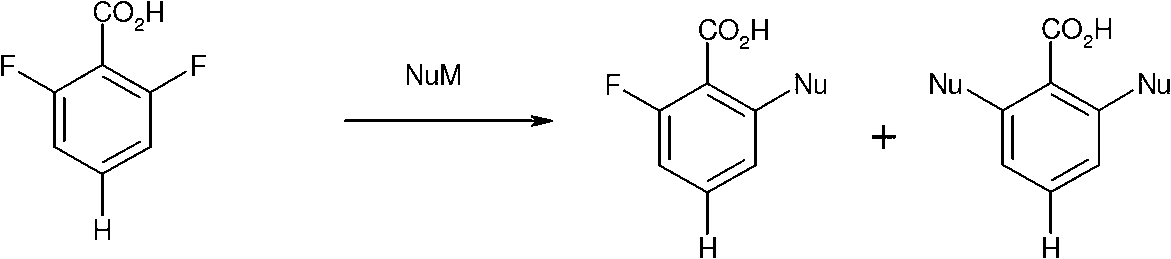
Method for preparing chemical compounds of interest by nucleophilic aromatic substitution of aromatic carboxylic acid derivatives supporting at least one electro-attractive group
A technology for aromatic carboxylic acids and carboxylic acid derivatives, which is applied in the preparation of carboxylate, the preparation of organic compounds, the preparation of cyanide reactions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example
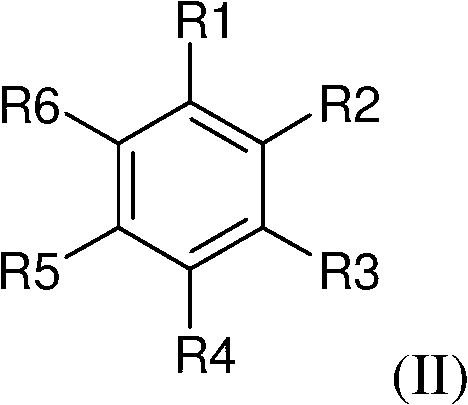
[0049] Presence of asymmetric carbon
[0050] According to a preferred embodiment, there is an asymmetric carbon on the aromatic carboxylic acid derivative, preferably on the benzoic acid derivative of the general formula (II) and / or on the nucleophile, and the obtained general formula Compounds of (I) are asymmetric. Very advantageously, the aromatic carboxylic acid derivative, preferably the benzoic acid derivative of general formula (II), has at least one chiral leaving group.
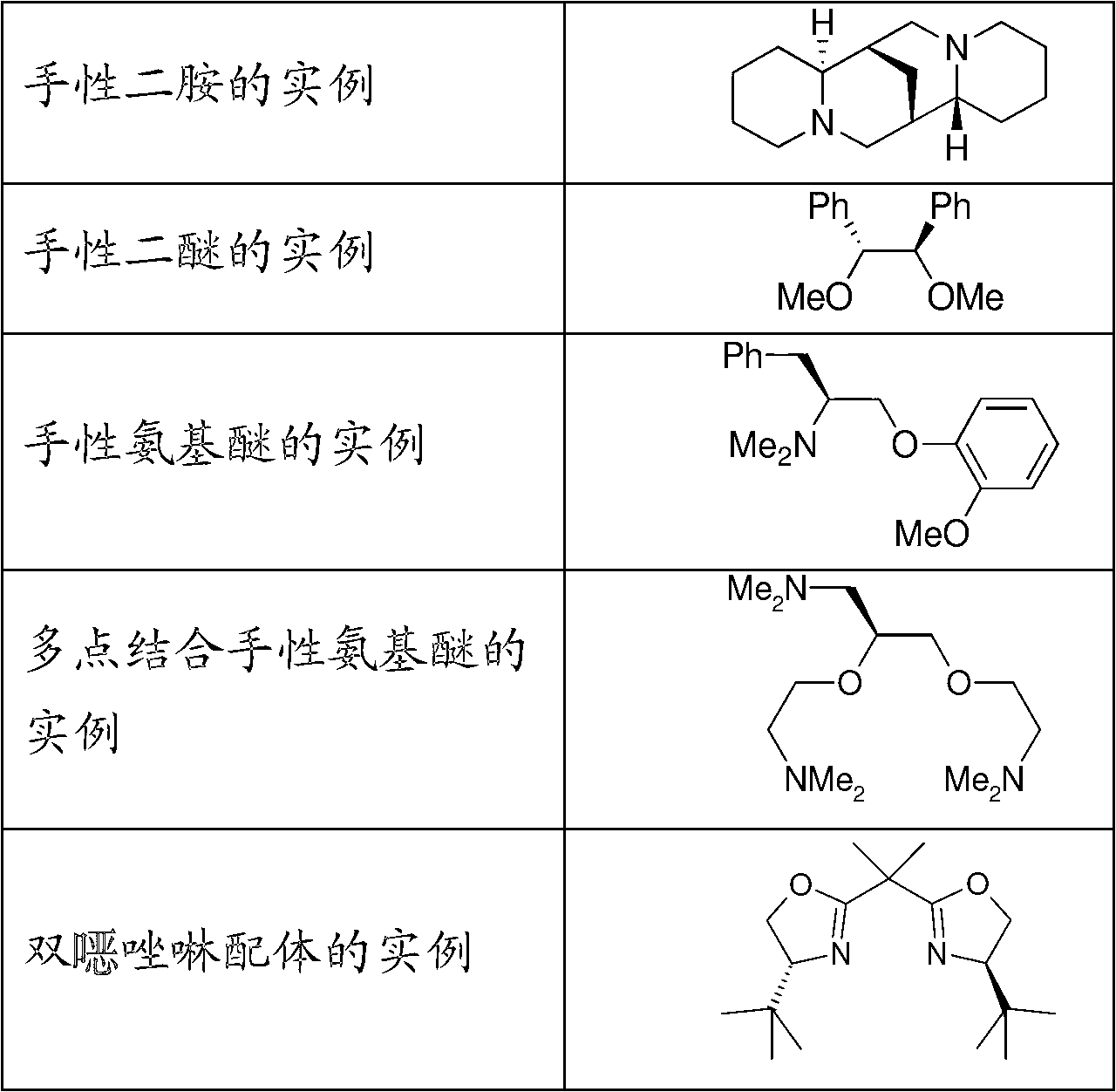
[0051] Use of Chiral Ligands
[0052] In a particular embodiment, a chiral ligand is added to the reaction mixture; this ligand serves to impart chirality to the reaction product (I) of the invention.
[0053] According to the present invention, the chiral ligand can be selected from chiral diamines, chiral diethers, chiral amino ethers, multi-point binding chiral amino ethers and bis Bisoxazoline ligands. Examples of chiral ligands that can be used are described in Table 1.
[0054]
...
Embodiment 1
[0125] Embodiment 1-preparation of 2-n-butyl-6-fluorobenzoic acid
[0126]
[0127] n-BuLi (6.9 mL, 11 mmol, 1.6M in hexane) was added to a solution of 2,6-difluorobenzoic acid (791 mg, 5 mmol) in anhydrous THF (30 mL) at -78 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at this temperature for 2 h, then iodomethane (1.25 mL, 12 mmol) was added. The solution was hydrolyzed with water (20 mL) at room temperature and the two phases were separated. The aqueous phase was washed with ethyl acetate (3 x 40 mL). The aqueous phase was then acidified to pH 1 and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 x 40 mL). Combined organic phases in MgSO 4 Dry over and concentrate under vacuum. The residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (cyclohexane: ethyl acetate 95:5) to give 2-butyl-6-fluorobenzoic acid (425 mg, 2.17 mmol, 43%) as a yellow oil. Adding iodomethane before hydrolysis did not change the reaction outcome. 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 11.04(s large, 1H), 7.35(td, JHF=5.7Hz, J=8....
Embodiment 2
[0128] Embodiment 2-preparation 2,6-di-sec-butylbenzoic acid
[0129]
[0130] This compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 1 from 2,6-difluorobenzoic acid (791 mg, 5 mmol) and s-BuLi (10.7 mL, 15.0 mmol, 1.4M in cyclohexane). The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 4 h. Purification by recrystallization (cyclohexane / ethyl acetate) afforded 2,6-di-sec-butylbenzoic acid (650 mg, 2.77 mmol, 55%) as a white solid (mp 125-126°C). Adding iodomethane before hydrolysis did not change the reaction outcome. 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 7.36(t, J=7.8Hz, 1H), 7.13(d, J=7.8Hz, 2H), 2.73(sext, J=7.0Hz, 2H), 1.75-1.55(m, 4H), 1.27( dd, J=1.6Hz, J=6.8Hz, 6H), 0.85(t, J=7.4Hz, 6H). 13 C NMR (100MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 176.2, 143.2, 133.4, 129.5, 122.8, 38.7, 30.9, 22.0, 12.1. IR (ATR, cm -1 ): 2955, 2925, 2864, 1705, 1594, 1585, 1456, 1390, 1379, 1260, 1134, 1003, 908, 803, 764, 699, 609.C 15 h 26 NO 2 HRMS[M+NH 4 ] + Calculated: 252.1964, Measured: 252.1963.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com