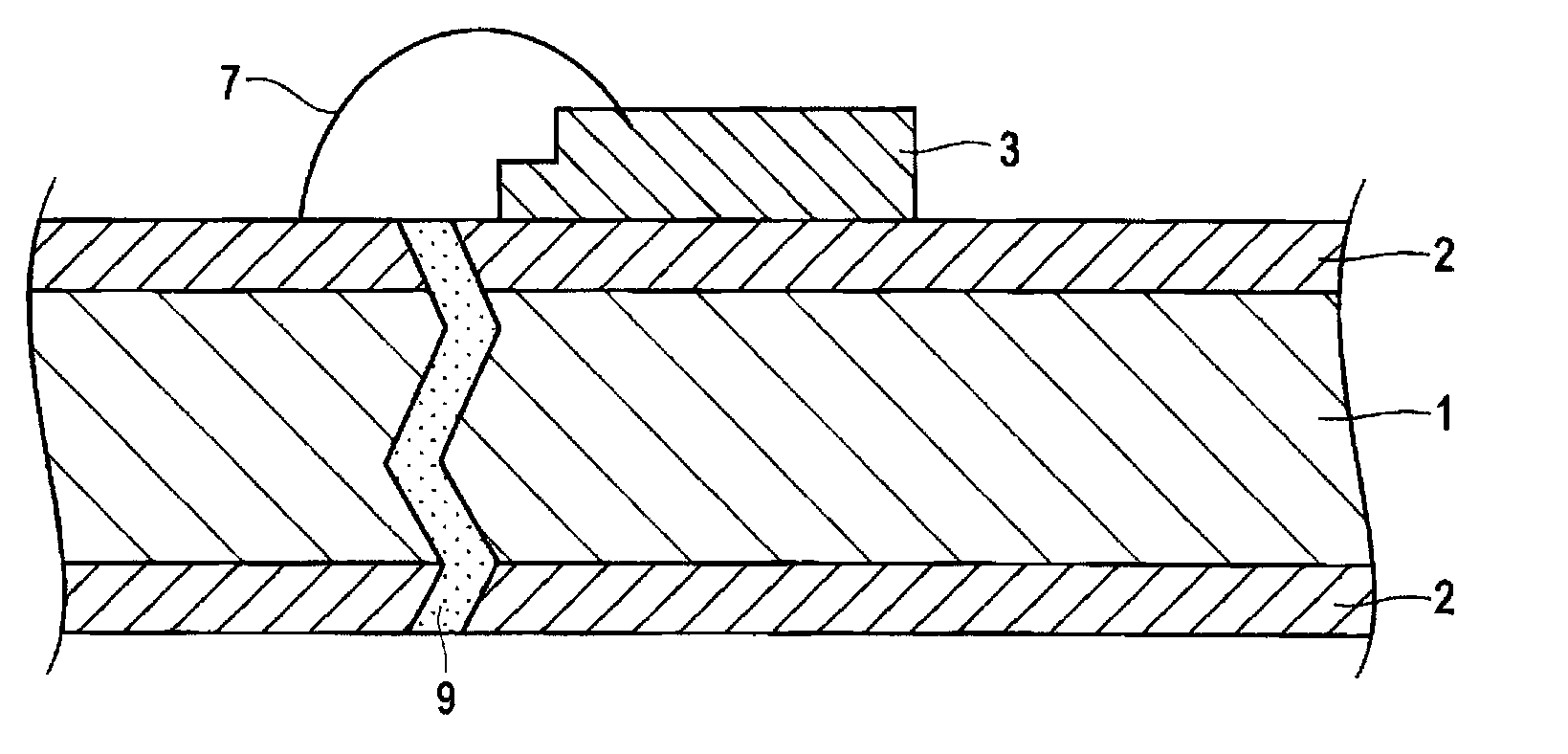
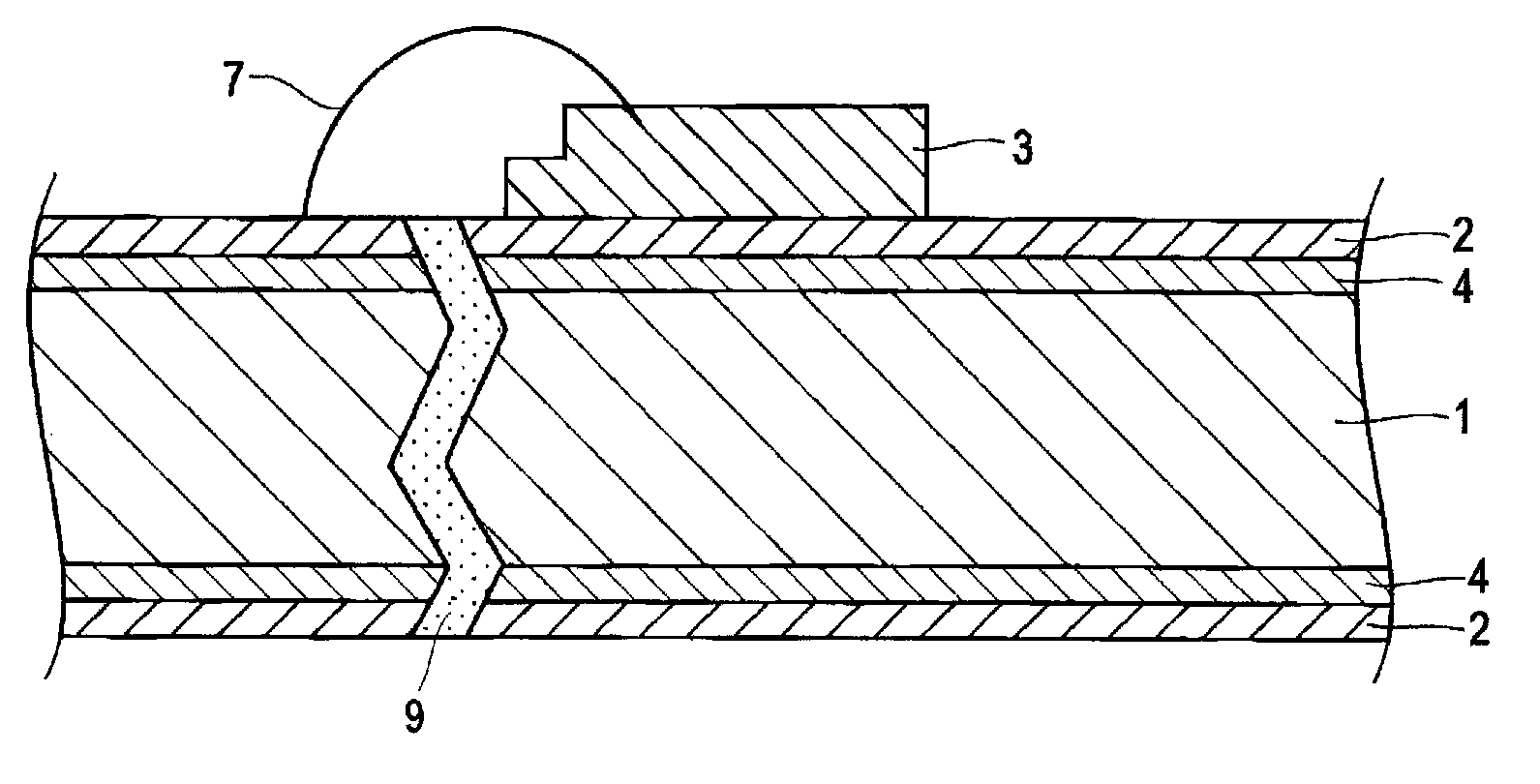
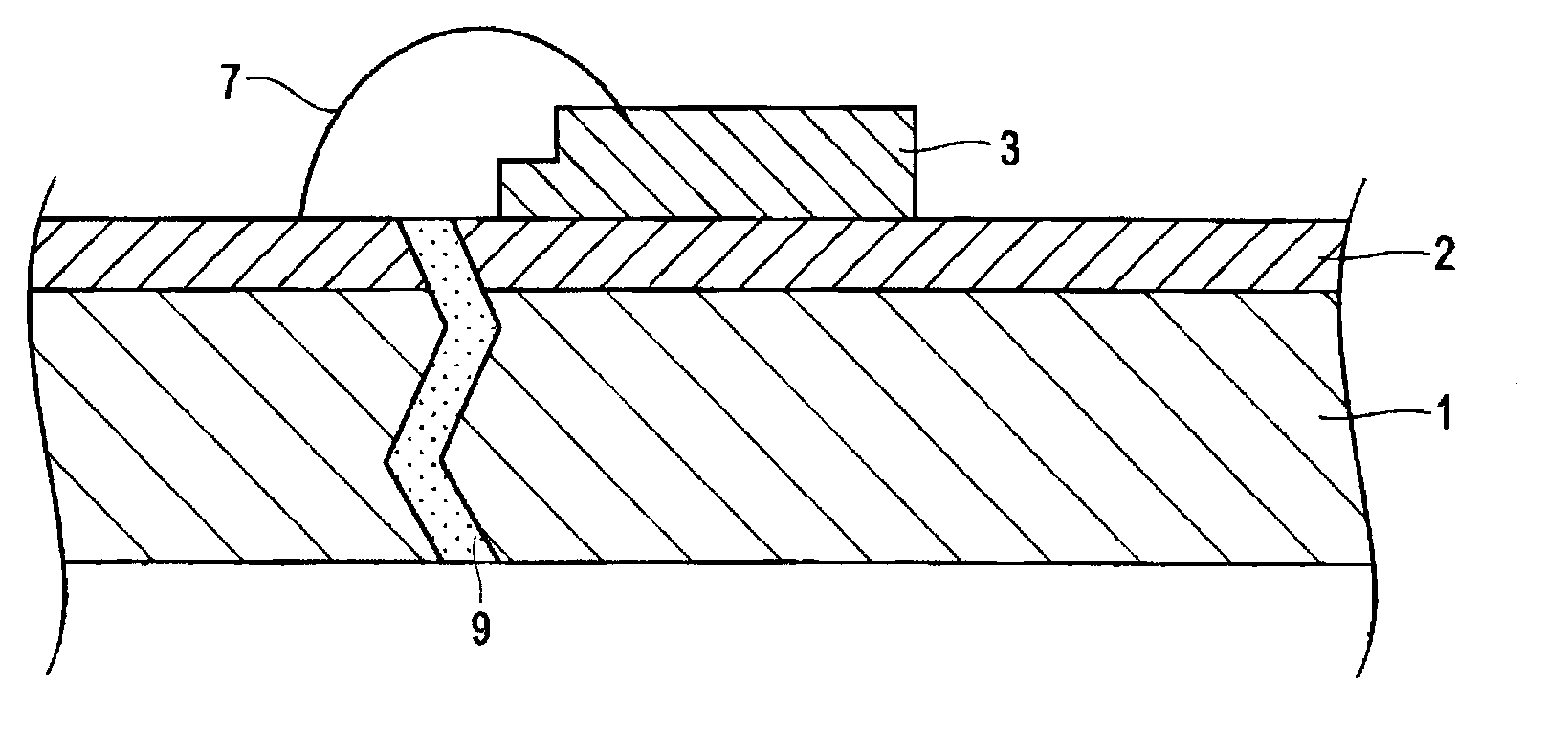
Leadframe for optical semiconductor device, method for manufacturing leadframe for optical semiconductor device, and optical semiconductor device
A technology for optical semiconductor devices and lead frames, which is applied to semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device components, optics, etc., and can solve problems such as reflectivity decline and reflectivity degradation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0179] As Example 1, after the pretreatment shown below was performed on the substrate with a width of 100 mm shown in Table 1, the plating treatment shown below was performed. In order to make the overall plate thickness including the coating thickness after rolling 0.2 mm, the plate thickness at the time of the initial formation of the reflective layer (during plating) was changed in consideration of the processing rate during the rolling process after the reflective layer was formed, and the thickness was changed by plating. Initially a reflective layer is formed. After that, using a 6-stage rolling mill (manufactured by Hitachi, Ltd.), using a roll with a surface roughness Ra of about 0.03 μm of the rolled workpiece roll, rolling was performed according to the area reduction ratio shown in Table 1 to a thickness of 0.2 mm, Thus, samples (rolled finished products) of Invention Examples 1 to 38 and Reference Examples 1 to 3 having the structures shown in Table 1 were obtaine...
Embodiment 2
[0249] As Example 2, the substrate shown in Table 3 with a width of 100 mm was pretreated in the same manner as in Example 1 above, and then subjected to the plating treatment shown in Table 3 in the same manner as in Example 1 above. Using a substrate with a plate thickness of 0.25 mm and 0.83 mm, Ag plating is performed on both sides of the substrate so that the Ag coating thickness after rolling is 3 μm, and the processing ratio during rolling after forming a reflective layer is 40%. Rolling is carried out to obtain strips with a plate thickness of 0.15 mm and 0.5 mm. After that, after performing blanking by pressing, plating was performed to form a plated film with good solder wettability only on the outer lead portion using a resist mask, and the resist was removed, and the results shown in Table 3 were obtained. Invention examples 39-50 and reference examples 6-9 of the structure.
[0250] In addition, in Conventional Examples 5 to 8, Ag plating was performed on strips ...
Embodiment 3
[0274] Example 3 is an example of an aspect characterized by the above-mentioned plating structure remaining rate.
[0275] As Example 3, the electroconductive substrate shown in Table 5 having a thickness of 0.25 mm and a width of 180 mm was subjected to the same pretreatment as above, and then subjected to plating treatment in the same manner as above. Thereafter, in order to plastically deform the Ag plating layer, the working rate was changed by rolling or pressing, and lead frames of Examples 101 to 121 of the present invention and Reference Example 101 were fabricated. Reference Example 102 simulated Comparative Example 1 of Patent Document 3, and Reference Example 103 simulated Example 2 of Patent Document 3, and prepared samples (heat-treated finished products) subjected to heat treatment at 240° C. for 4 hours after rolling. In addition, regarding the plated finished product of Conventional Example 101, after performing the same pretreatment as above on the conductive...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com