Method for degradation of microcystin in water by means of electron beam irradiation
A technology of electron beam irradiation and electron beam radiation, which is applied in the field of sewage treatment, can solve problems such as incompleteness, low efficiency, and secondary pollution, and achieve the effects of good treatment effect, low preparation cost, and great application potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
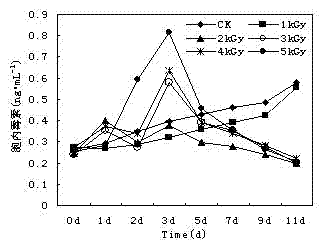
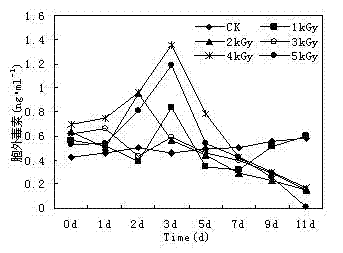
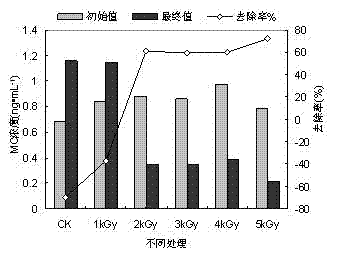
[0016] The method of the present invention is achieved through the following steps (taking the toxin secreted by Microcystis aeruginosa as an example):
[0017] (1) Carry out different doses of irradiation, the radiation energy is kept at 1.8MeV, the beam current is set at 1.0mA, and the primary radiation dose is 1kGy; the radiation doses used in the experiment are 1kGy, 2kGy, 3kGy, 4kGy, 5kGy respectively.
[0018] (2) Take 40ml of algae liquid every day to extract extracellular and intracellular toxins respectively. The algae solution is heated at 12000r·min -1 , centrifuged at 4°C for 10 min, and the precipitated part was set aside; the supernatant was filtered with a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and the filtrate was used for the determination of extracellular toxins. The collected algae cells were washed three times with ultrapure water to remove the toxins on the surface of the algae cells. Add a small amount of ultrapure water to the washed precipitate, freeze and thaw rep...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com