Method for preparing phosphotungstic acid-polyvinylidene fluoride composite proton exchange membrane
A polyvinylidene fluoride and proton exchange membrane technology, which is used in fuel cell parts, fuel cells, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as uneven distribution of agglomeration and loss of heteropolyacids, and avoid agglomeration, loss, and swelling. The effect of reducing the degree of alcohol resistance and good resistance to alcohol
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
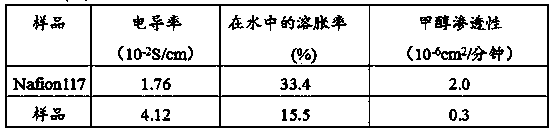
[0029] Dissolve 20g of polyvinylidene fluoride in 380g of dimethyl sulfoxide to form solution A; heat solution A to 60°C, stir for 2 hours to obtain solution B, cast solution B on a clean glass plate and dry it in vacuum at 70°C to obtain Film; put the film in 6mol / L sodium hydroxide solution, treat it in an oil bath at 60°C for 8 hours, take it out, wash it repeatedly with water until neutral, and dry it at 105°C to form a film; dissolve 10g of dry film in A mixture of 190g dimethyl sulfoxide and 21.6mL water forms a solution C; heat the solution C to 80°C, stir for 2 hours, then drop the temperature to 70°C, add 2 g of sodium tungstate and 1.25g of concentrated phosphoric acid, and stir for 2 Cool down after 1 hour, heat up the vacuum oil bath to 130°C, stir for 1.5 hours until all the water in the solution evaporates, and then cool down to room temperature to form solution D; pour solution D on a polytetrafluoroethylene plate, and vacuum dry at 90°C to obtain Phosphotungsti...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Dissolve 15g of polyvinylidene fluoride in 240g of dimethyl sulfoxide to form solution A, heat solution A to 50°C, stir for 2 hours to obtain solution B, cast solution B on a clean glass plate and dry it in vacuum at 60°C film; put the film in 7mol / L sodium hydroxide solution, treat it in an oil bath at 70°C for 9 hours, take it out, wash it repeatedly with water until neutral, and dry it at 110°C to form a film; dissolve 8g of dry film in A mixture of 128g dimethyl sulfoxide and 13mL water forms solution C; heat solution C to 85°C, stir for 2 hours, then lower the temperature to 60°C, add 1.25g sodium tungstate and 0.88g concentrated phosphoric acid, stir for 2 hours After cooling down, the vacuum oil bath was heated to 110°C, and stirred for 1 hour until all the water in the solution evaporated, and then cooled to room temperature to form solution D; pour solution D on a polytetrafluoroethylene plate, and vacuum dry at 95°C to obtain phosphorus Tungstic acid-polyvinyl...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Dissolve 10g of polyvinylidene fluoride in 180g of dimethyl sulfoxide to form solution A, heat solution A to 60°C, stir for 2 hours to obtain solution B, cast solution B on a clean glass plate and dry it in vacuum at 80°C Film; put the film in 7mol / L sodium hydroxide solution, treat it in an oil bath at 80°C for 10 hours, take it out, wash it repeatedly with water until neutral, and dry it at 115°C to form a film; dissolve 6g of dry film in A mixture of 108g dimethyl sulfoxide and 10mL water forms solution C; heat solution C to 90°C, stir for 2.5 hours, then lower the temperature to 65°C, add 0.71g sodium tungstate and 0.41g concentrated phosphoric acid, stir for 2 hours After cooling down, the vacuum oil bath was heated to 120°C, and stirred for 2 hours until all the water in the solution evaporated, and then cooled to room temperature to form solution D; pour solution D on a polytetrafluoroethylene plate, and vacuum dry at 95°C to obtain phosphorus Tungstic acid-polyv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com