Novel titanium alloy partitioned beta heat treatment process
A titanium alloy and process technology, which is applied in the field of titanium alloy partition β heat treatment process, to achieve the effect of ensuring uniform structure, good comprehensive performance and low fatigue crack growth rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
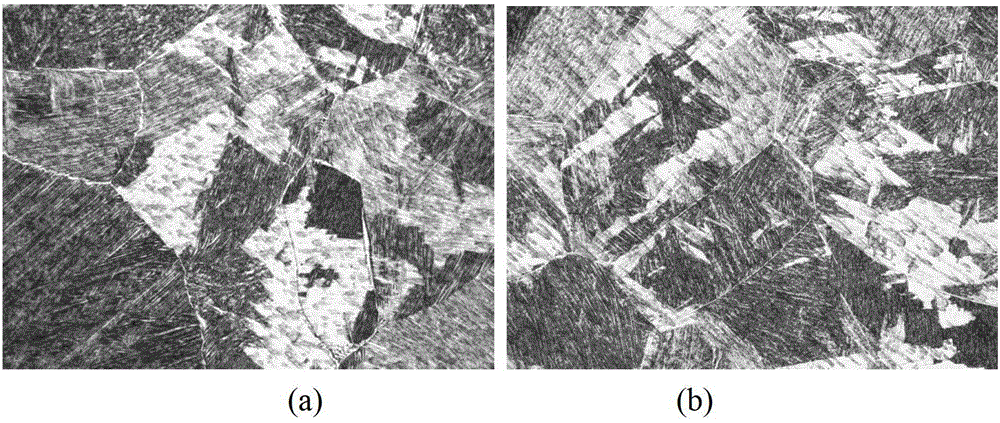
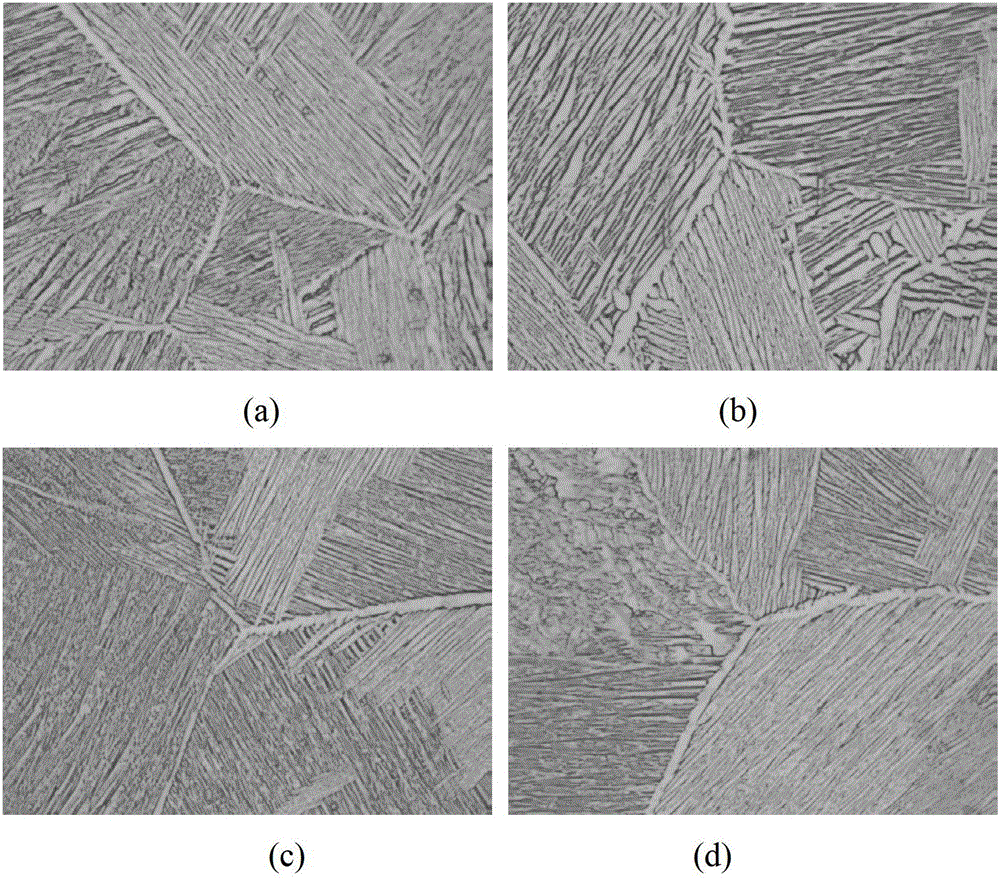
[0026] TC4-DT titanium alloy is a large complex variable cross-section free forging after forging in the α + β zone (the maximum size of the outer shape is 2400 (L) mm × 590 mm (T) × 260 mm (ST), the maximum thickness is 260 mm, and the minimum thickness is 100 mm. The weight of the forging is up to 800kg). After adopting the above-mentioned divisional β heat treatment process, it is then kept at 730°C for 4 hours and air-cooled. The results of chemical anatomy analysis show that the microstructure uniformity of different parts of the forging is good ( figure 1 ), the uniformity of mechanical properties is good (Table 2 and Table 3), and the strength-plasticity-toughness matching is good.
[0027] Table 1 Tensile properties of different parts of free forgings
[0028]
[0029]
[0030] Table 2 Fracture toughness of different parts of free forgings
[0031]
Embodiment 2
[0033] TC4-DT titanium alloy is a large and complex variable cross-section die forging after forging in the α+β zone (the maximum size of the outer shape is 1720mm×1120mm×217mm, the maximum thickness is 217mm, the minimum thickness is 113mm, and the weight of a single piece is nearly 500Kg), using the above-mentioned partition β After the heat treatment process, the microstructure after being kept at 730°C for 4 hours and air-cooled is as follows: figure 2 As shown, it can be seen that the organization is a lamellar organization with good uniformity. The mechanical properties are shown in Table 3 and Table 4. Good strength-plasticity-toughness matching and low da / dN values can be obtained after zoned β heat treatment.
[0034] Table 3 Tensile properties of different parts of die forgings
[0035]
[0036]
[0037] Table 4 Fracture toughness and crack growth rate of different parts of die forgings
[0038]
Embodiment 3
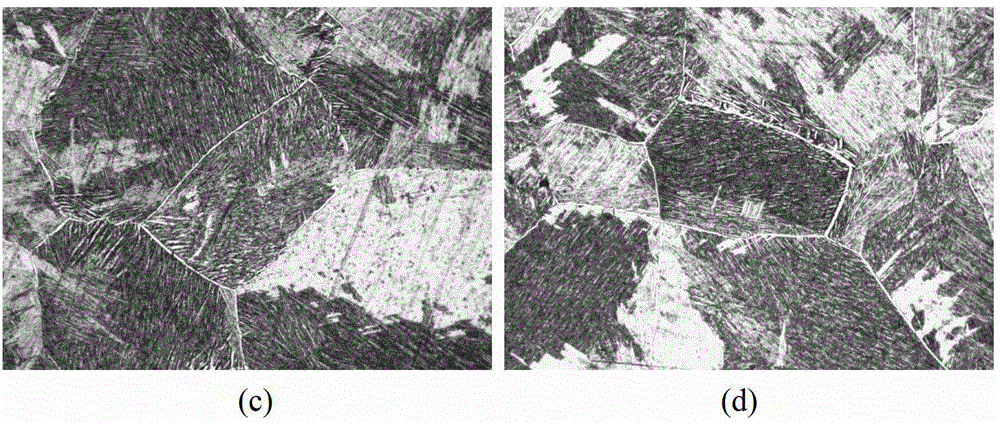
[0040] TC4-DT titanium alloy is a large and complex variable cross-section die forging after forging in the α+β zone (the maximum size of the outer profile is 1900mm×1375mm×160mm, the maximum thickness is 160mm, the minimum thickness is 130mm, and the weight of a single piece is nearly 500Kg), using the above-mentioned partition β After the heat treatment process, the microstructure after being kept at 730°C for 4 hours and air-cooled is as follows: image 3 As shown, it can be seen that the organization is a uniform lamellar organization. The mechanical properties are shown in Table 5 and Table 6. It can be seen from the table that the tensile properties and fracture toughness are higher than the standard requirements, and a good strength-plasticity-fracture toughness matching is obtained.
[0041] Table 5 Tensile properties of different parts of die forgings
[0042]
[0043] Table 6 Fracture toughness of die forgings
[0044]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com