Layer-number-controllable graphite film based on nickel-copper composite substrate and preparation method of film
A graphene film and composite substrate technology, applied in the direction of graphene, chemical instruments and methods, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of graphene film size limitation, high hardware investment and preparation cost, complex process, etc., to achieve shape and The effect of less size limitation, strong layer number control ability and wide process window
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
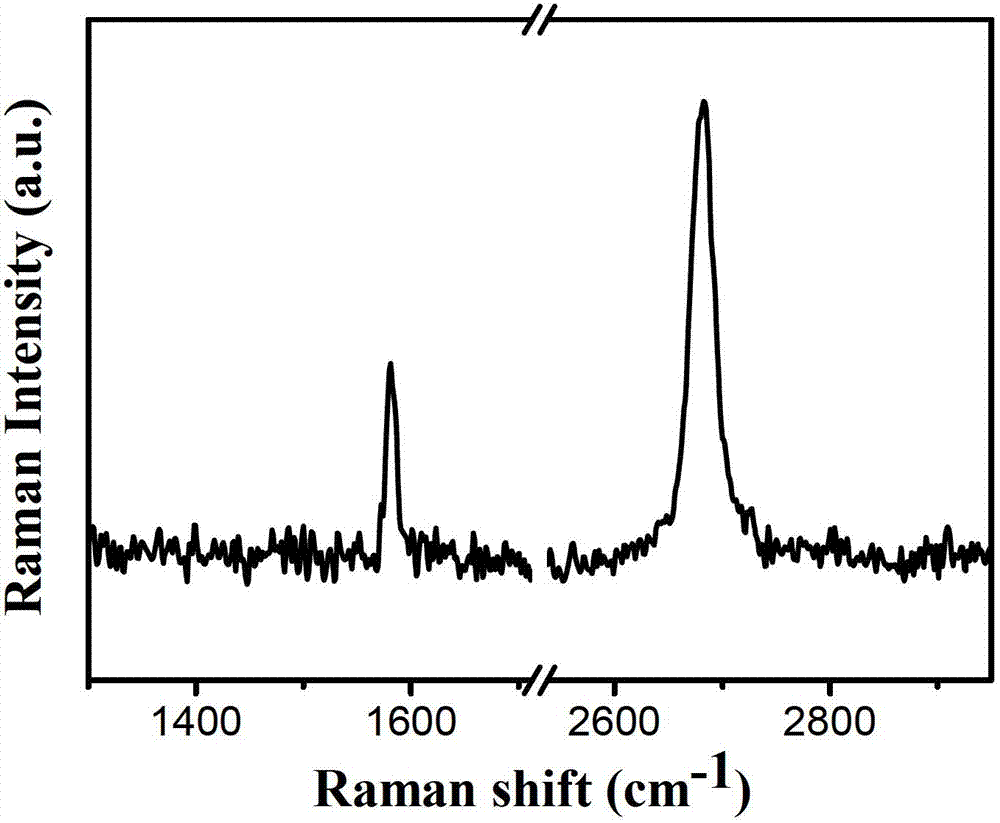
[0039] Example 1 Preparation of single-layer graphene
[0040] 1. Experimental method
[0041] 1) Ni-Cu composite substrate: cut copper foil with a thickness of 25μm, the purity of the copper foil is 99.8%, the width is 10cm, and the length is 50cm. The copper foil is cleaned with acetone and isopropanol and dried with nitrogen. Industrial nickel plating process (refer to electrodeposition nanocrystalline material technology for nickel plating method, edited by Tu Zhenmi, etc., National Defense Industry Press, Publication Date: April 1, 2008, ISBN: 9787118055528) was used to form a 150nm metal Ni layer on the Cu surface.
[0042] 2) Carburizing process: use liquid benzene as carbon source, heat to 150-200℃, substrate temperature at 300℃, hold for 30 minutes, Ar flow at 300sccm, H 2 The flow rate is 2sccm.
[0043] 3) Carbon evolution process: cut off the carbon source, raise the substrate temperature to 500°C, keep it for 60 minutes, and the Ar flow rate is 300 sccm, H 2 The flow rat...
Embodiment 2
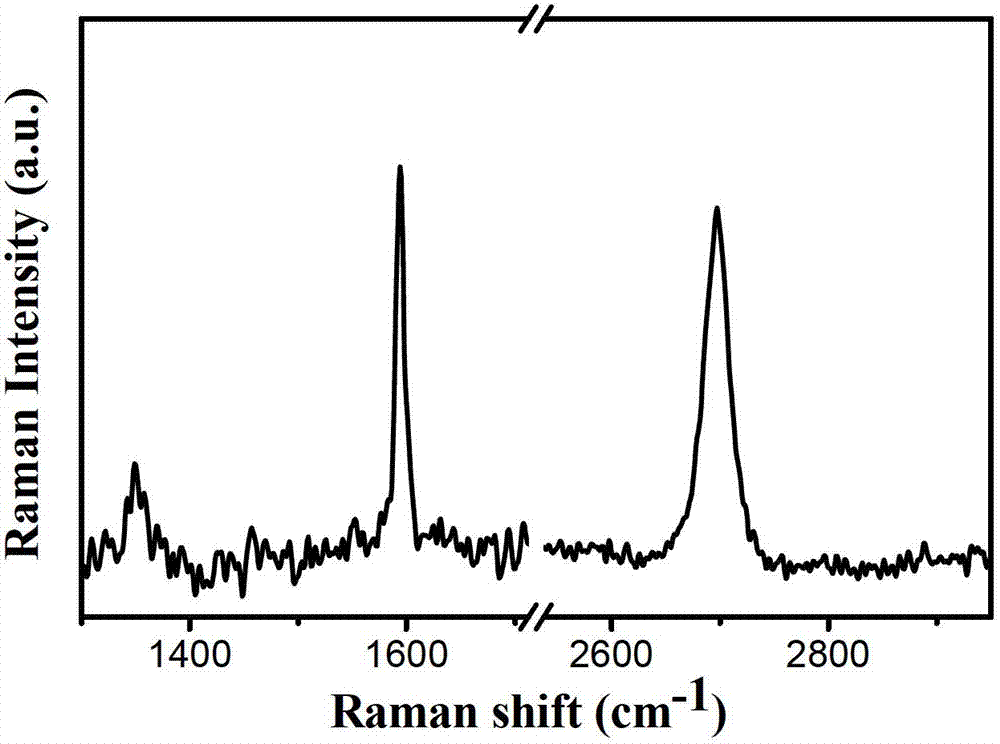
[0046] Example 2 Preparation of single-layer graphene
[0047] The carbon source is replaced with solid carbon sources such as phenanthrene, pyrene, polystyrene, polymethyl methacrylate, etc. to prepare the graphene film on the nickel-copper composite substrate. Other parameters are the same as in Example 1, and the method is as follows:
[0048] method one:
[0049] 1) Ni-Cu composite substrate: cut copper foil with a thickness of 25μm, the purity of the copper foil is 99.8%, the width is 10cm, and the length is 50cm. The copper foil is cleaned with acetone and isopropanol and dried with nitrogen. Industrial nickel plating process is used to form a 150nm nickel layer on the surface of copper foil.
[0050] 2) Carburizing process: Take phenanthrene as the carbon source, weigh 0.015g of phenanthrene, heat it to 100-150℃, the substrate temperature is 300℃, hold for 60 minutes, and the Ar flow rate is 300sccm.
[0051] 3) Carbon evolution process: Cut off the carbon source, raise the sub...
Embodiment 3
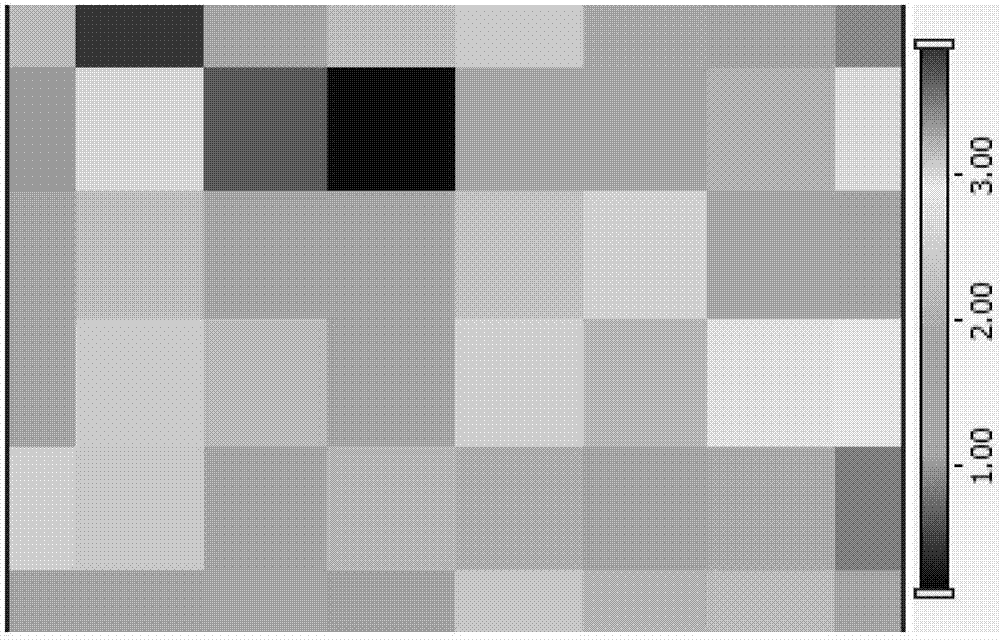
[0068] Example 3 Preparation of multilayer graphene
[0069] 1. Experimental method
[0070] 1) Ni-Cu composite substrate: cut copper foil with a thickness of 25μm, the purity of the copper foil is 99.9%, the width is 20cm, and the length is 20cm. The cut copper foil was cleaned with acetone and isopropanol and then dried with nitrogen. Industrial nickel plating process is used to form a 600nm nickel layer on the surface of copper foil.
[0071] 2) Carburizing process: Using Nai as carbon source, heating to 80~120℃, substrate temperature at 300℃, keeping for 60 minutes, Ar flow at 300sccm, H 2 The flow rate is 2sccm.
[0072] 3) Carbon evolution process: the substrate temperature is increased to 650℃, the temperature is kept for 20-180 minutes, the Ar flow rate is 300sccm, H 2 The flow rate is 1sccm.
[0073] 2. Experimental results: Raman results show that there is carbon signal after 20 minutes of heat preservation, but no graphene, and double layer graphene is formed after 40 minut...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com