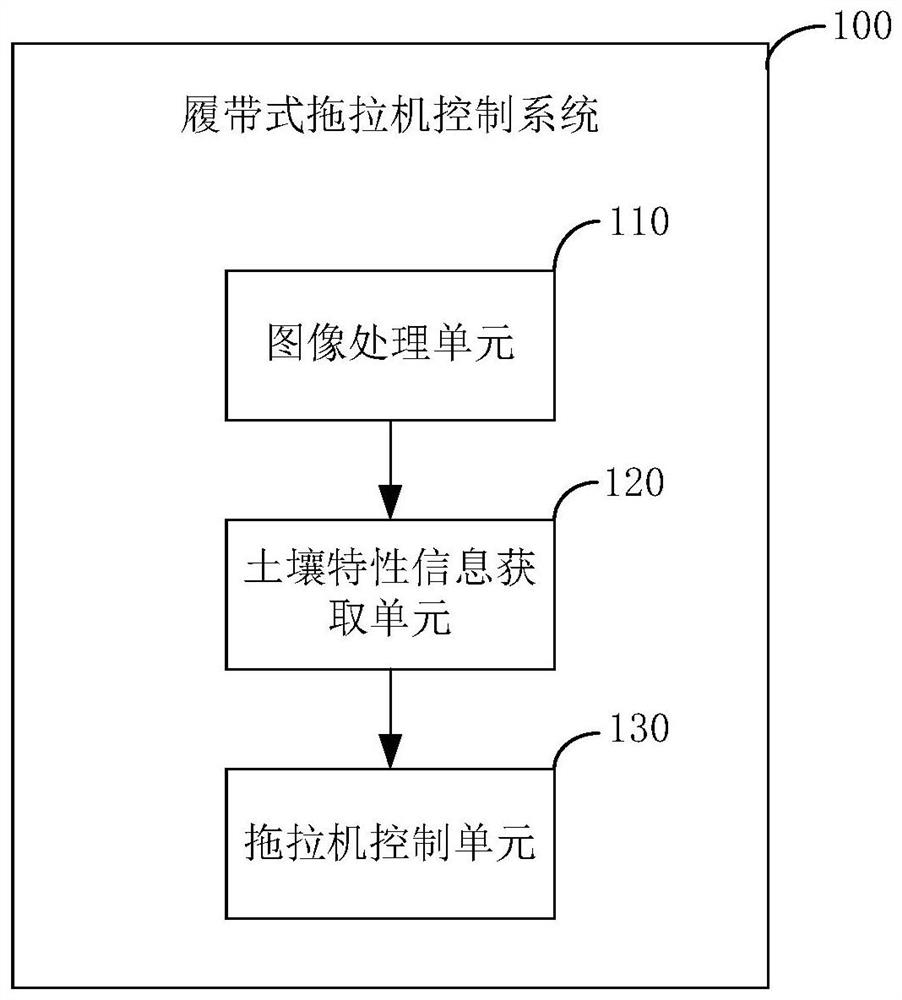
Crawler tractor control method and system
ActiveCN112124312AOptimizing the Slip Rate CurveImprove performanceEndless track vehiclesSoil characteristicsAgricultural engineering
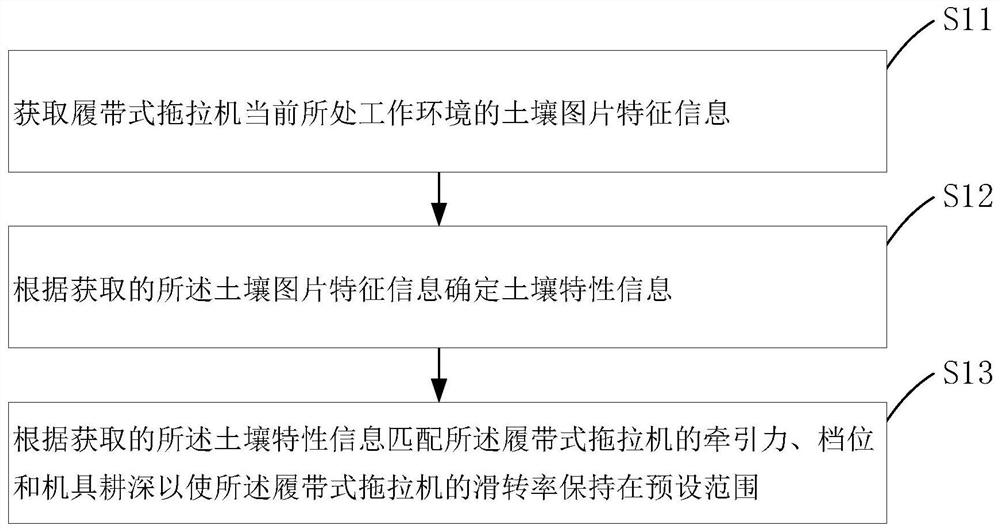
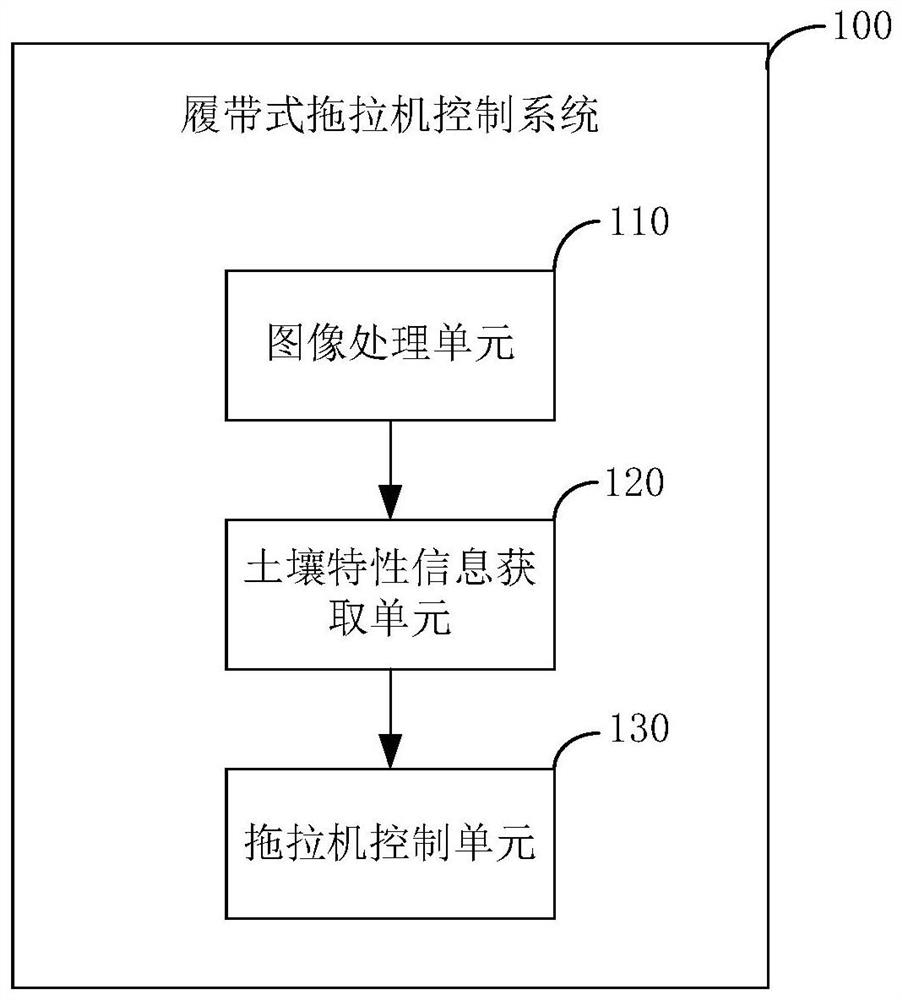
The invention discloses a crawler tractor control method and system. The crawler tractor control method comprises the steps: obtaining the soil picture feature information of a current working environment of a crawler tractor, determining soil characteristic information according to the obtained soil picture feature information, and according to the obtained soil characteristic information, matching a traction force, a gear and a machine tool tilling depth of the crawler tractor so as to enable a slip rate of the crawler tractor to be maintained in a preset range. By means of the crawler tractor control method and system, the working efficiency and stability of the crawler tractor can be improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
A gis-based method for estimating the load of nitrogen runoff loss in distributed paddy fields
The invention relates to a GIS (geographic information system)-based distributed-type rice field nitrogen runoff loss load estimating method. The method includes: 1), collecting basic information of a studied area, namely collecting daily rainfall, evaporation capacity, administrative area, land use map and soil map of the studied area; 2), investigating basic data of fertilizing and field moisture management; 3), generating a related space distribution grid map layer; 4), measuring and calculating dynamic changing rules of rice field surface water nitrogen concentration under different soil types, namely dynamically monitoring rice field surface water under different soil types and different fertilizing levels, and calculating fitting equation parameters of the rice field surface water; 5), calculating rice field nitrogen runoff loss load including a water quantity balance module, an initial concentration calculating module and a load output module. By the GIS-based distributed-type rice field nitrogen runoff loss load estimating method, temporal and spatial change of non-point-source-generated pollution discharging coefficient can be reflected, few basic data and parameters are needed, model building is easy, and running efficiency is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Soil image shadow detection method based on improved subtraction histogram
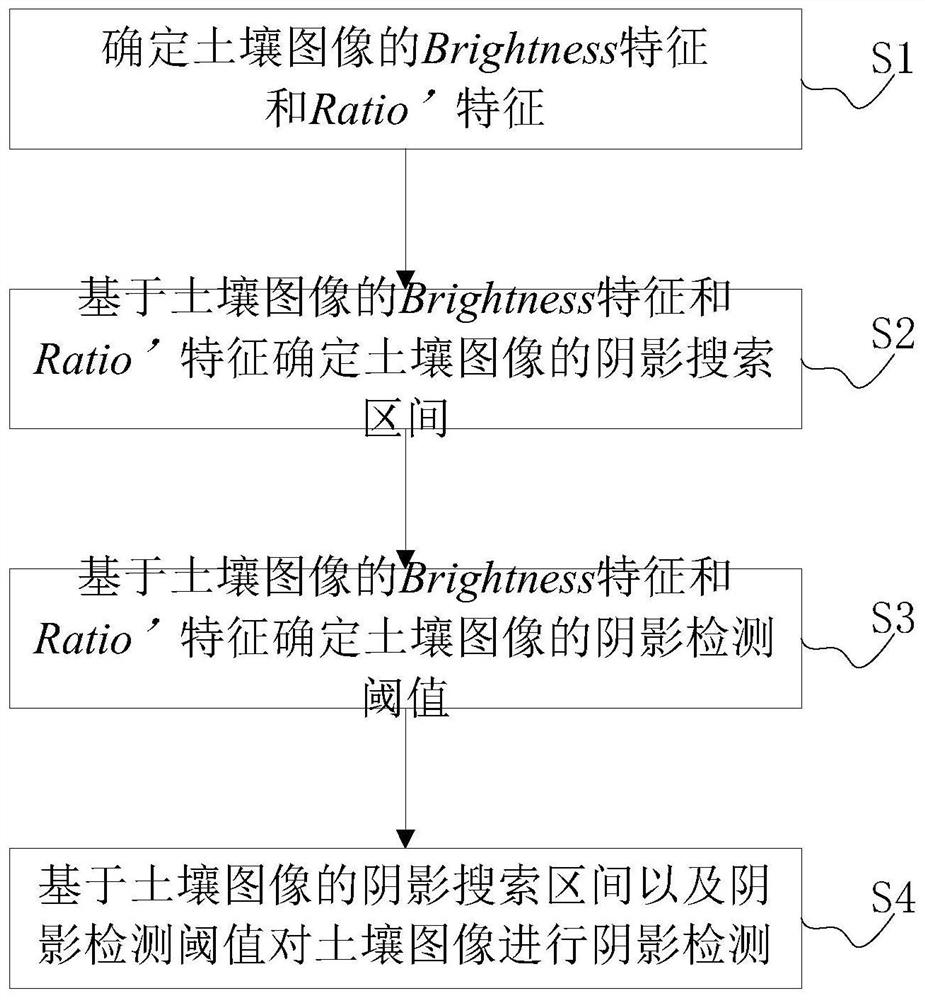
ActiveCN113240619AAccurate identificationAccurate segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisSoil mapThresholding
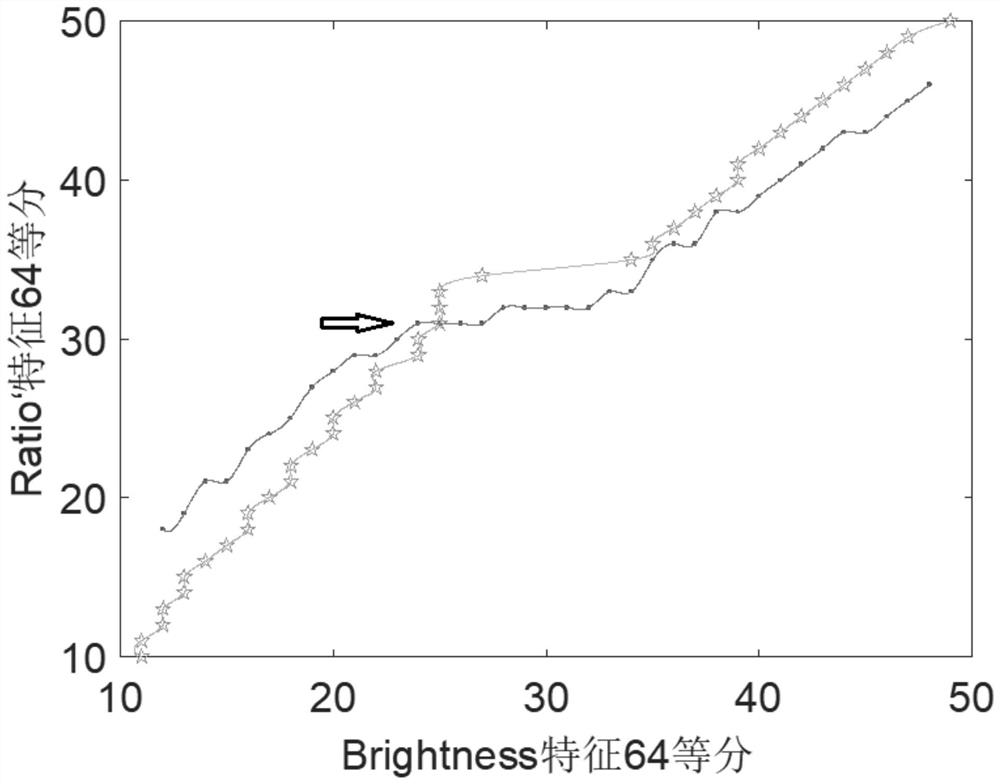
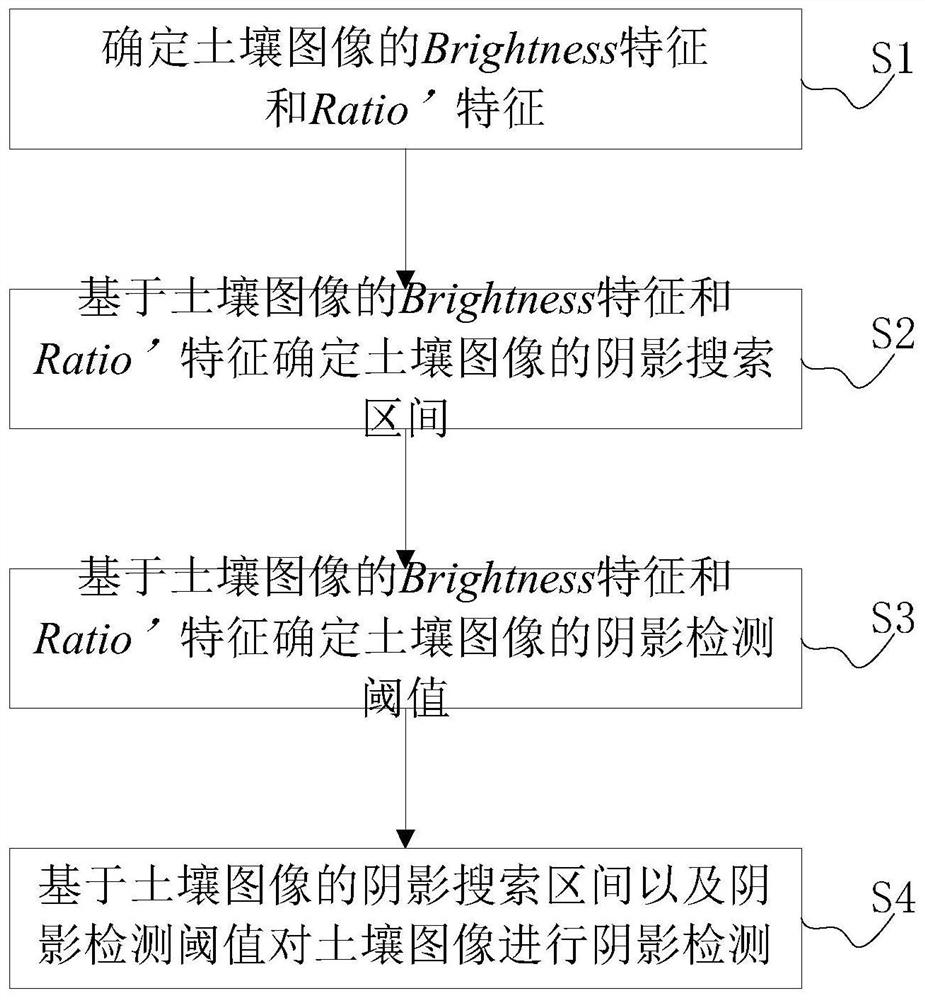
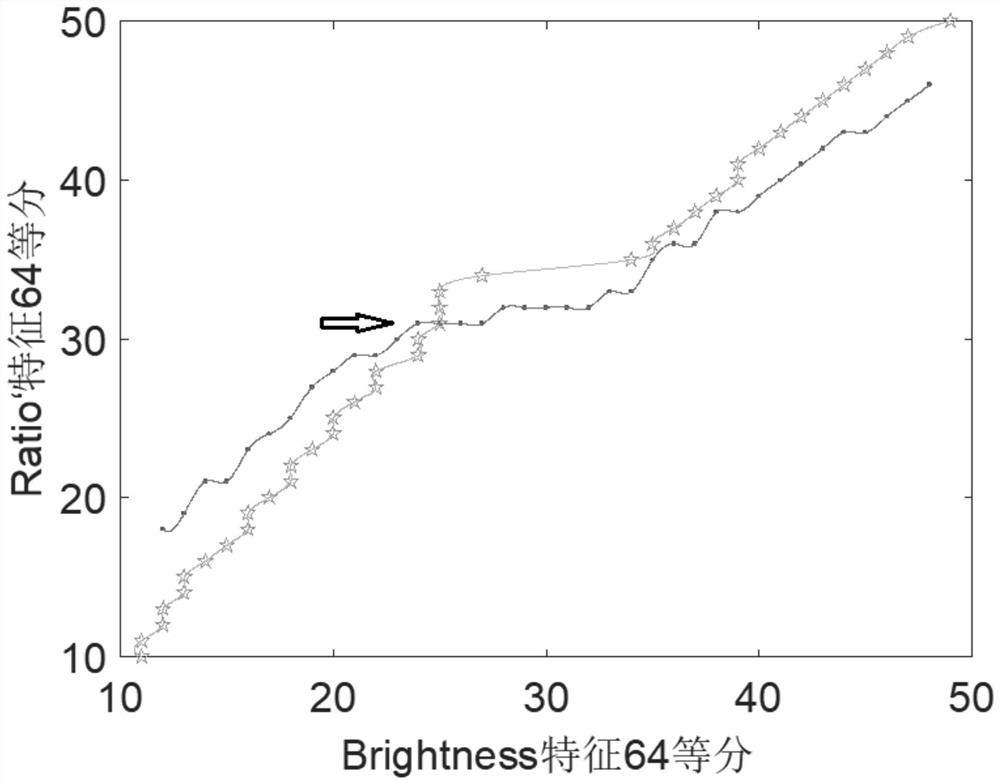
The invention provides a soil image shadow detection method based on an improved subtraction histogram. The method comprises the following steps: S1, determining a Bright feature and a Ratio' feature of a soil image; S2, determining a shadow search interval of the soil image on the basis of the Bright feature and the Ratio'feature of the soil image; S3, determining a shadow detection threshold value of the soil image based on the Briggle feature and the Ratio'feature of the soil image; S4, carrying out shadow detection on the soil image based on the shadow search interval and the shadow detection threshold value of the soil image. According to the method, the shadow and non-shadow areas of the soil image can be effectively and accurately identified and segmented, so the detection precision of the shadow of the soil image is ensured, redundancy does not exist in the algorithm, the detection efficiency is effectively improved, and good robustness is achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
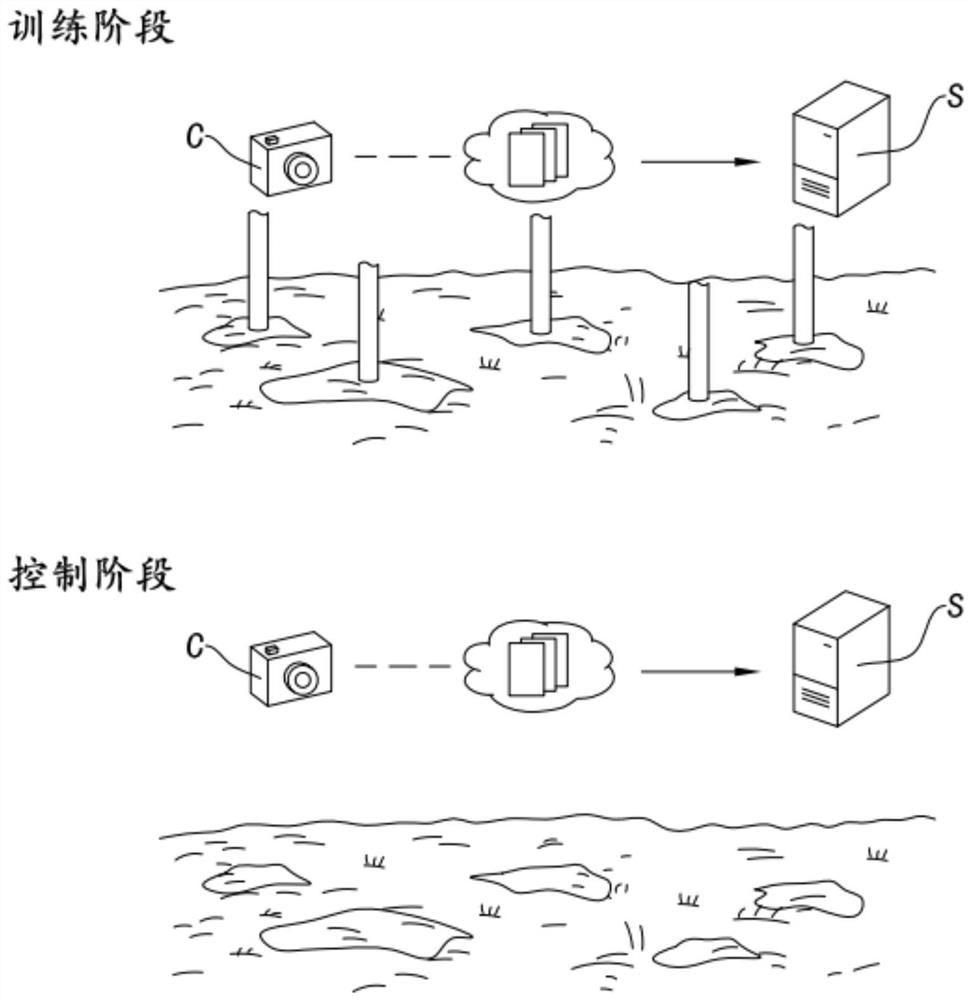
Intelligent control method for remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil
InactiveCN112750112AImprove repair effectImage enhancementImage analysisSoil sciencePetroleum Pollution
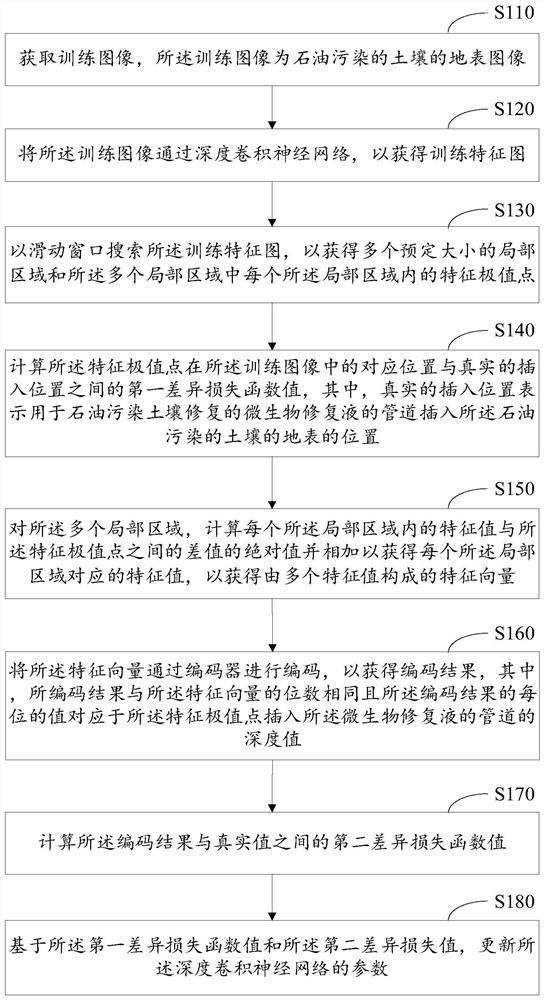
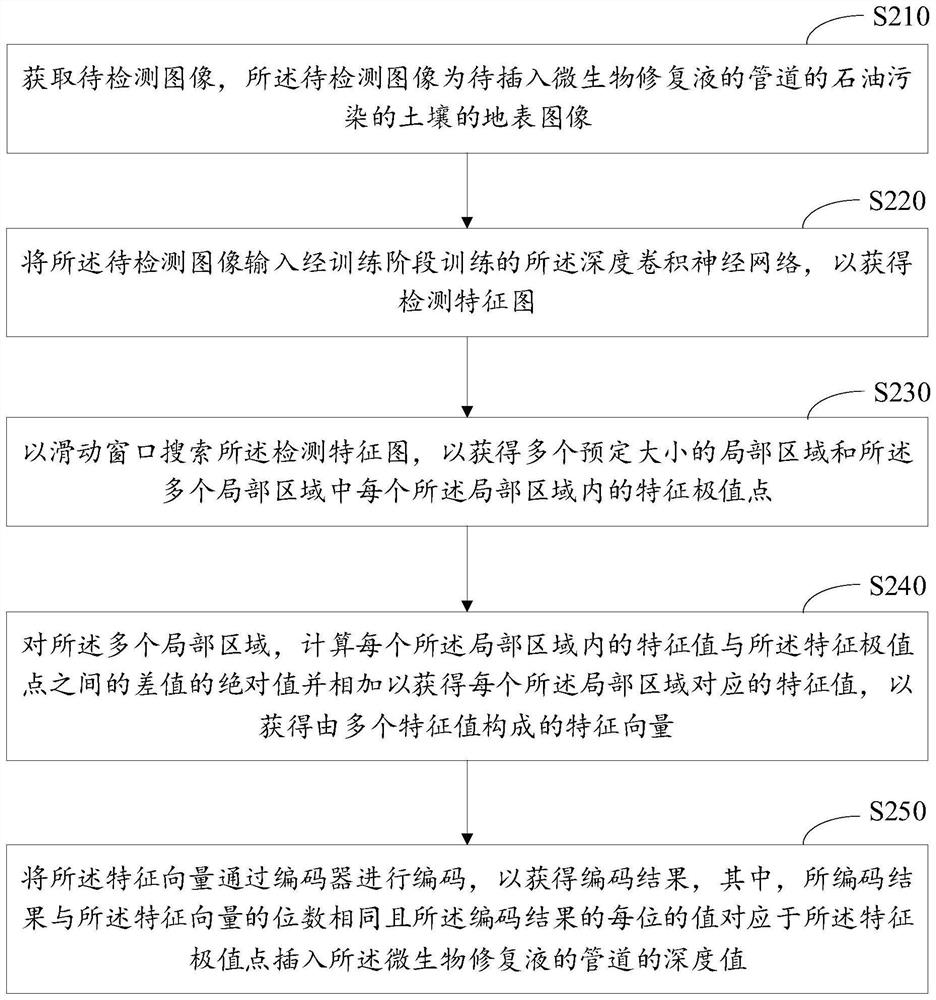
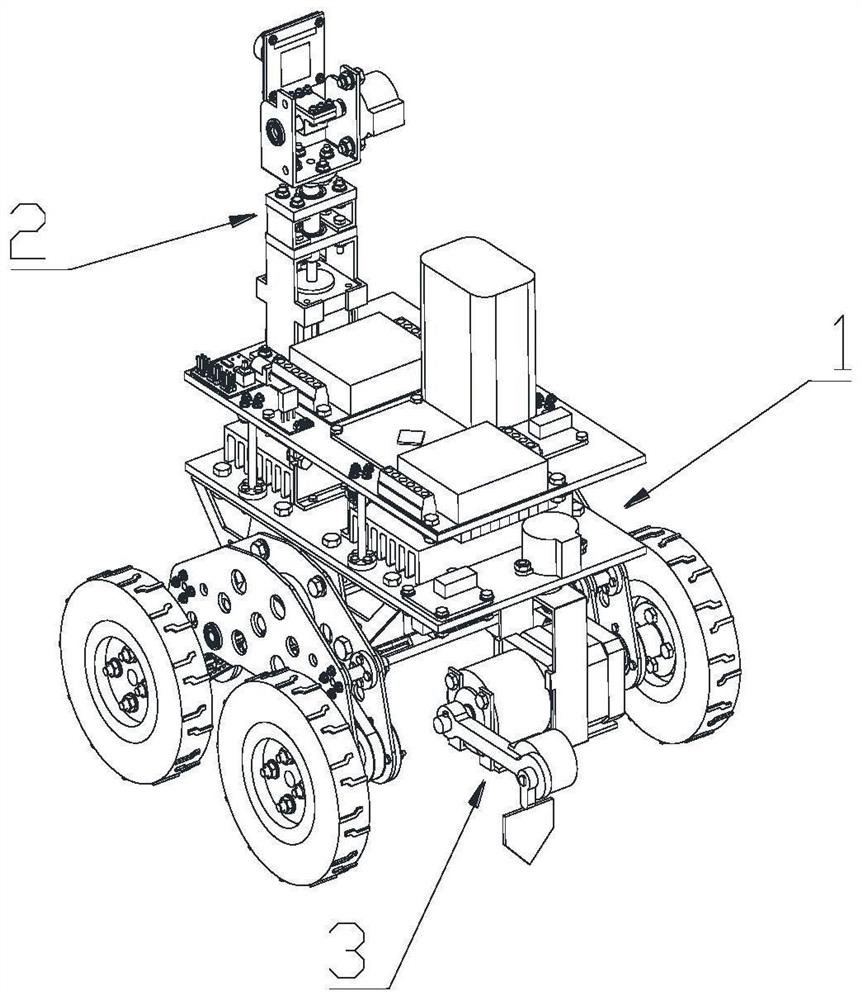
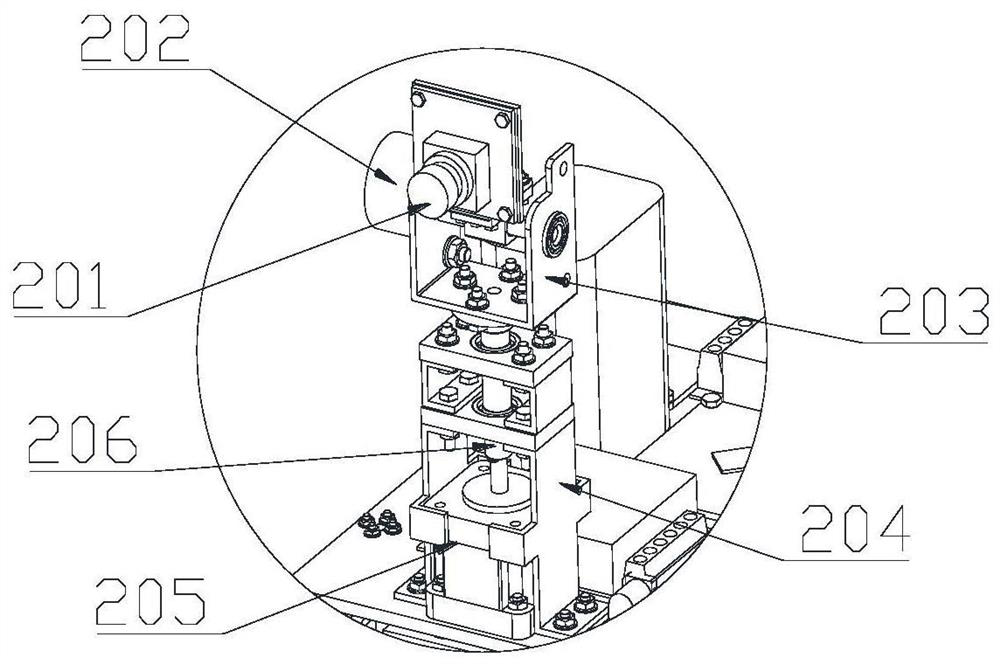
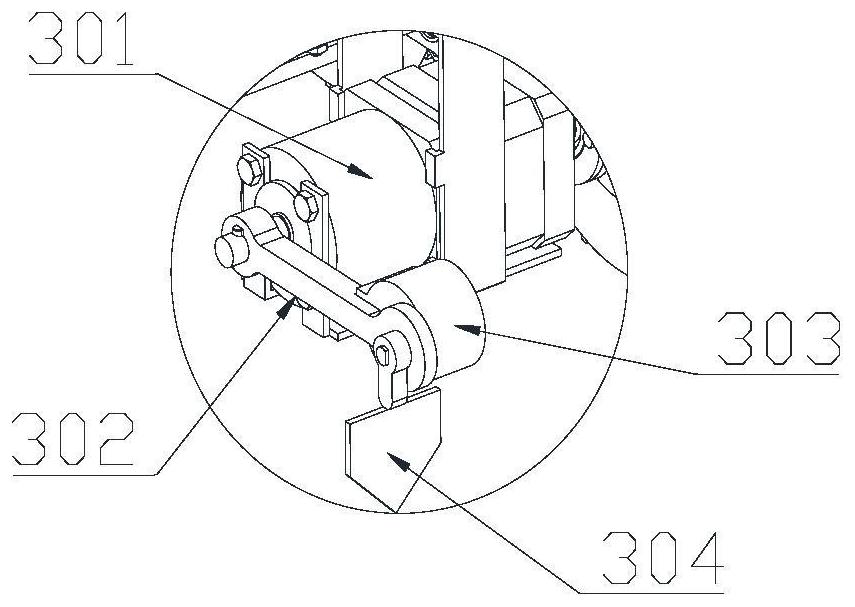
The invention relates to an intelligent control decision in the field of intelligent environmental protection, and particularly discloses an intelligent control method for repairing petroleum-contaminated soil, which comprises the following steps of: searching a feature extreme value of a soil image in a local area in a high-dimensional space through a sliding window; the convolutional neural network being trained through a difference loss function between a training position corresponding to the extreme point and a real position, so that the trained convolutional neural network can extract position features of the liquid outlet pipeline inserted into the soil; the absolute value of the difference value between the characteristic value in the local area and the characteristic extreme point being added and coded through a coder, so that a coding result is obtained, and the value of each bit of the coding result corresponds to the depth value of the characteristic extreme point inserted into the pipeline of the microbial remediation liquid. Therefore, according to the scheme, the insertion position and the insertion depth of the liquid outlet pipeline can be intelligently controlled, so that the remediation effect of contaminated soil is improved.
Owner:成都市春昂耒网络科技有限公司
Soil environment precise monitoring equipment and method based on machine vision
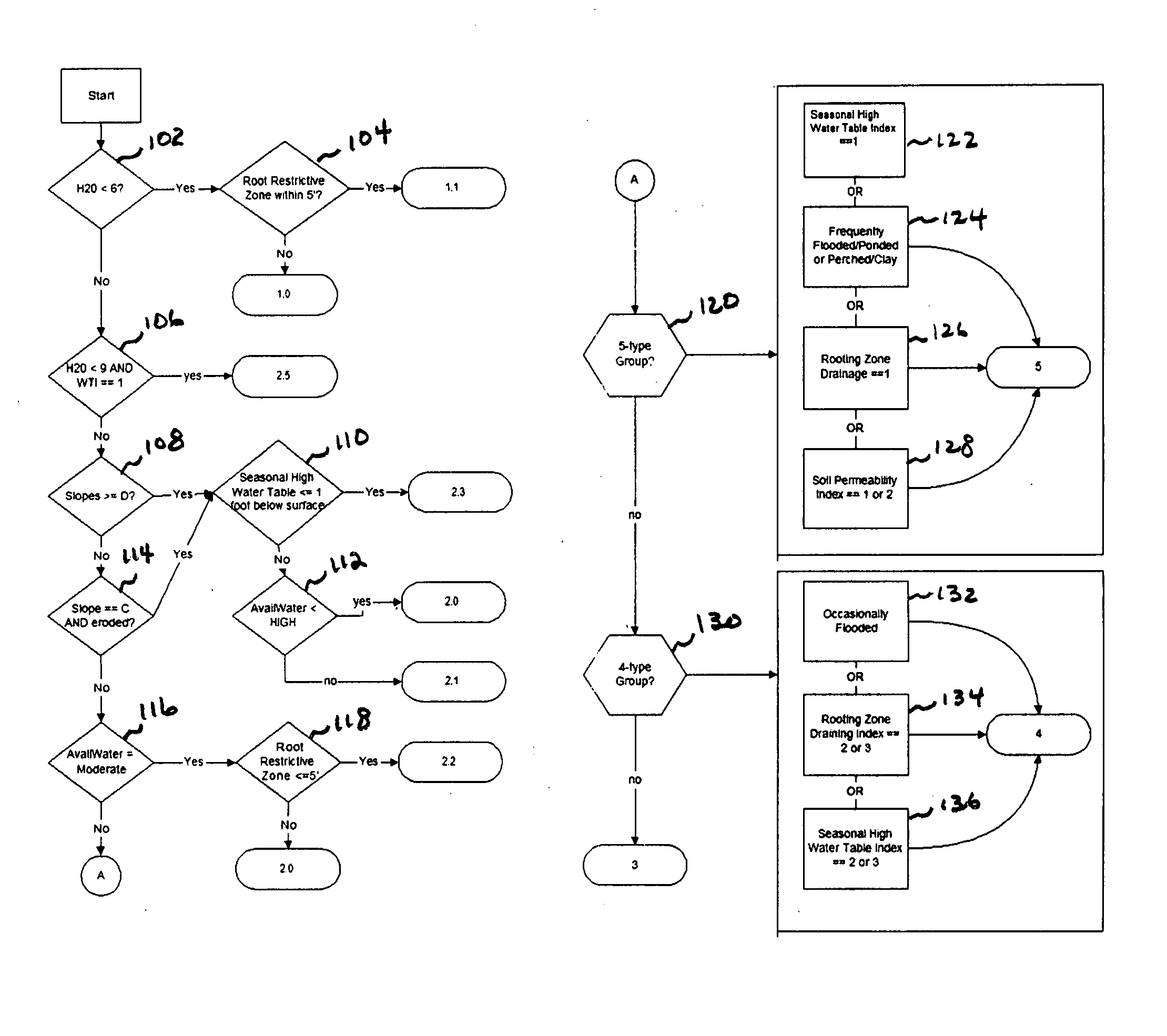
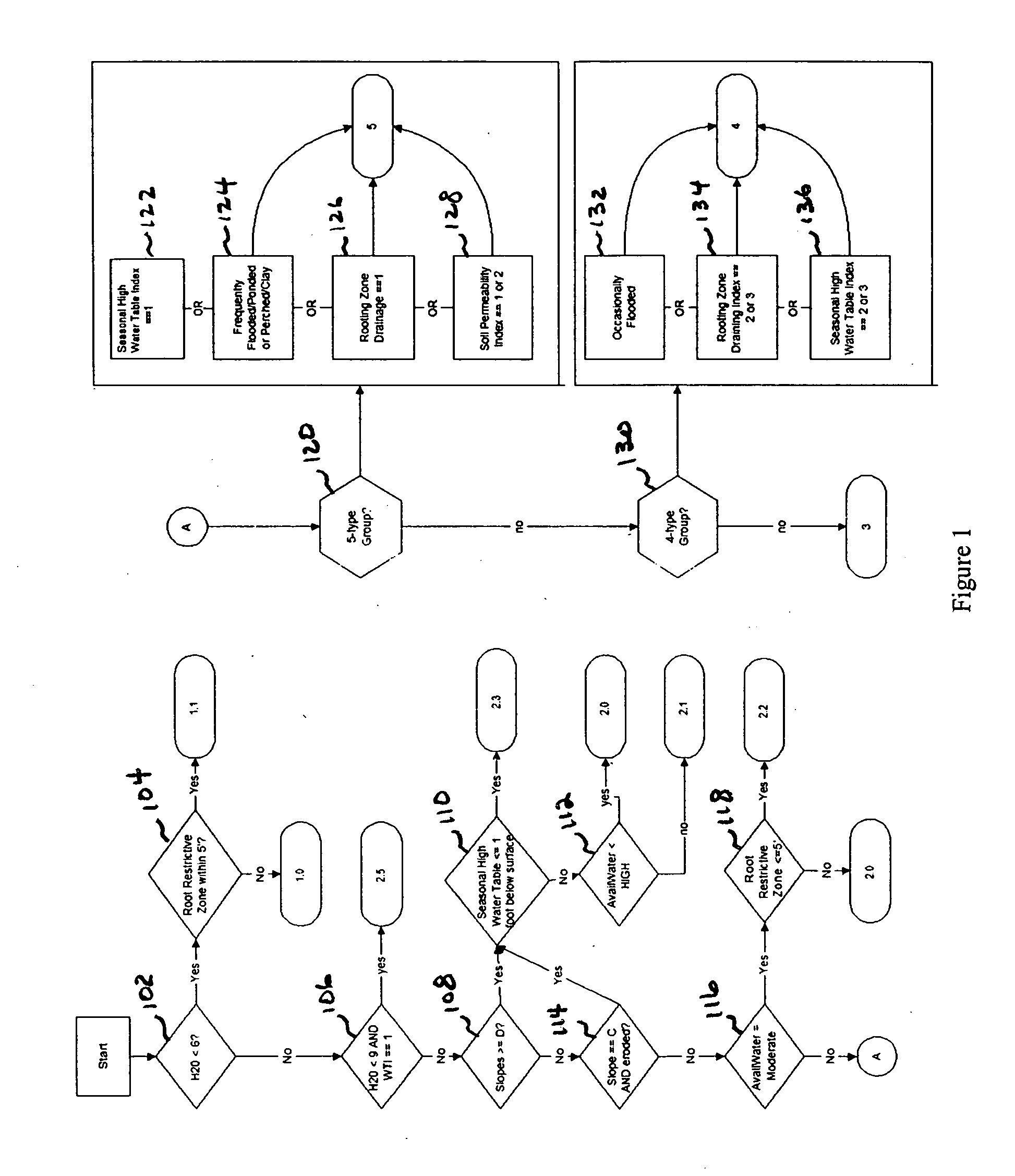
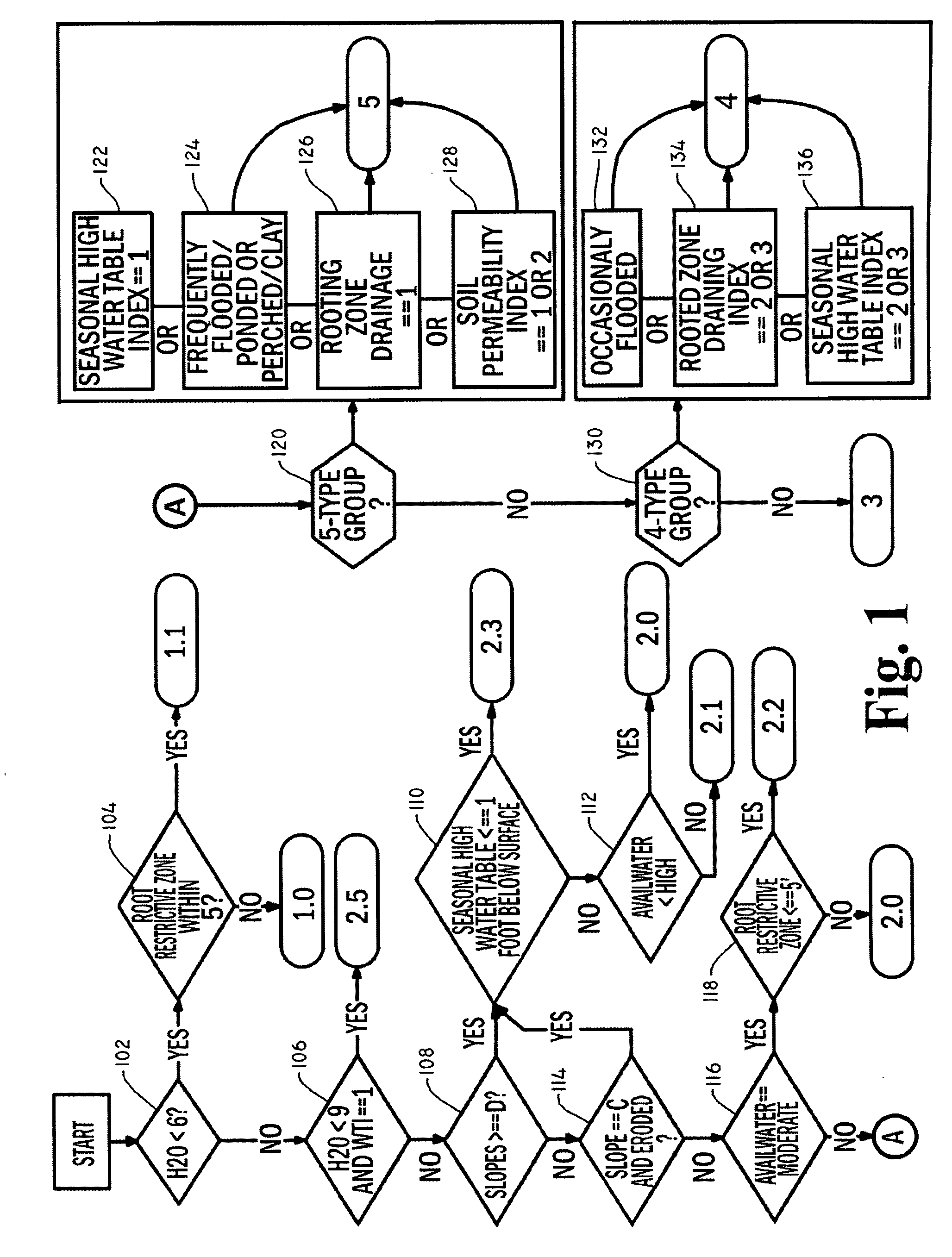
PendingCN113468742AReal time monitoringRealize intelligent detectionImage enhancementImage analysisSoil scienceMachine vision
The invention discloses soil environment precise monitoring equipment and method based on machine vision. The soil environment precise monitoring equipment comprises a soil information acquisition device, a soil information processing device, and a communication device. The soil information acquisition device comprises a moving trolley, an image acquisition module arranged on the moving trolley and a digging module located in front of the image acquisition module in the advancing direction of the moving trolley. A mathematical model about soil humidity and soil acidity and alkalinity is constructed in the soil information acquisition device. After the soil information acquisition device acquires a soil image, the soil information acquisition device processes the acquired soil image to obtain an average yellowness value and an average gray value of the soil image, and the average yellowness value and the average gray value are input into the mathematical model to obtain a soil humidity value and a soil pH value corresponding to the soil image. The method is higher in precision and lower in implementation cost.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Soil Image Shadow Detection Method Based on Improved Subtraction Histogram
ActiveCN113240619BAccurate identificationAccurate segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisSoil mapThresholding
A soil image shadow detection method based on the improved subtraction histogram provided by the present invention comprises the following steps: S1. determining the Brightness feature and the Ratio' feature of the soil image; S2. determining the soil image based on the Brightness feature and the Ratio' feature of the soil image The shadow search interval of the soil image; S3. Determine the shadow detection threshold of the soil image based on the Brightness feature and the Ratio' feature of the soil image; S4. Perform shadow detection on the soil image based on the shadow search interval of the soil image and the shadow detection threshold; it can effectively detect the soil The shadow and non-shadow areas of the image are accurately identified and segmented to ensure the detection accuracy of the soil image shadow, and there is no redundancy in the algorithm, which effectively improves the detection efficiency and has good robustness.
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
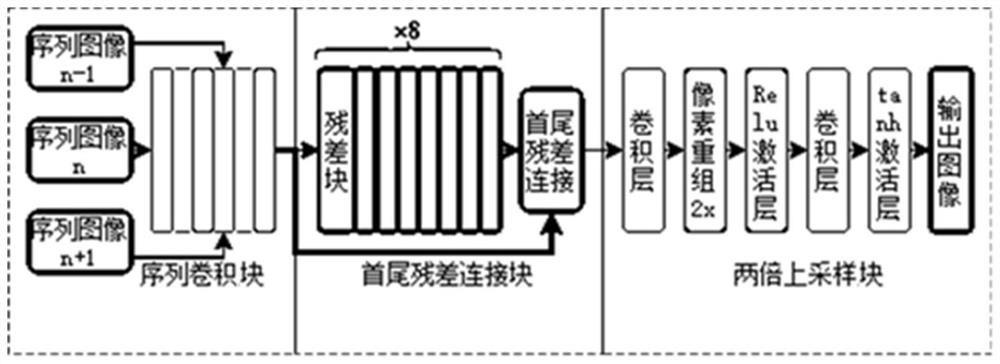
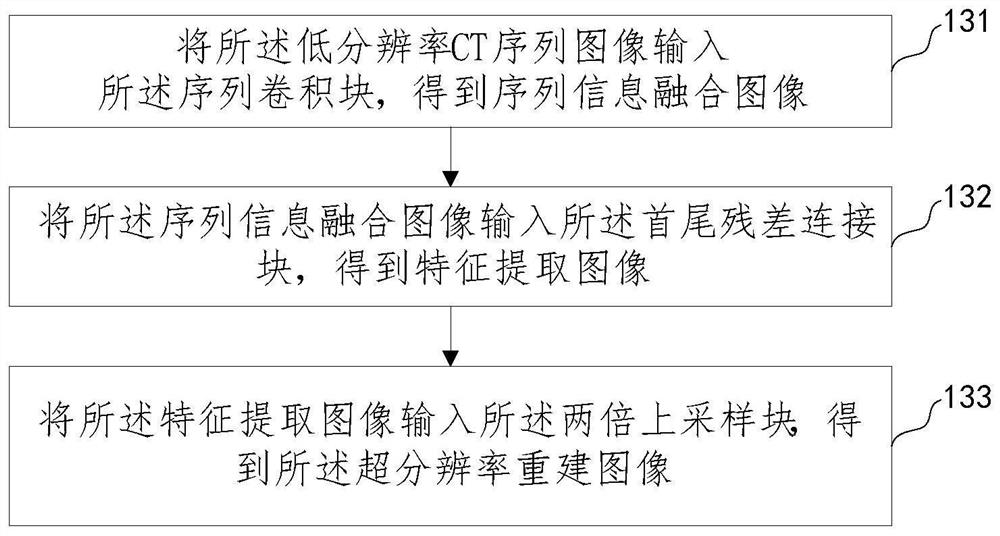
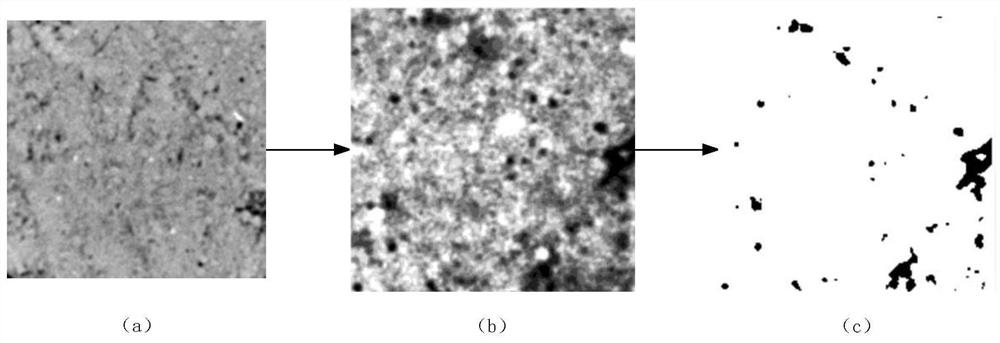
Super-resolution reconstruction method and device based on soil CT image
ActiveCN113469882AAchieving AdaptivenessAdaptableImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage resolution
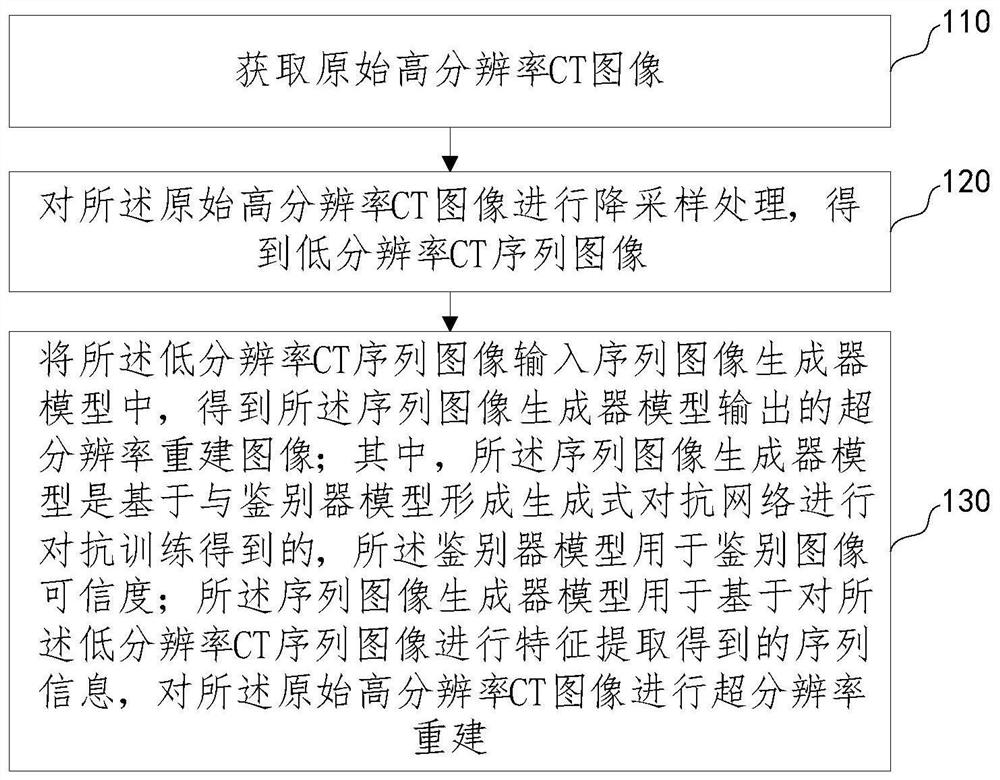
The invention provides a super-resolution reconstruction method and device based on a soil CT image. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an original high-resolution CT image; performing down-sampling processing on the original high-resolution CT image to obtain a low-resolution CT sequence image; and inputting the low-resolution CT sequence image into a sequence image generator model to obtain a super-resolution reconstructed image output by the sequence image generator model, wherein the sequence image generator model is obtained by performing adversarial training based on a generative adversarial network formed by the sequence image generator model and a discriminator model, and the discriminator model is used for discriminating the image credibility. The deep learning neural network-based sequence image generator model is used for performing super-resolution reconstruction on the soil CT image, so that the problems of low definition of the soil CT image and fuzzy pore boundary are solved, and clear and reliable data are provided for soil morphology research.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
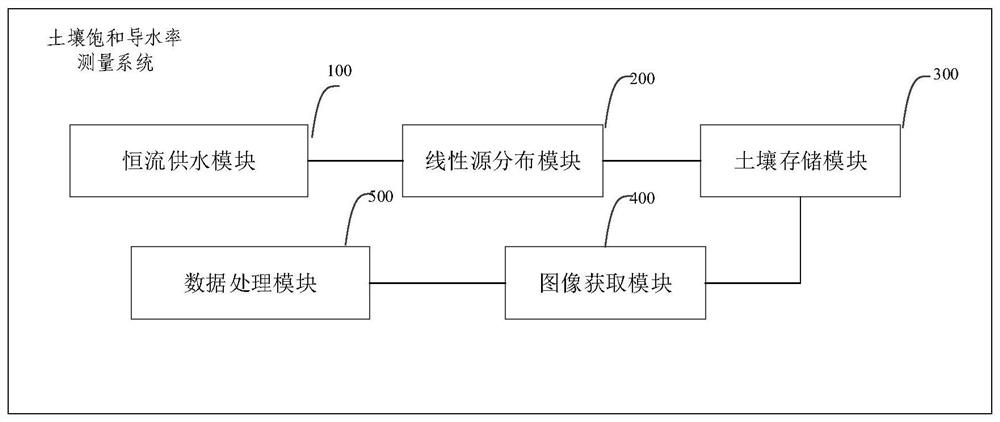
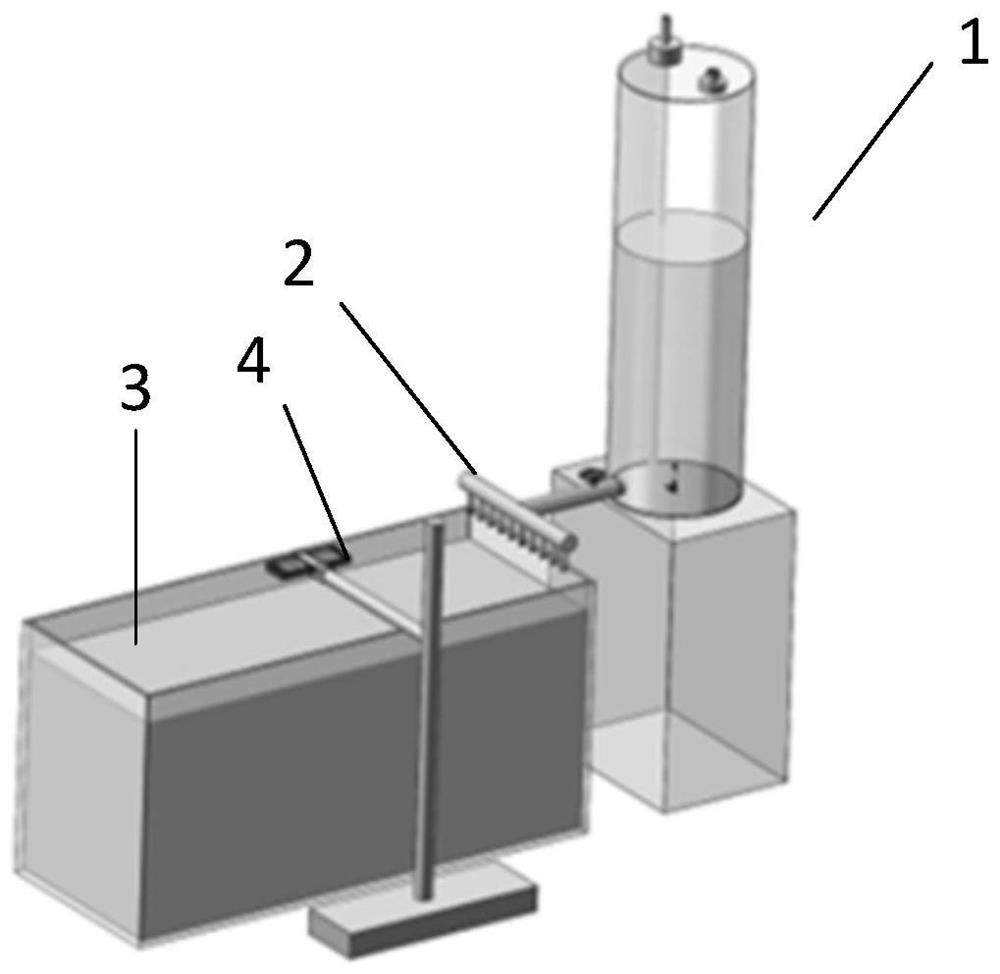
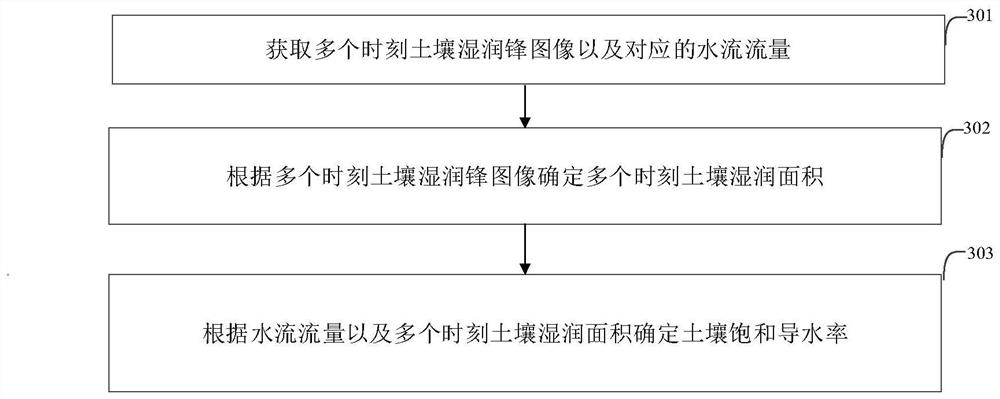
Soil saturated hydraulic conductivity measuring system and method, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114136857AQuick measurementEasy to measurePermeability/surface area analysisSoil scienceWetting front
The invention discloses a soil saturated hydraulic conductivity measurement system and method, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The system comprises a constant-flow water supply module, a linear source distribution module, a soil storage module, an image acquisition module and a data processing module, the constant-flow water supply module is connected with the linear source distribution module and is used for supplying water to the linear source distribution module at a constant flow and monitoring the water flow output at the current moment; the linear source distribution module is located above the soil storage module and used for enabling water flow from the constant-flow water supply module to flow into soil in the soil storage module in a linear source mode. The image acquisition module is used for acquiring soil wetting front images at multiple moments; the data processing module is used for determining the soil saturation hydraulic conductivity according to the soil wetting front images at the multiple moments. Under the action of the linearly distributed water flow, the soil saturation hydraulic conductivity can be obtained after the picture of the wetting front is shot to obtain the soil wetting front images at multiple moments, and simple and accurate measurement of the soil saturation hydraulic conductivity is realized.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
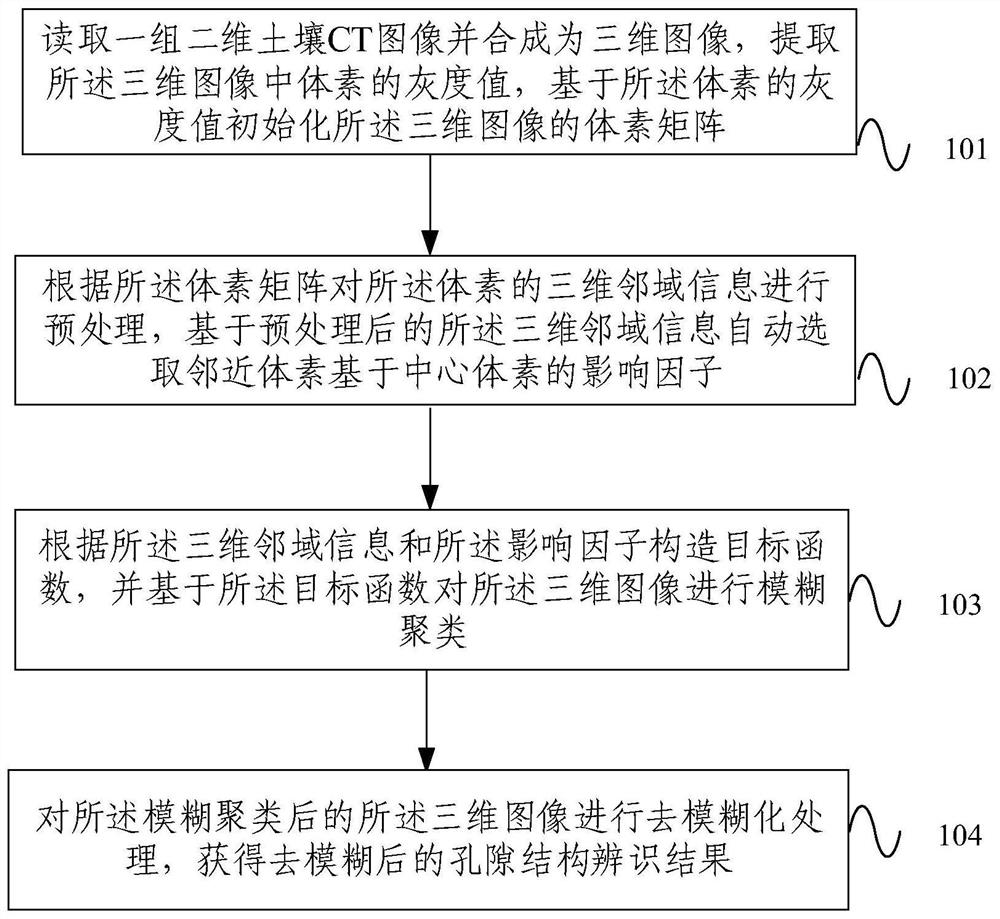
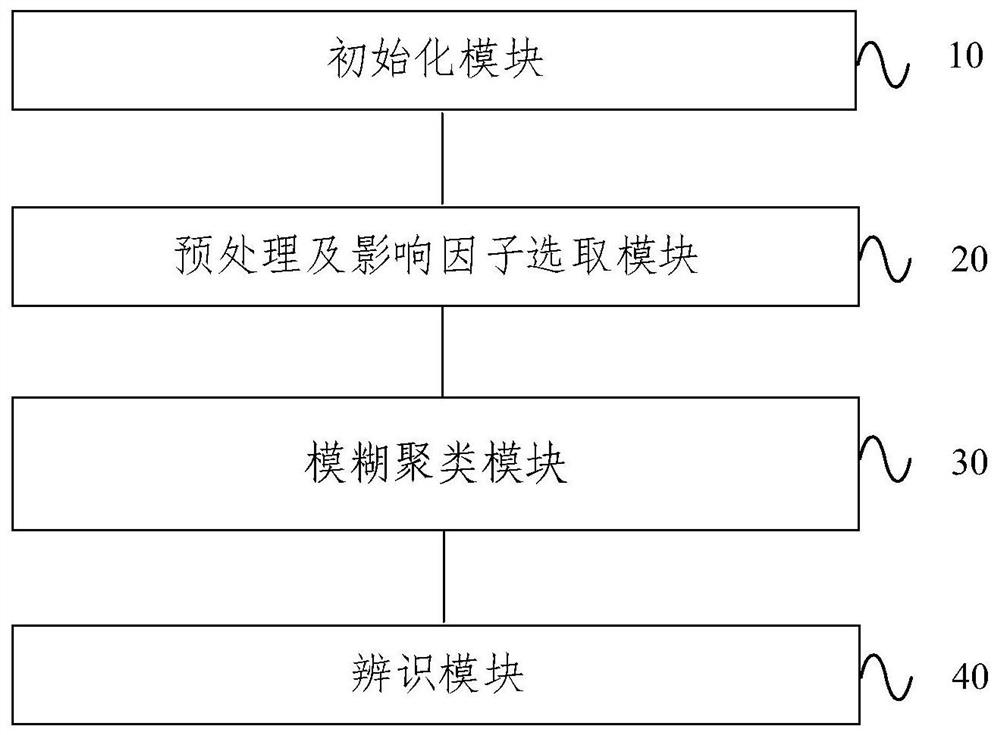
Method and system for three-dimensional segmentation of soil pores based on fuzzy clustering
ActiveCN110223249BGuaranteed execution efficiencyUniversalDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementPattern recognitionVoxel
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
A control method and control system for a crawler tractor
ActiveCN112124312BOptimizing the Slip Rate CurveImprove performanceEndless track vehiclesSoil characteristicsSoil properties
The invention discloses a crawler tractor control method and a control system. The crawler tractor control method includes: acquiring soil picture characteristic information of the current working environment of the crawler tractor; determining soil characteristics according to the acquired soil picture characteristic information Information; matching the traction force, gear position and implement plowing depth of the crawler tractor according to the obtained soil characteristic information so as to keep the slip rate of the crawler tractor within a preset range. The invention can improve the working efficiency and stability of the crawler tractor.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Intelligent ploughing auxiliary system and method for electric tractor
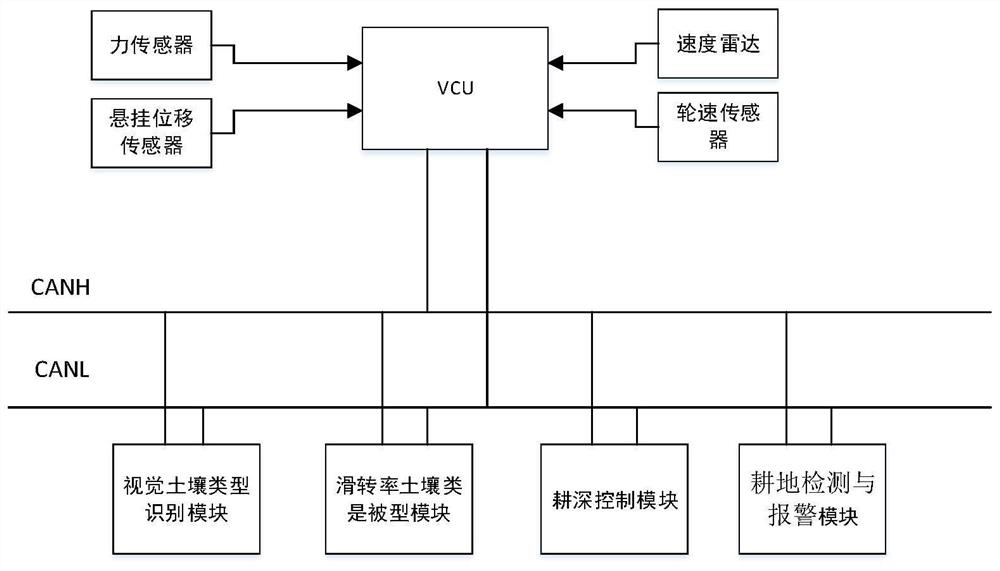
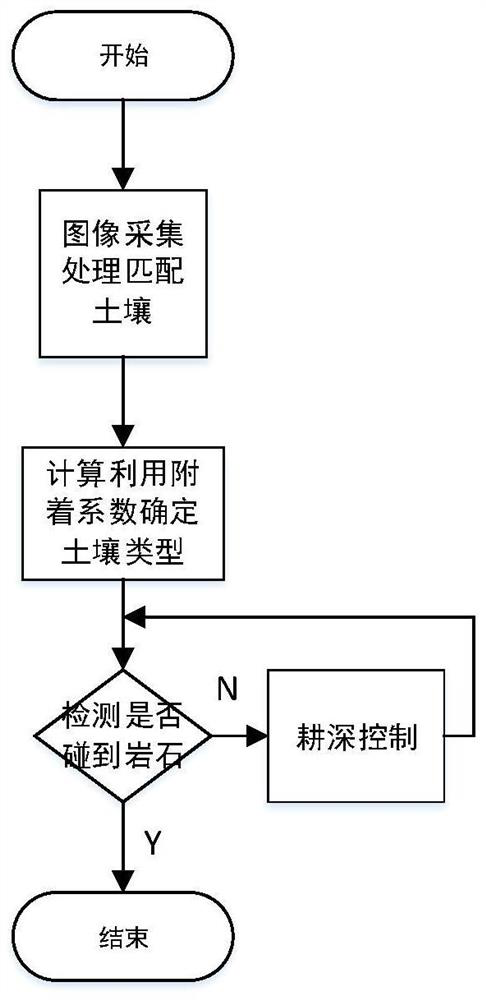
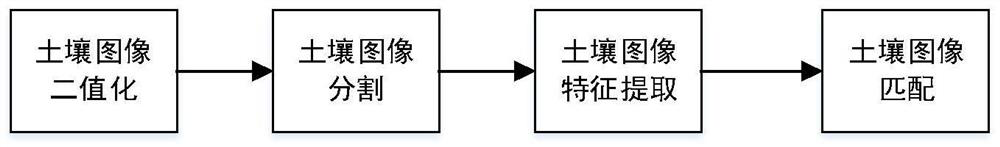
The invention discloses an intelligent ploughing auxiliary system and method for an electric tractor, and relates to the field of intelligent ploughing of tractors. A visual soil type identification part is mainly used for acquiring a soil image through a camera and matching the soil image with a database to obtain an approximate soil type; after the approximate soil type is obtained, the soil type and the optimal slip rate threshold value are finally determined through further calculation and utilization of the adhesion coefficient by a slip rate soil identification part; whether a plough is collided or not is judged through a cultivated land detection and alarm part and a Logistic regression model, and when collision occurs, an alarm is given to remind a driver and stop the whole system; and a tilling depth control part controls an electric control suspension to adjust the tilling depth in real time according to the soil type and the determined optimal slip rate control threshold value. According to the intelligent ploughing auxiliary system and method, the soil type can be detected in real time, the slip rate threshold value can be obtained according to the soil type for tilling depth control, and the safety and high efficiency of tilling can be ensured.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com