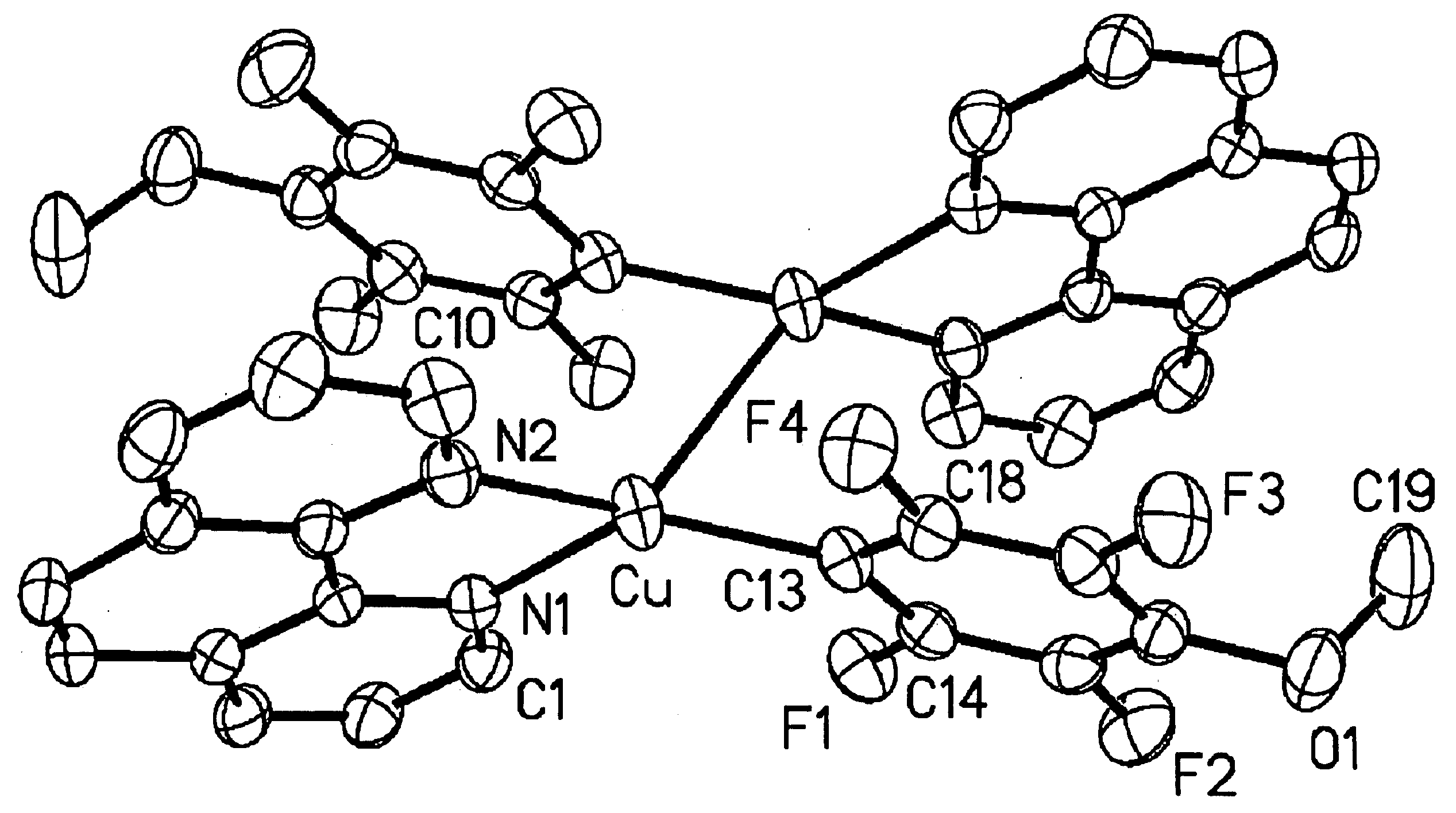
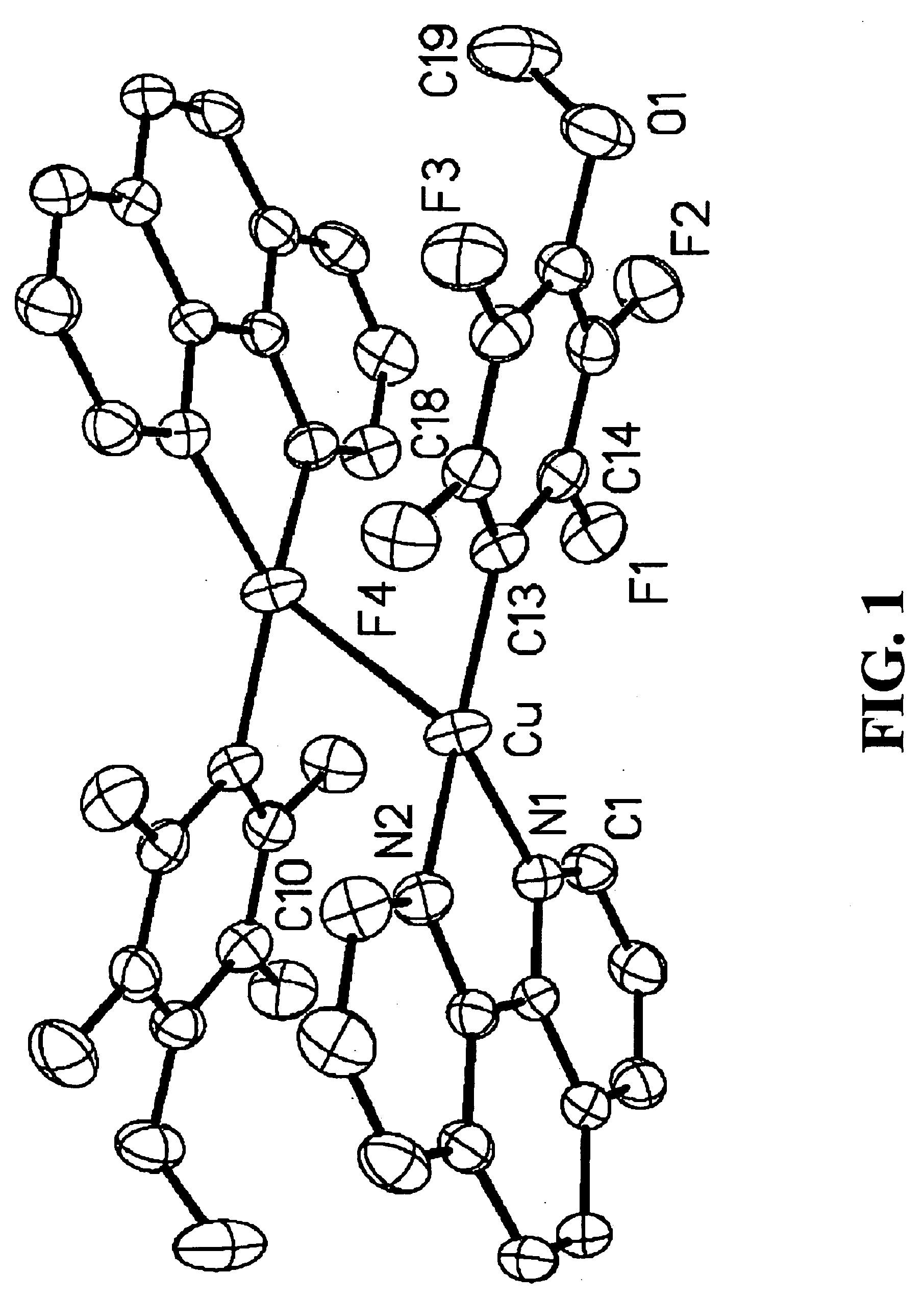
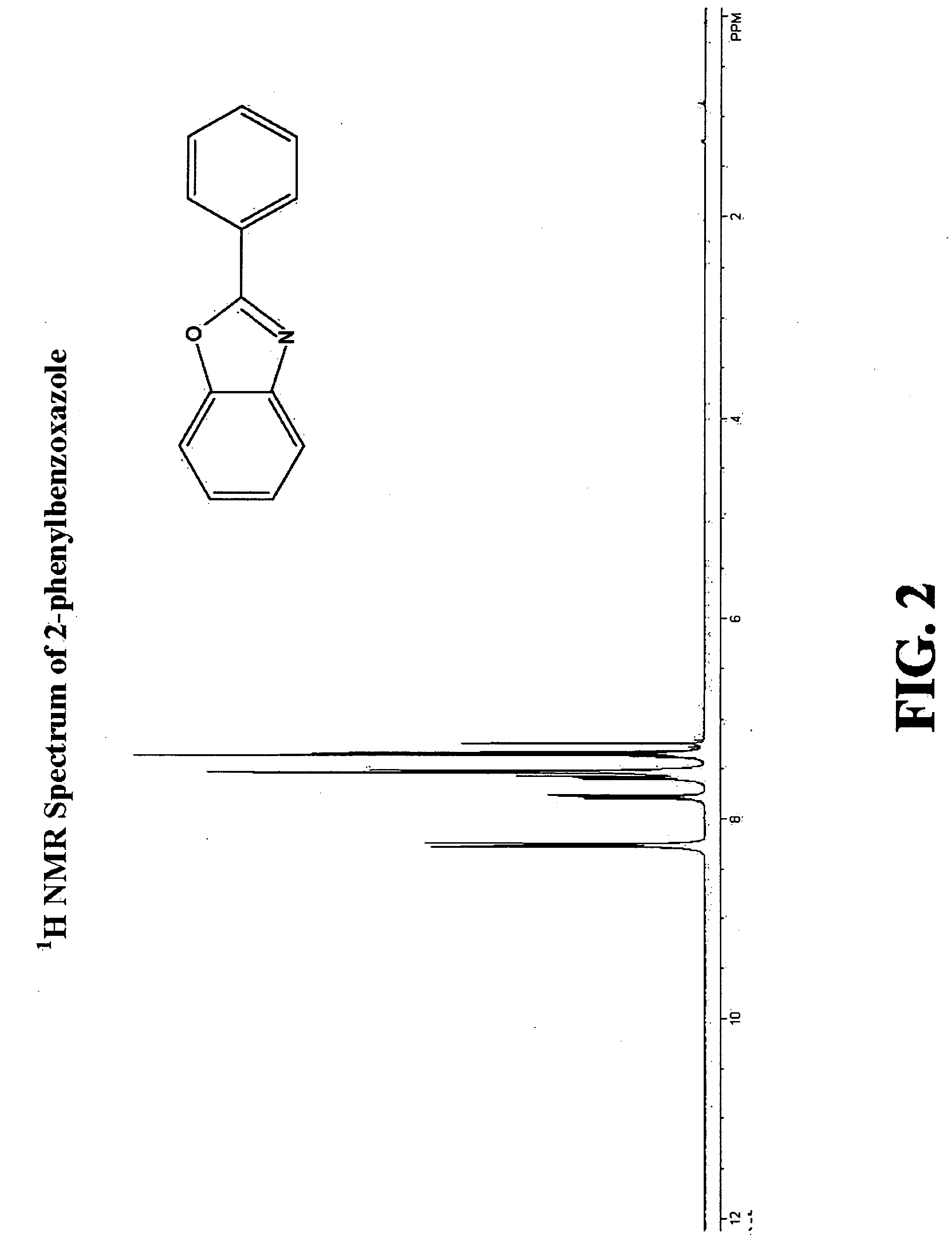
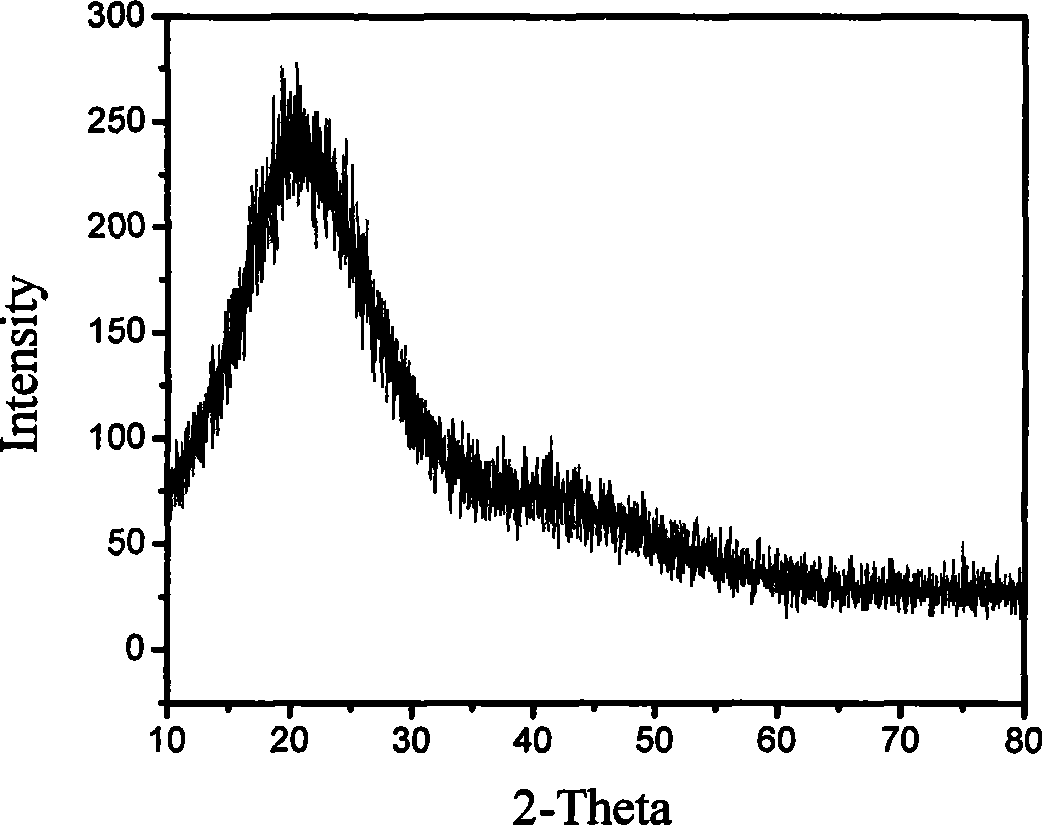
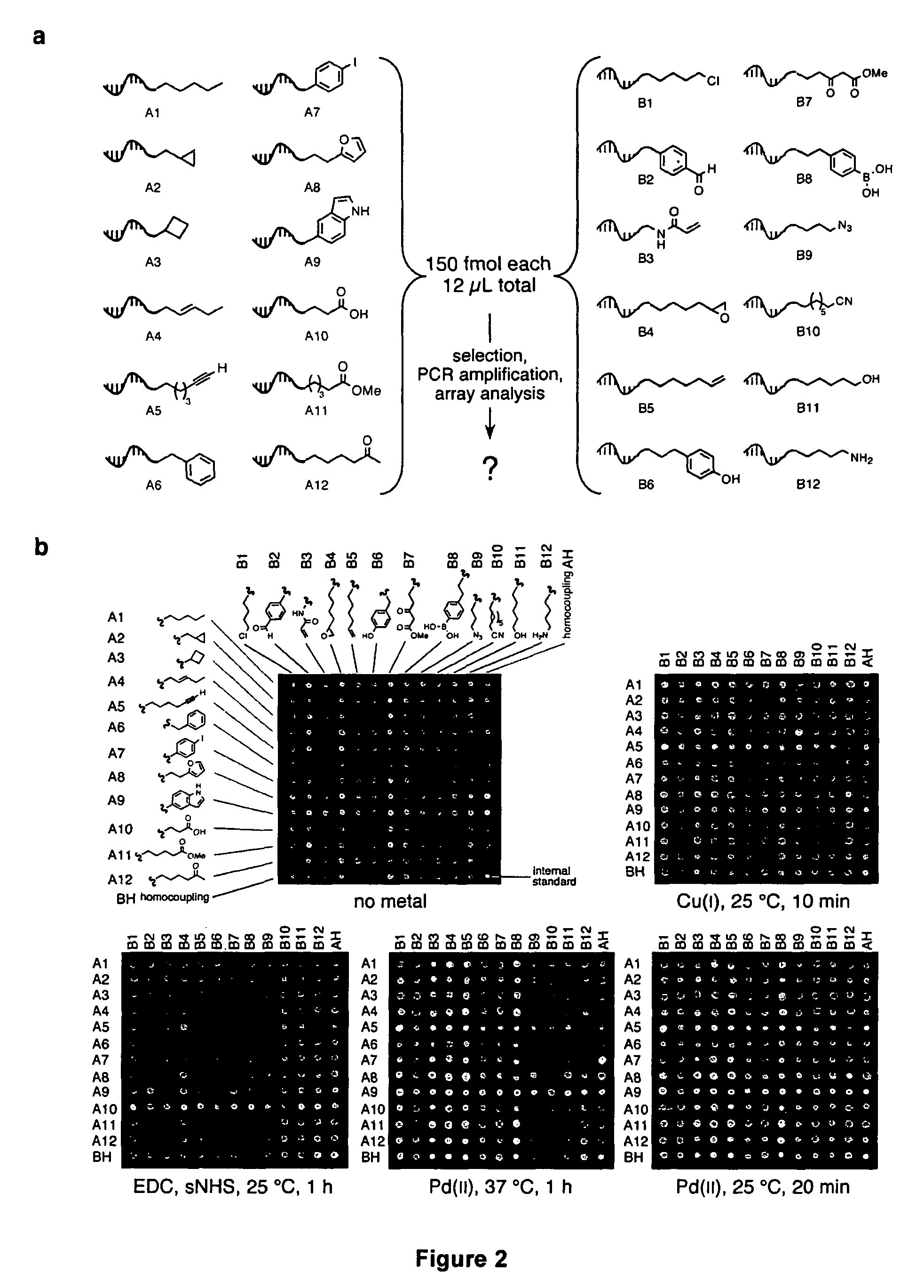
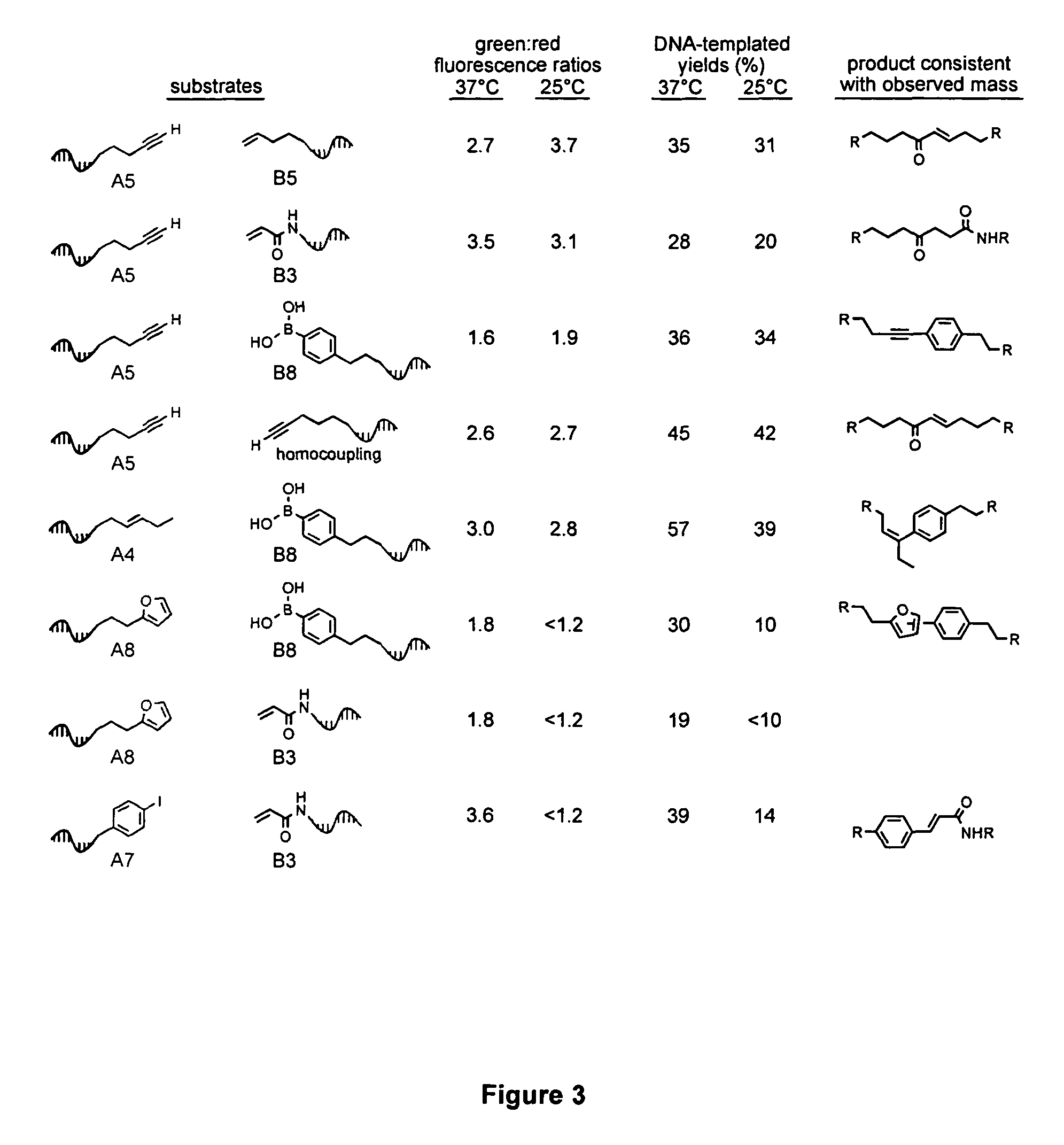
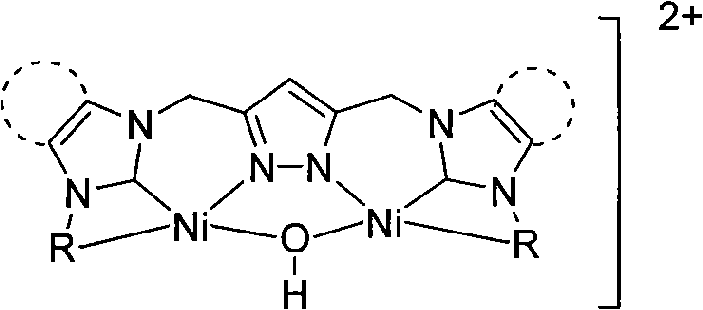
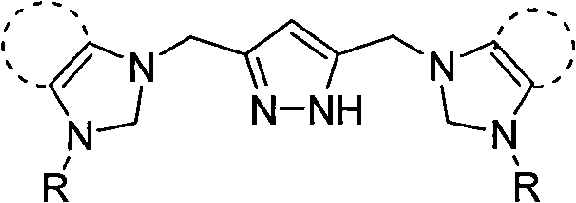
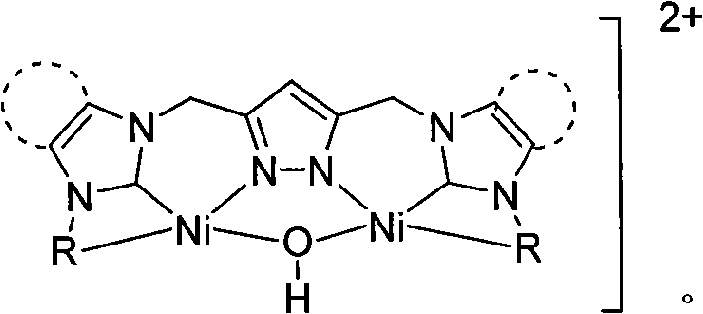
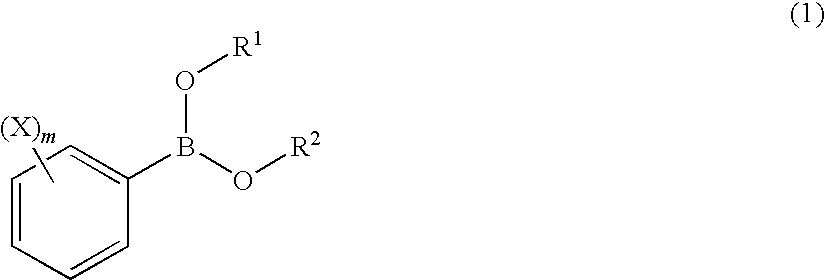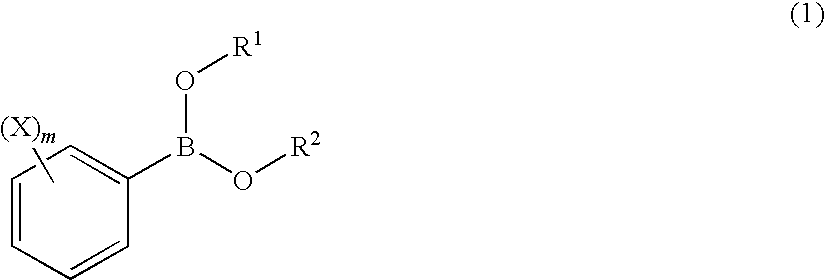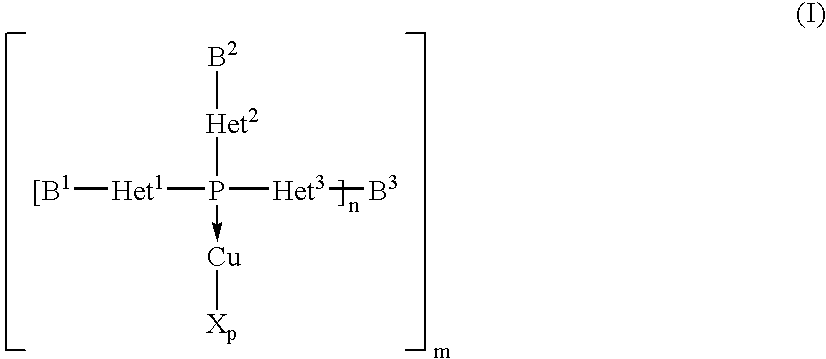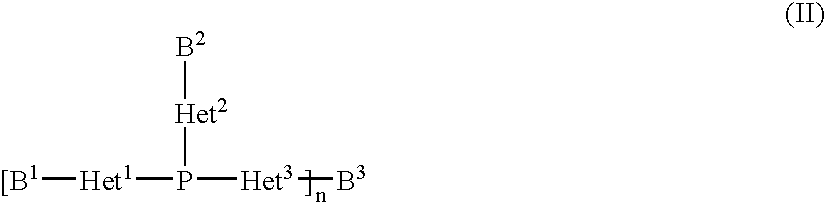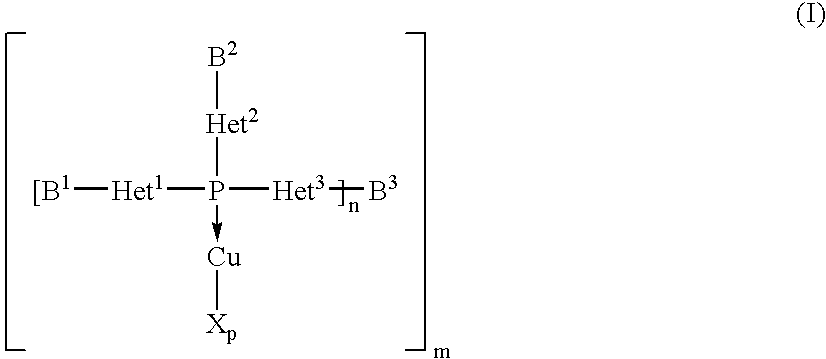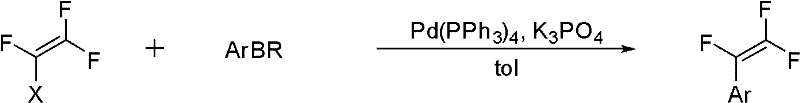Patents
Literature
426results about "Organic substitution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
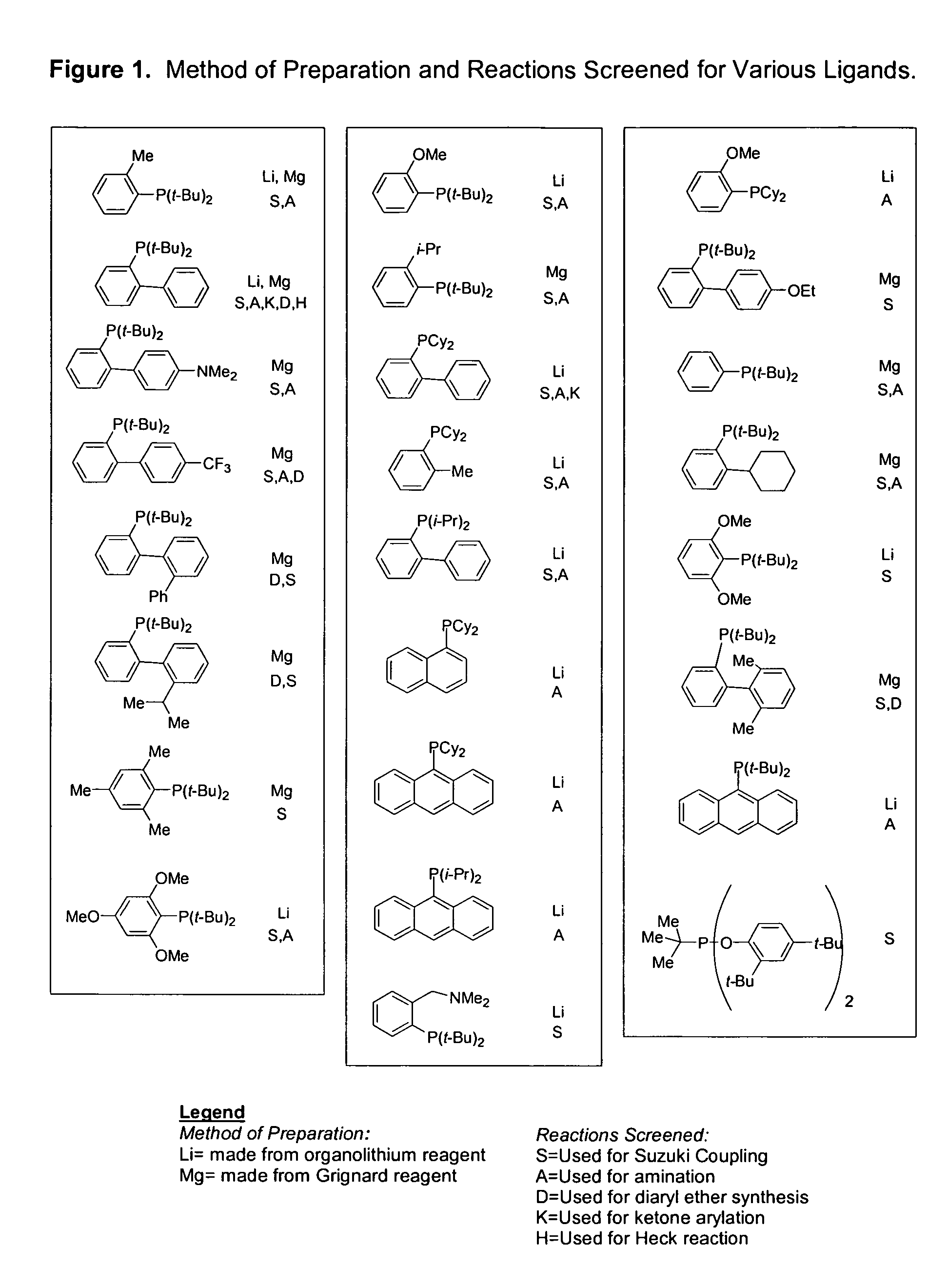
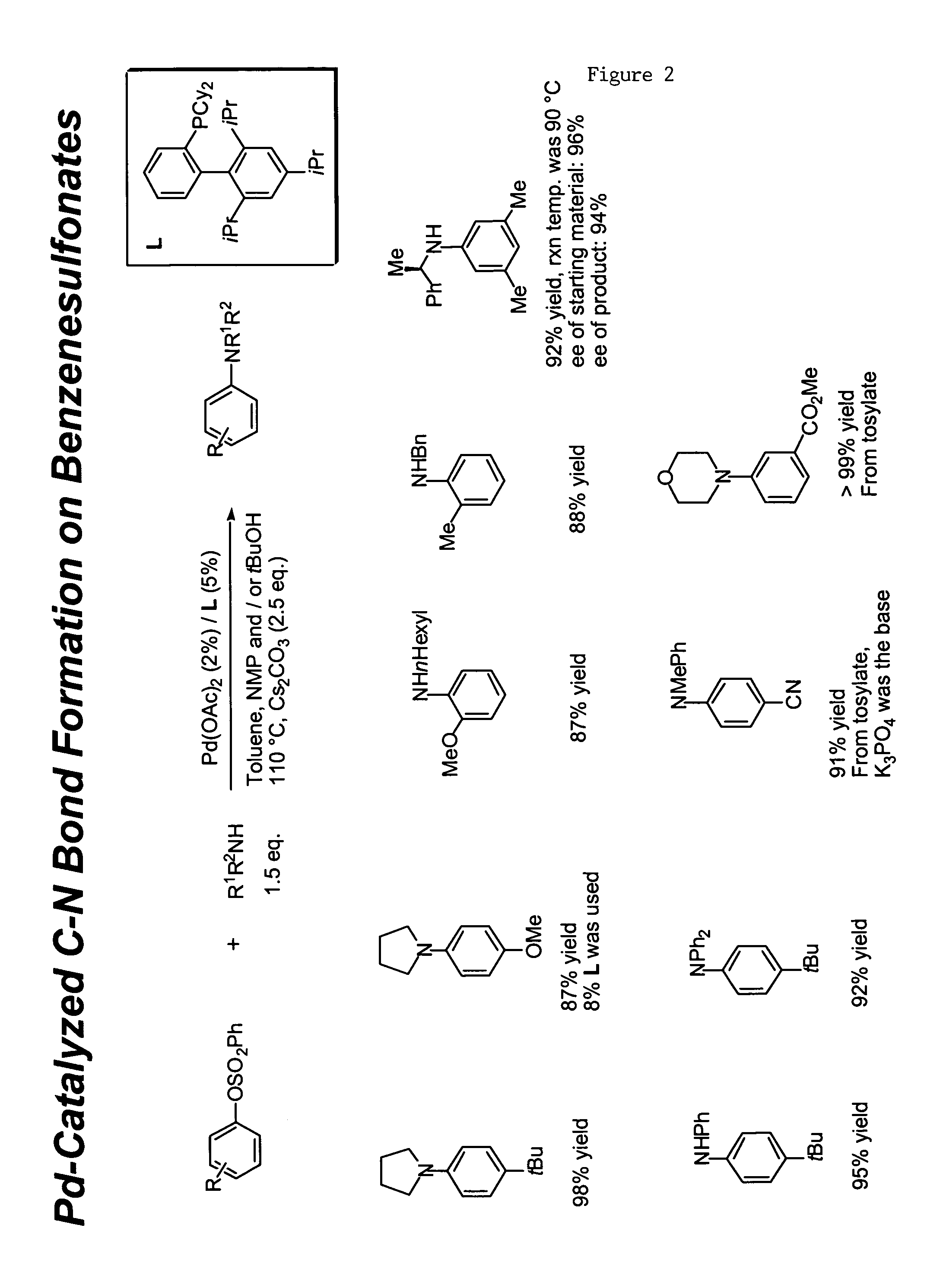
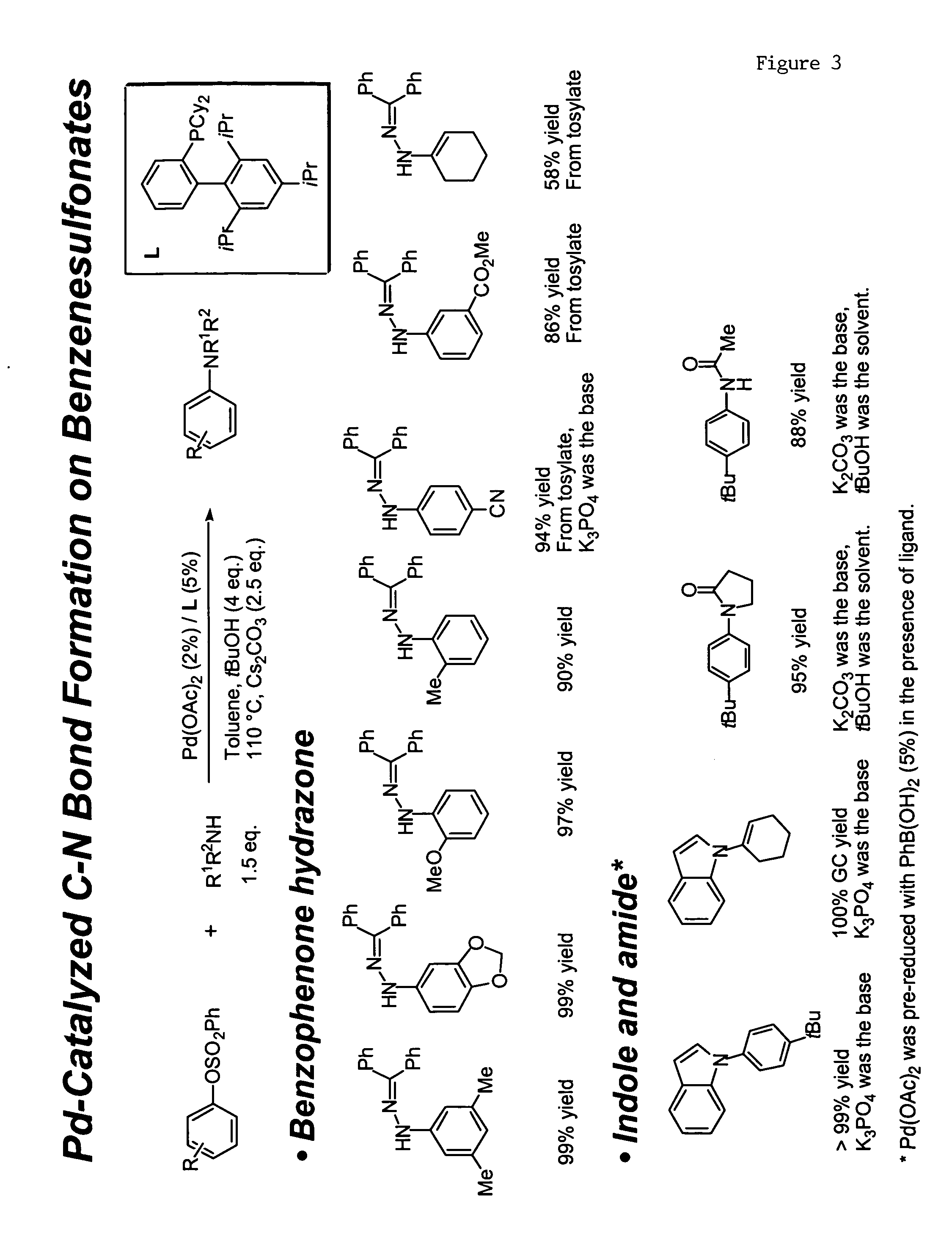
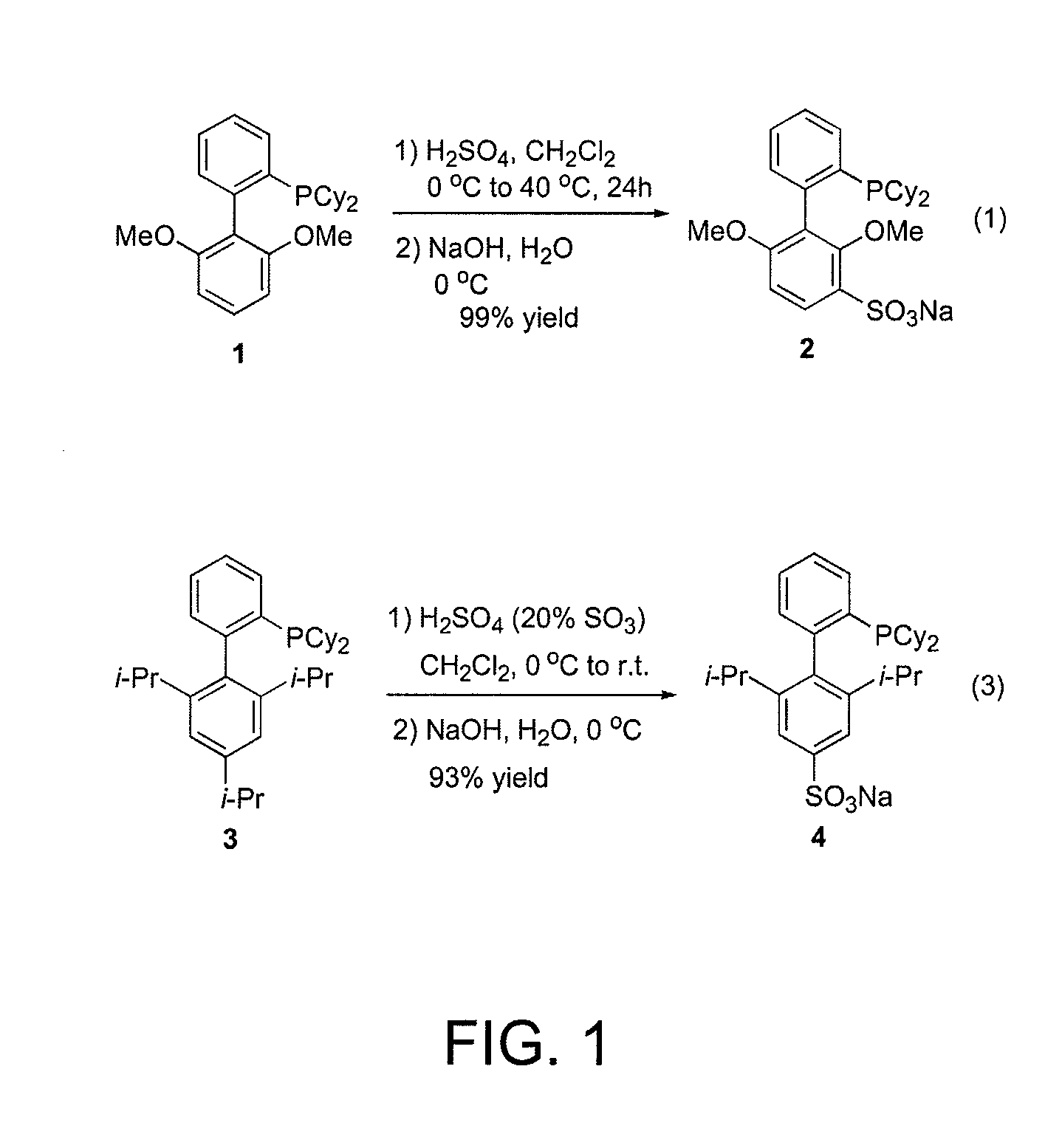
Ligands for metals and improved metal-catalyzed processes based thereon
InactiveUS7223879B2More featureEasy to useCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationCarbon–carbon bondHeteroatom
One aspect of the present invention relates to ligands for transition metals. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the use of catalysts comprising these ligands in transition metal-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions. The subject methods provide improvements in many features of the transition metal-catalyzed reactions, including the range of suitable substrates, reaction conditions, and efficiency.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Continuous process for the alkylation of hydrocarbons
A continuous alkylation process performed in an apparatus comprising a series of at least two zone A reactors and a series of at least two zone B reactors, in which the zone A reactors and the zone B reactors cycle between alkylation mode and mild regeneration mode, and wherein the alkylation mode comprises introducing an alkylation agent into a first reactor of the zone through which the alkylatable compound passes, reacting a portion of the alkylatable compound with a portion of the alkylation agent to produce a product stream, and performing this operation at least once more in a downstream reactor in the same zone employing, instead of alkylatable compound, a stream comprising the product stream.
Owner:ALBEMARLE NETHERLANDS BV
Copper-catalyzed formation of carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bonds
InactiveUS6867298B2Cheap and practicalLow costUrea derivatives preparationCarbamic acid derivatives preparationCarbon–oxygen bondHydrazine compound
The present invention relates to copper-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond-forming methods. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between the nitrogen atom of an amide or amine moiety and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In additional embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between a nitrogen atom of an acyl hydrazine and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In other embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between the nitrogen atom of a nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic, e.g., indole, pyrazole, and indazole, and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-oxygen bond between the oxygen atom of an alcohol and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. The present invention also relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-carbon bond between a reactant comprising a nucleophilic carbon atom, e.g., an enolate or malonate anion, and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. Importantly, all the methods of the present invention are relatively inexpensive to practice due to the low cost of the copper comprised by the catalysts.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Organic metal framework supported palladium, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101733162AImprove stabilityHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemical industryN dimethylformamide
The invention discloses an organic metal framework supported palladium in the technical field of chemical industry, a preparation method and application thereof. The organic metal framework supported palladium is prepared by the method comprising the steps of: dissolving terephthalic acid and zinc nitrate hexahydrate into N, N-dimethylformamide, dripping triethylamine with the stirring, continuing stirring the obtained solution, filtering the obtained solution, and washing a precipitate to obtain a solid, namely MOF-5; and dissolving Na2PdC14 into the N, N-dimethylformamide to obtain solution, adding the MOF-5 into the solution, and then dripping hydrazine hydrate to obtain Pd@MOF-5 through stirring, filtration, washing and vacuum drying. The invention also relates to the method for preparing the organic metal framework supported palladium, application thereof taken as a catalyst in a Sonogashira reaction, and the method for preparing diaryl acetylene. The organic metal framework supported palladium in the invention has good stability, can catalyze the reaction with high selectivity and high efficiency under rather low loading of the catalyst, and can be repeatedly used.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Copper-catalyzed c-h bond arylation
ActiveUS20090076266A1Carboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationHydrogenOrganic synthesis
The present invention is a one-step method for efficiently converting carbon-hydrogen bonds into carbon-carbon bonds using a combination of aryl halides, a substrate, and a copper salt as catalyst. This method allows faster introduction of complex molecular entities, a process that would otherwise require many more steps. This invention is particularly relevant for the organic synthesis of complex molecules such as, but not limited to, pharmacophores and explosives.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Method for preparing compound in biphenyl class
InactiveCN101050157ACarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationArylPolyethylene glycol
This invention provides an air-enhanced method for preparing biphenyl compounds from chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons and aryl boric acid by Suzuki crosslinking reaction catalyzed by nanoscale Pd in situ grown in poly(ethylene glycol). The method does not need any ligand, phase transfer agent, promoter or inert gas protection. Catalyzed by nanoscale Pd in situ grown in poly (ethylene glycol), chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons and aryl boric acid react in a mild condition to obtain biphenyl compounds with a high efficiency. In an optimized condition, the conversion rate of chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons and the yield of biphenyl compounds are 95-100% and 90-99%, respectively.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Carbonyl arylations and vinylations using transition metal catalysts
The invention is directed to a process for preparing an alpha-arylated or vinylated carbonyl-containing compounds, comprising reacting a compound having a carbonyl group with an arylating or vinylating compound in the presence of a base and a transition metal catalyst. The transition metal catalyst has the formula XnM(ER1-4)m, wherein X is an optional ligand, M is a group 8 transition metal, E is an element bearing a nonbonding electron pair when E is not bonded to the metal, and R is a substituent bonded to E through a carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur atom, with the proviso that R3 cannot contain 3 aryl groups, n is an integer from 0 to 4, and m is an integer from 1-4. The process of the invention is useful for preparation of alpha-arylated or vinylated carbonyl-containing compounds which are significant in the development of pharmacologically active compounds and polymers and oligomers.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method for preparing carboneous solid acid catalyst
InactiveCN101485997ALow priceLess corrosiveOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCelluloseBiodiesel
The invention relates to a method for preparing a sulfonated carbon solid acid catalyst, which uses a sulfonic aromatic compound to replace sulfuric acid. The method uses glucide as a raw material and an aromatic compound with sulfonic group as a sulfonating reagent to generate the carbon solid acid catalyst in one step through solvent heat treatment at a temperature of between 150 and 200 DEG C. The method has the advantages that the prepared solid acid has controllable surface acid content and good stability; the glucide as the raw material has rich resource and low price; the reaction condition is mild, and the preparation process is simple; and concentrated sulfuric acid or fuming sulfuric acid are not adopted as the sulfonating reagent, so equipment can be corroded less. The solid acid can be used as the catalyst of hydrolyzation of cellulose, alkylation reaction, biodiesel preparation and other reactions. Compared with the prior sulfuric acid catalyst, the catalyst has the advantages of non corrosion, easy separation, reusage and non production of waste acid or sewage, and has better advantages in the application field with special requirement, such as fine chemistry industry and pharmaceutical synthesis.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
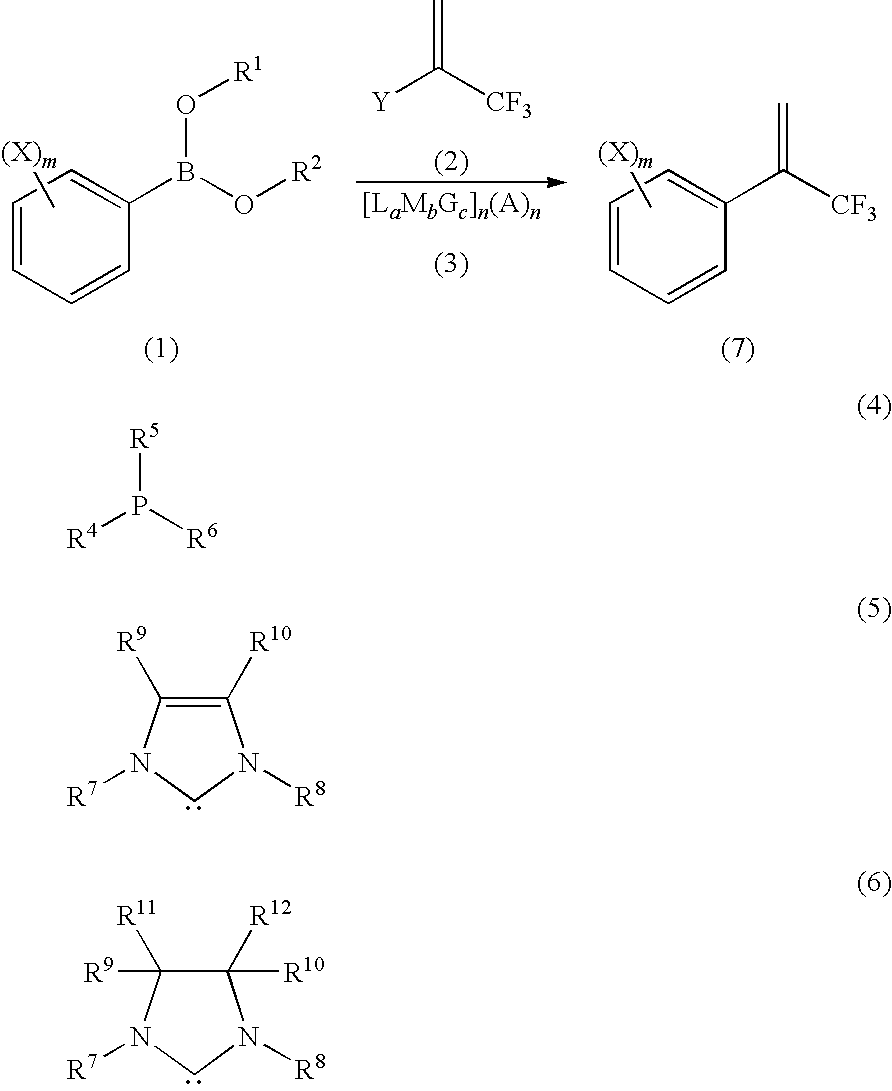
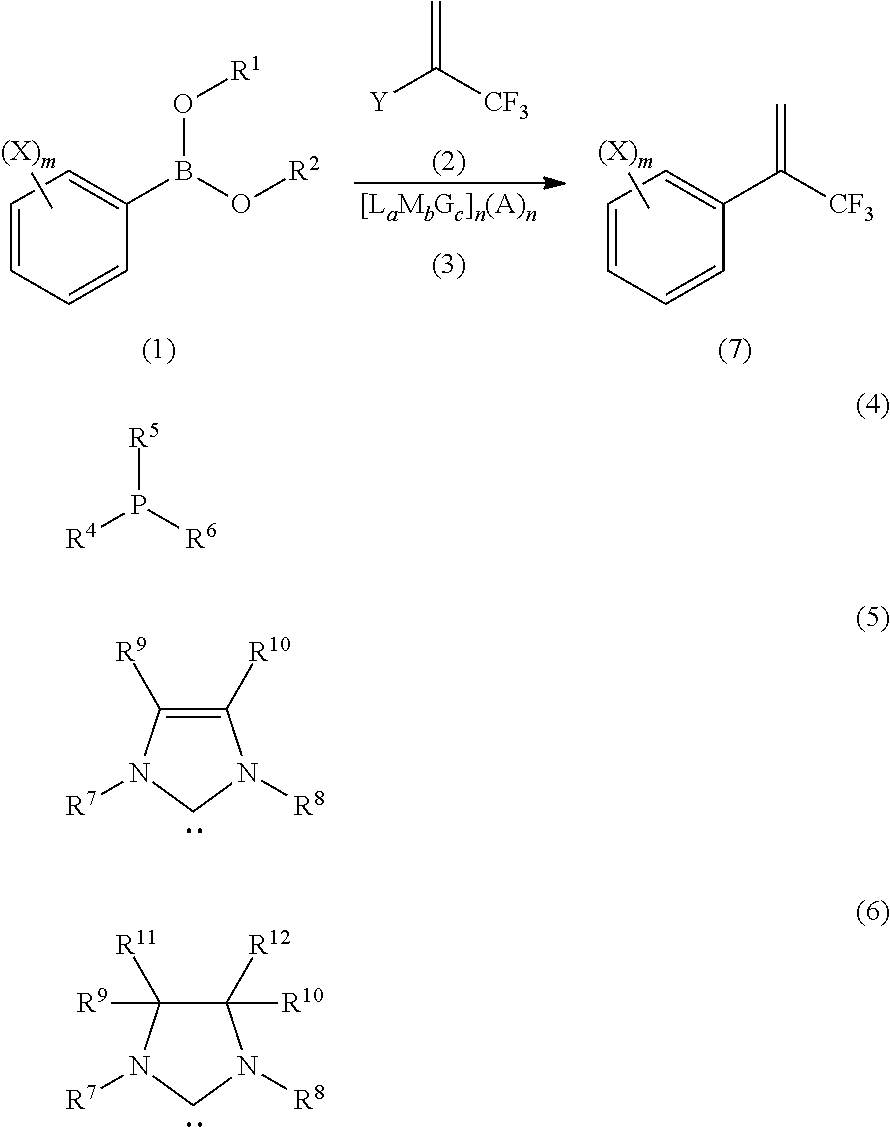
Process for Production of 2-(Substituted Phenyl)-3,3,3-Trifluoropropene Compound
ActiveUS20100160683A1Improve efficiencyHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationHalogenOxidation state
There is provided a novel process for production of a 2-(substituted phenyl)-3,3,3-trifluoropropene.Disclosed is a process for production of a 2-(substituted phenyl)-3,3,3-trifluoropropene compound represented by the formula (7) or a salt thereof The process comprises reacting a compound represented by the formula (1) (X is an alkyl group, etc.) with a compound represented by the formula (2) (Y is a halogen atom, etc.) in the presence of a catalyst represented by the formula (3) (M is an ion of a metal belonging to Group 10 on the elementary periodic table which has an oxidation state number of 1 to 8; G is a unidentate or multidentate ligand; L is a phosphine compound represented by the formula (4) which is bound to the center metal M or is a carbene selected from those represented by the formulae (5) and (6), provided that L's may be same as or different from one another when a is 2 to 5; A represents a univalently or multivalently charged anion; b represents an integer of 1 to 3; a represents an integer of 1 to 5·b; c represents 0 or an integer of 1 to 4·b; and n represents an integer of 1 to 6).
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Use of a catalyst system comprising nickel palladium or platinum and imidazoline-2-ylidene or imidazolidine-2-ylidene in stille coupling reactions
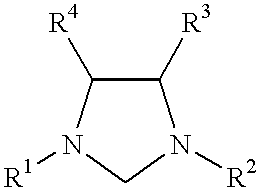
InactiveUS6362357B1High yieldEliminate needHydrocarbon by isomerisationOrganic compound preparationLiquid mediumOxidation state
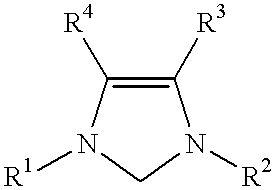
This invention provides a process for conducting Stille coupling reactions. The processes of the present invention make use of N-heterocyclic carbenes as ancillary ligands in Stille couplings of aryl halides. A Stille coupling can be carried out by mixing, in a liquid medium, at least one strong base; at least one aryl halide or aryl pseudohalide in which all substituents are other than stannyl groups, wherein the aryl halide has, directly bonded to the aromatic ring(s), at least one halogen atom selected from the group consisting of a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, and an iodine atom; at least one organotin compound wherein the tin atom is quaternary, wherein one group bound to the tin atom is unsaturated at the alpha or beta position, and wherein each of the remaining groups bound to the tin atom is a saturated group; at least one metal compound comprising at least one metal atom selected from nickel, palladium, and platinum, wherein the formal oxidation state of the metal is zero or two; and at least one N-heterocyclic carbene. One preferred type of N-heterocyclic carbene is an imidazoline-2-ylidene of the formulawherein R1 and R2 are each, independently, alkyl or aryl groups having at least 3 carbon atoms, R3 and R4 are each, independently, a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, or a hydrocarbyl group.
Owner:RES & TECH FOUND UNIV OF NEW ORLEANS
Metal-containing organosilica catalyst; process of preparation and use thereof
InactiveUS20110190115A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPtru catalystMetal catalyst
The invention relates to a metal-containing organosilica catalyst, and use thereof in metal-catalyzed reactions. The invention relates to a process of preparation of the metal-containing organosilica catalyst comprising i) mixing a silicon source with an hydrolytic solvent; ii) adding one or more metal catalyst or a precursor thereof; iii) treating the mixture of step ii) with a condensation catalyst and iv) optionally treating the mixture resulting from step iii) with one or more reducing or oxydating agent such as to provide the required oxidation level to the metal catalyst.
Owner:SILICYCLE INC
Acylation reactions of aromatic substrates
InactiveUS6630606B2Increase ratingsHigh selectivityCarbonyl compound preparation by condensationHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon condensationAlkyl transferProduct formation
Method of performing alkylation or acylation reactions of aromatic substrates under supercritical or near-critical reaction conditions. In particular, a method of performing Friedel-Crafts alkylation or acylation reactions is disclosed under those conditions. Friedel-Crafts reactions may be effected using a heterogeneous catalyst in a continuous flow reactor containing a super-critical or near-critical reaction medium. Selectivity of product formation can be achieved by varying one or more of the temperature, pressure, catalyst, flow rates and also by varying the ratios of aromatic substrate to acylating or alkylating agent.
Owner:THOMAS SWAN & CO LTD +1
Process for production of 2-(substituted phenyl)-3,3,3-trifluoropropene compound
ActiveUS7964758B2Improve efficiencyHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationHalogenOxidation state
There is provided a novel process for production of a 2-(substituted phenyl) -3,3,3-trifluoropropene.Disclosed is a process for production of a 2-(substituted phenyl)-3,3,3-trifluoropropene compound represented by the formula (7) or a salt thereof The process comprises reacting a compound represented by the formula (1) (X is an alkyl group, etc.) with a compound represented by the formula (2) (Y is a halogen atom, etc.) in the presence of a catalyst represented by the formula (3) (M is an ion of a metal belonging to Group 10 on the elementary periodic table which has an oxidation state number of 1 to 8; G is a unidentate or multidentate ligand; L is a phosphine compound represented by the formula (4) which is bound to the center metal M or is a carbene selected from those represented by the formulae (5) and (6), provided that L's may be same as or different from one another when a is 2 to 5; A represents a univalently or multivalently charged anion; b represents an integer of 1 to 3; a represents an integer of 1 to 5·b; c represents 0 or an integer of 1 to 4·b; and n represents an integer of 1 to 6).
Owner:NISSAN CHEM CORP
Process for the arylation of olefins
The present invention relates to a process for the arylation of olefins by reaction of haloaromatics or arylsulfonates with olefins in the presence of a palladium catalyst, a bulky nitrogen base and a salt.
Owner:LANXESS DEUTDCHLAND GMBH
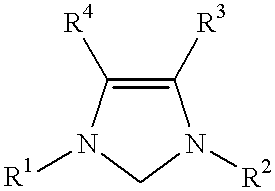
Use of a catalyst system comprising nickel, palladium, or platinum and imidazoline-2-ylidene or imidazolidine-2-ylidene in kumada coupling reactions
InactiveUS6369265B1Good yieldEliminate needOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsLiquid mediumGrignard reagent
This invention provides a process for conducting Kumada coupling reactions. The processes of the present invention make use of N-heterocyclic carbenes as ancillary ligands in Kumada couplings of aryl halides. A Kumada coupling can be carried out by mixing, in a liquid medium, at least one aryl halide, wherein the aryl halide has, directly bonded to the aromatic ring(s), at least one halogen atom selected from the group consisting of a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, and an iodine atom; at least one Grignard reagent; at least one metal compound comprising at least one metal atom selected from nickel, palladium, and platinum, wherein the formal oxidation state of the metal is zero or two; and at least one N-heterocyclic carbene. One preferred type of N-heterocyclic carbene is an imidazoline-2-ylidene of the formulawherein R1 and R2 are each, independently, alkyl or aryl groups having at least 3 carbon atoms, R3 and R4 are each, independently, a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, or a hydrocarbyl group. Homocoupling of aryl pseudohalides is also feasible using the processes of this invention.
Owner:UNIV OF NEW ORLEANS RES TECH FOUND
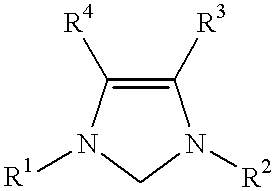
Use of catalyst system comprising nickel, palladium, or platinum and imidazoline-2-ylidene or imidazolidine-2-ylidene in amination reactions
InactiveUS6403802B1High yieldEliminate needGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCarboxylic acid esters preparationLiquid mediumOxidation state
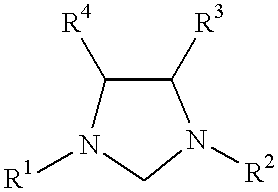
This invention provides a process for conducting amination reactions. The processes of the present invention make use of N-heterocyclic carbenes as ancillary ligands in aminations of aryl halides and aryl pseudohalides. An amination can be carried out by mixing, in a liquid medium, at least one strong base; at least one aryl halide or aryl pseudohalide in which all substituents are other than amino groups, wherein the aryl halide has, directly bonded to the aromatic ring(s), at least one halogen atom selected from the group consisting of a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, and an iodine atom; at least one primary amine and / or at least one secondary amine; at least one metal compound comprising at least one metal atom selected from nickel, palladium, and platinum, wherein the formal oxidation state of the metal is zero or two; and at least one N-heterocyclic carbene. One preferred type of N-heterocyclic carbene is an imidazoline-2-ylidene of the formulawherein R1 and R2 are each, independently, alkyl or aryl groups having at least 3 carbon atoms, R3 and R4 are each, independently, a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, or a hydrocarbyl group.
Owner:UNIV OF NEW ORLEANS RES TECH FOUND
Copper complexes and their use
InactiveUS7179946B2Easy to prepareImprove efficiencyOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCouplingCoupling reaction
The invention relates to copper complexes of phosphorus compounds, to a process for their preparation and to their use in catalytic coupling reactions.
Owner:LANXESS DEUTDCHLAND GMBH
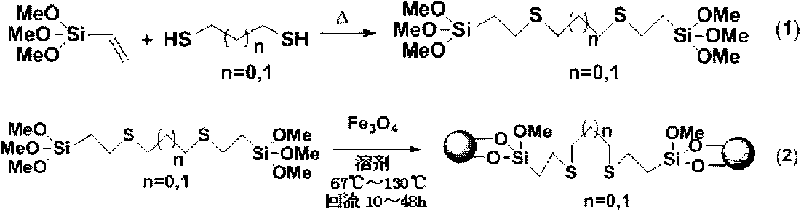
Preparation method of magnetic sulfur-containing bidentate palladium ligand catalyst
InactiveCN101757948AAchieve recyclingEasy to operateCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationPalladiumSulfur containing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a magnetic sulfur-containing bidentate palladium ligand catalyst, relating to a preparation method of a catalyst and solving the problem of difficult recovery of the traditional homogeneous-phase palladium ligand catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a sulfur-containing bidentate ligand containing an active group; (2) preparing a Fe3O4-immobilized sulfur-containing bidentate ligand; and (3) preparing the magnetic sulfur-containing bidentate palladium ligand catalyst to obtain the magnetic sulfur-containing bidentate palladium ligand catalyst. By adopting the preparation method, the homogeneous-phase palladium ligand catalyst is immobilized on superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nano particles, and because the superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nano particles have the characteristics that the superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nano particles can be magnetized in an external magnetic field and the magnetism disappears when the external magnetic field is removed, the magnetic sulfur-containing bidentate palladium ligand catalyst can realize the recovery of the catalyst and has the advantages of simple operation and strong practicality.
Owner:INST OF PETROCHEM HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
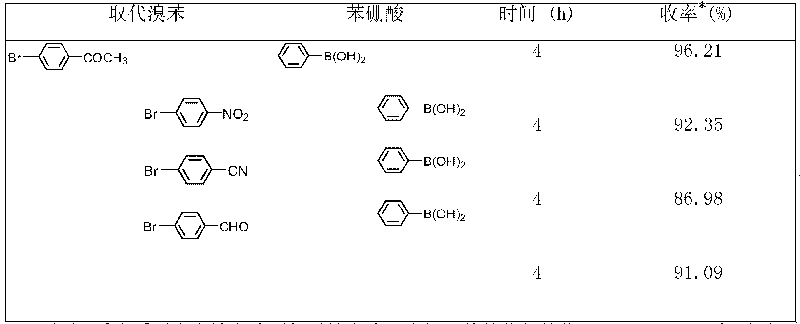
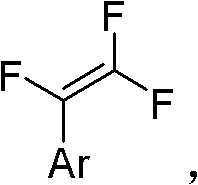
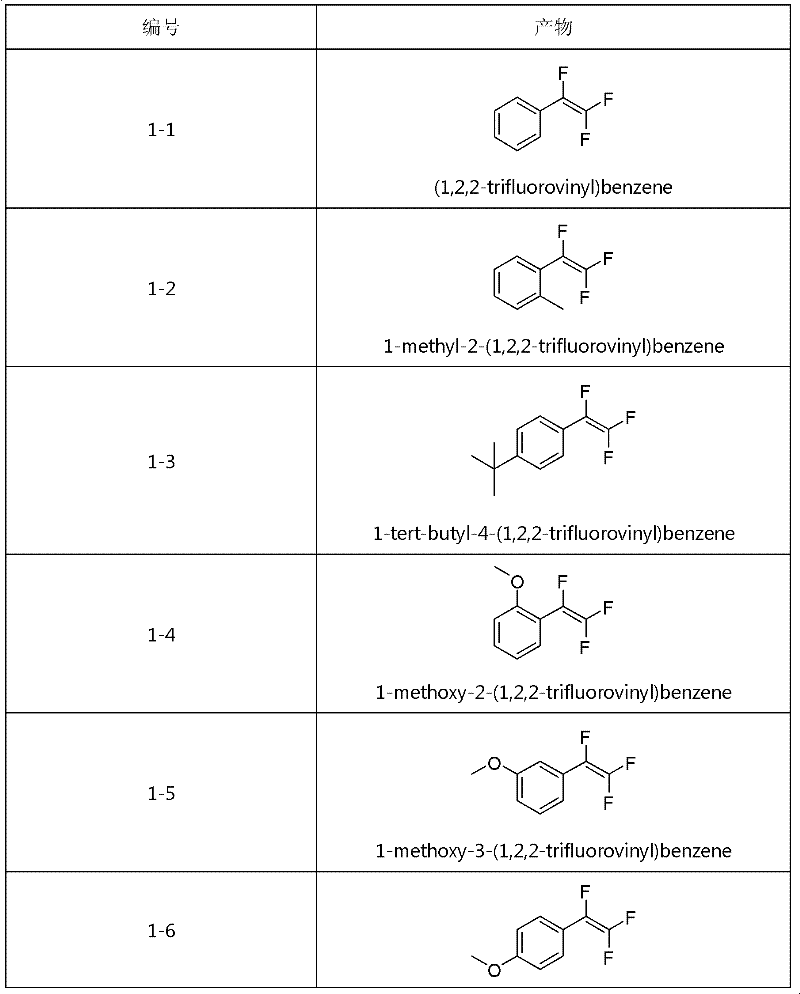
Method for synthesizing trifluorostyrene fluorine-containing monomer
InactiveCN102241554ARaw materials are easy to getSimple methodCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationAmino preparation from aminesRefluxTriphenylphosphine
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a trifluorostyrene fluorine-containing monomer. The monomer is obtained by making halogenated trichloroethylene react with ArBR under the catalytic actions of tetra(triphenylphosphine) palladium and potassium phosphate at reflux temperature. Raw materials are readily available, and the method is easy and convenient, and is a method suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phosphine compound, its intermediate, its complex with palladium and a manufacturing method of unsaturated compounds by using the palladium complex
ActiveUS7129367B2Carboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationHydrogen atomMethylenedioxy
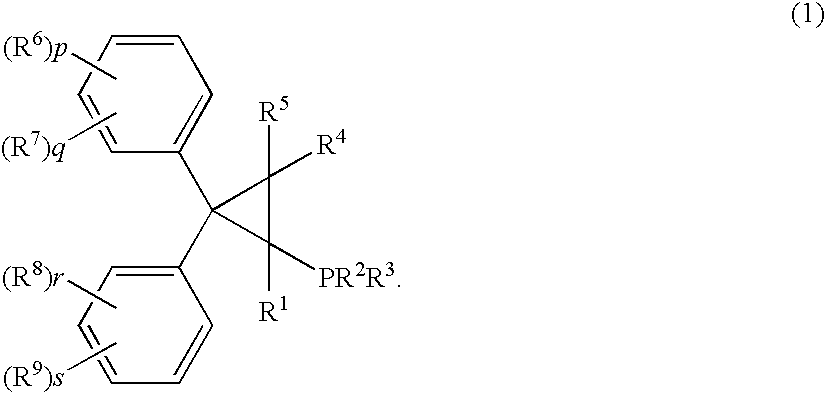
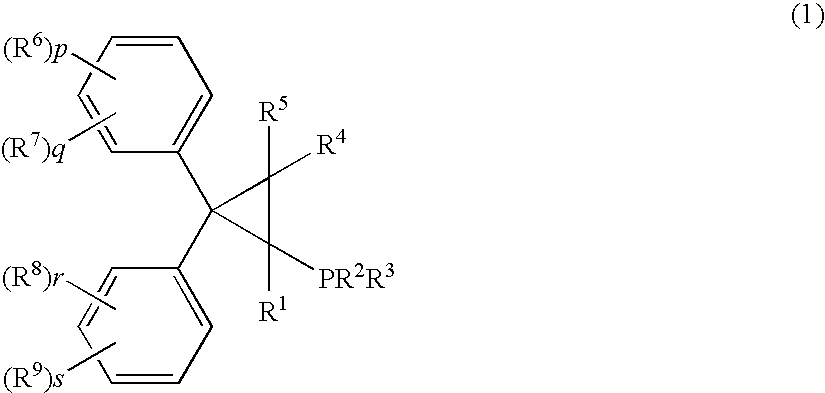
Palladum-phosphine complexes obtained by reacting a 5 compound of formula (1) below with a palladium compound: F(I) (wherein R1 is a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group or a phenyl group which may be substituted; R2 and R3 are each, the same or different, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group or a phenyl group which may be substituted; R4 and R5 are each, the same or different, a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group or a phenyl group which may be substituted; R6, R7, R8 and R9 are each, the same or different, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, a phenyl group which may be substituted, an alkoxyl group, a dialkylamino group, a halogen atom, a phenyl group, a benzyl group, a naphthyl group or a halogenated alkyl group; R6 and R7, R8 and R9 may be combined to form, each, a fused ring, a trimethylene group, a tetramethylene group or a 20 methylenedioxy group; p, q, r and s are each an integer of 0 to 5; and p+q, and r+s are each in the range of 0 to 5.), which is a novel and efficient catalyst for manufacturing various useful compounds
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
High throughput process for manufacturing molecular sieves
ActiveUS20070191660A1Improve throughputLow costHydrocarbon by isomerisationAluminium compoundsMolecular sieveSolid content
A method of crystallizing a crystalline molecular sieve having a pore size in the range of from about 2 to about 19 Å, said method comprising the steps of (a) providing a mixture comprising at least one source of ions of tetravalent element (Y), at least one hydroxide source (OH−), and water, said mixture having a solid-content in the range of from about 15 wt. % to about 50 wt. %; and (b) treating said mixture to form the desired crystalline molecular sieve with stirring at crystallization conditions sufficient to obtain a weight hourly throughput from about 0.005 to about 1 hr−1, wherein said crystallization conditions comprise a temperature in the range of from about 200° C. to about 500° C. and a crystallization time less than 100 hr.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
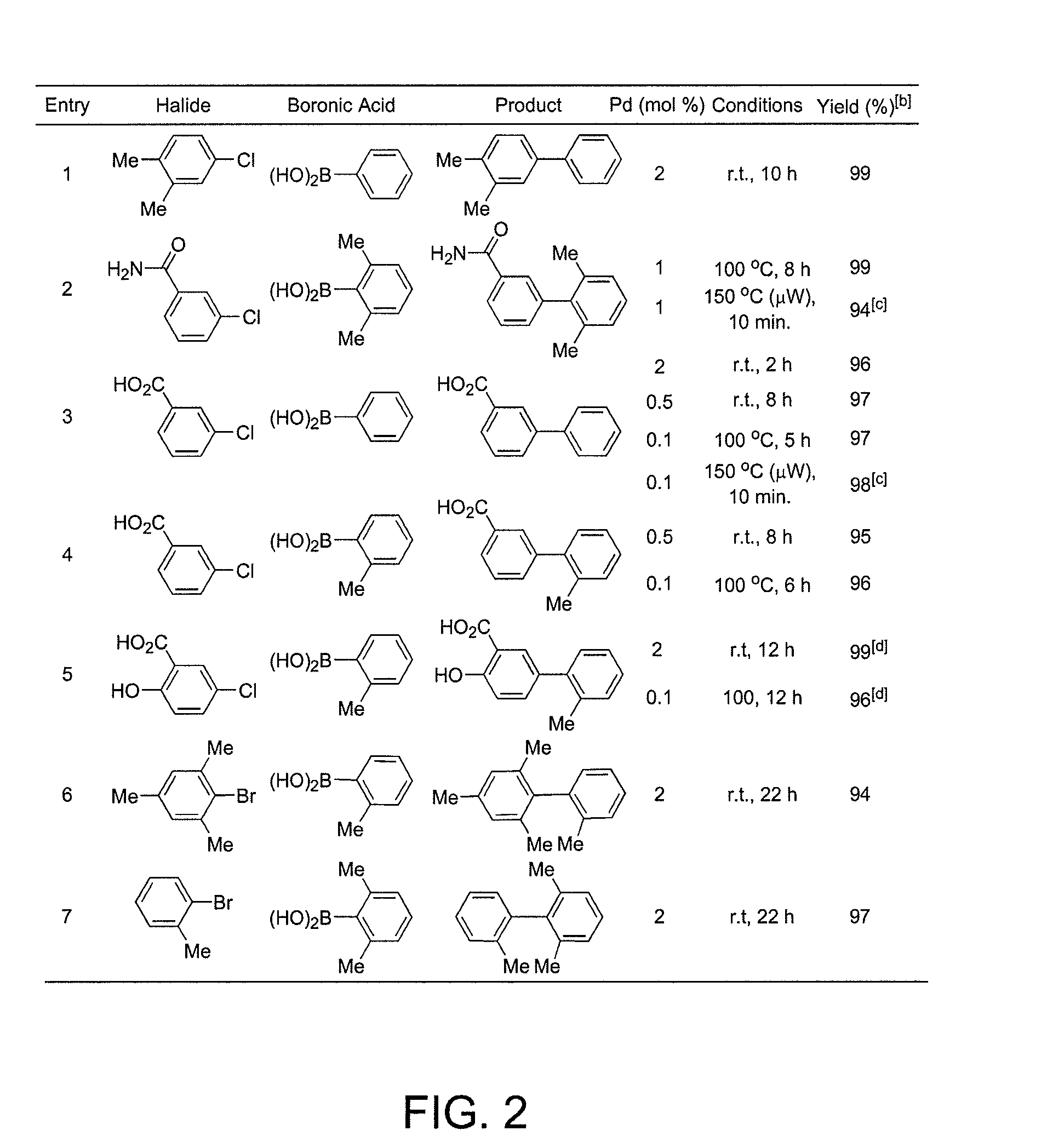
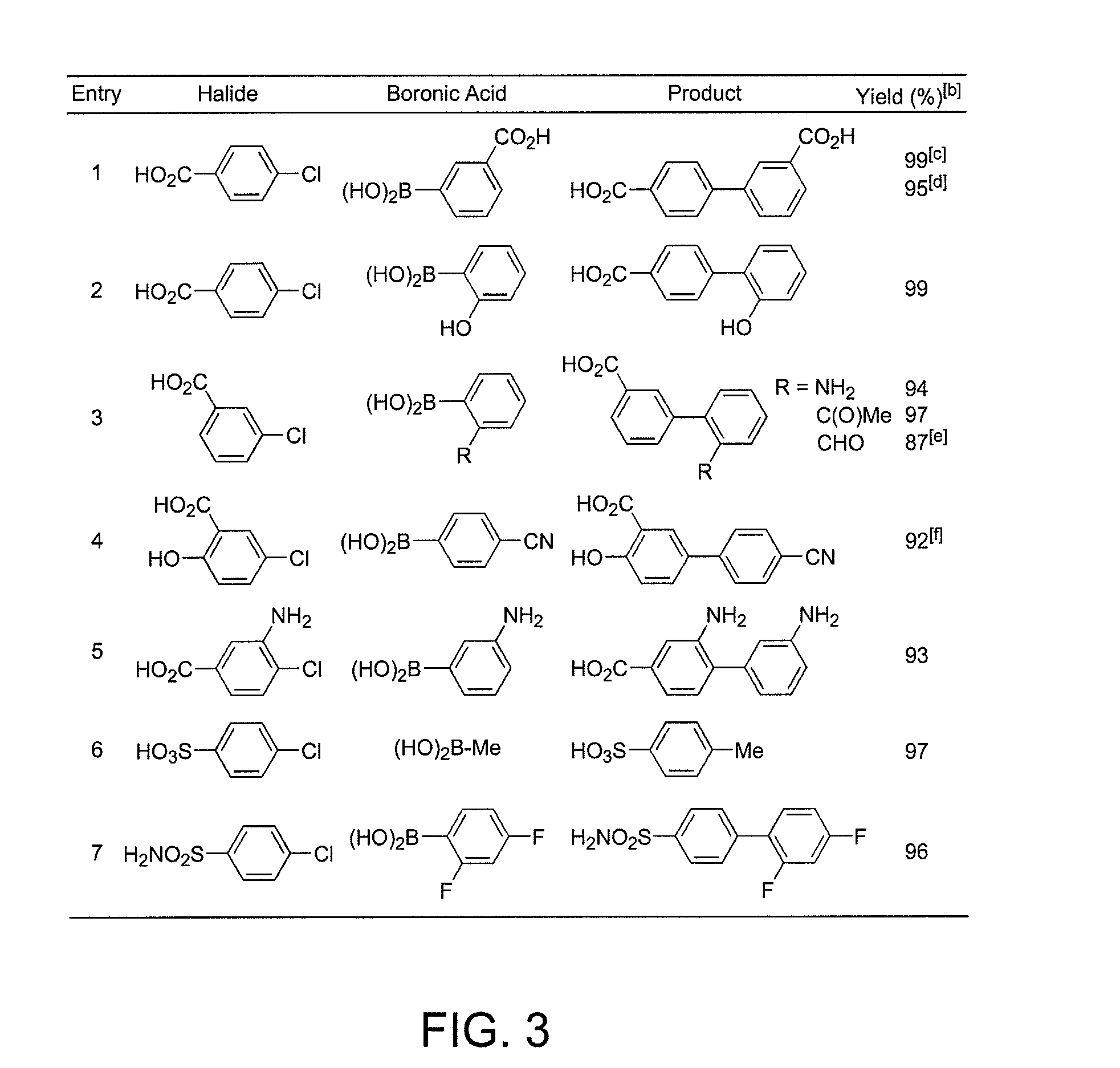
Transition-metal-catalyzed carbon-nitrogen and carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions
ActiveUS20060173186A1More featureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCarboxylic acid amides preparationCarbon–carbon bondCoupling
One aspect of the present invention relates to ligands for transition metals. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the use of catalysts comprising these ligands in various transition-metal-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions. The subject methods provide improvements in many features of the transition-metal-catalyzed reactions, including the range of suitable substrates, number of catalyst turnovers, reaction conditions, and efficiency. For example, improvements have been realized in transition metal-catalyzed: aryl amination reactions; aryl amidation reactions; Suzuki couplings; and Sonogashira couplings. In certain embodiments, the invention relates to catalysts and methods of using them that operate in aqueous solvent systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Palladium catalyst for catalyzing Suzuki coupling reaction, synthesis method, application and ligand
InactiveCN102744106AHigh activityReduce dosageCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationSynthesis methodsReaction temperature
The invention discloses a palladium catalyst for catalyzing a Suzuki coupling reaction, a synthesis method, application and a ligand. The chemical structural formula of the palladium catalyst is Pd6(L11)8(NO3)12. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: (A) heating 2,4,6-triethyl-1,3,5-trimesic acid and SOCl2 of a refluxing volume to carry out a refluxing reaction until the system is clear; (B) adding 5-(4-pyridyl) tetrazole to the reaction system, keeping the refluxing reaction for 2-3 hours in anhydrous pyridine, separating and purifying to obtain the ligand L; and (C) heating the ligand L and palladium nitrate in DMSO (dimethylsulfoxide) at the temperature of 60-70 DEG C for carrying out the refluxing reaction for 2-3 hours, separating and purifying to obtain the catalyst Pd6L8(NO3)12. The invention further provides the application of the palladium catalyst in catalyzing the Suzuki coupling reaction and the ligand. An oxygen-free operation is not needed for the novel palladium catalyst provided by the invention, reagents with larger toxicity, such as toluene, are avoided, the reaction temperature and the reaction time are greatly reduced and shortened, and the activity of the catalyst is higher. The invention is hopefully widely applied on the aspects of medicinal molecules requiring a Suzuki coupling technology and the cleaner production of the ligand.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Process for a carbon-carbon coupling reaction of aryl halides with olefins by heterogeneous catalysts
InactiveUS20020128478A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPalladium catalystChloride
This invention relates to a process for the Heck coupling reaction where heterogeneous palladium catalysts are used to activate aryl halides for a carbon-carbon coupling with olefins in the presence a base and an aprotic solvent to produce aryl-olefin compounds. The process, in particular, provides for the use of aryl chlorides substituted with electron-withdrawing or electron-donating group for the cross coupling with olefins.
Owner:KRSKA SHANE W +2
Synthesis method for asymmetric conjugate diyne compound
InactiveCN105001028AEasy to separateHigh yieldSilicon organic compoundsAmino preparation from aminesSynthesis methodsAlkyne
The invention provides a synthesis method for asymmetric conjugate diyne compound. According to the synthesis method, two kinds of different terminal alkynes are used as raw material, copper is used as catalyst, and the asymmetric conjugate diyne compound is synthesized; the copper which is cheap and easy to get is used as the catalyst, reaction is conducted in the air, precious metal and additive are not needed, prefunctionalization on the alkynes is not needed, special reaction conditions such as microwave radiation are not needed, and the production cost is lowered; the reaction condition is mild, the operation is simple, the applicability of substrate is wide, both the selectivity and productivity of product are high, and good industrial application prospect is achieved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for synthesizing cyclopropyl alkyl aromatic compound
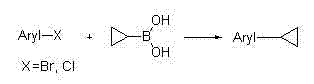
InactiveCN102391059AImprove stabilityEfficient catalytic activityCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationArylOrganic synthesis
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis, and particularly relates to application of a cyclopalladated ferrocenylimines-phosphine adduct in the synthesis of a cyclopropyl alkyl aromatic compound. Halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon Aryl-X, alkali and cyclopropyl borate which serve as raw materials, and the cyclopalladated ferrocenylimines-phosphine adduct is used as a catalyst. The catalyst has high stability, efficient catalytic activity and wide application range, and a corresponding coupling product can be synthesized in a mode of high yield (which is up to 96 percent) on the premise of small catalytic quantity; and the method is mild in reaction condition, wide in range of substrates and high in specifity of reaction.
Owner:TETRANOV PHARMA CO LTD
Transition-metal-catalyzed carbon-nitrogen and carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions
ActiveUS7560596B2More featureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCarboxylic acid amides preparationCarbon–carbon bondCoupling
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Palladium-catalyzed carbon-carbon bond forming reactions
ActiveUS7851658B2Organic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationCarbon–carbon bondAlkyne
A novel palladium-mediated carbon-carbon bond forming reaction has been discovered using DNA-templated chemistry. The inventive reaction involves the palladium-mediated coupling of a terminal alkyne with an alkene to form an enone. A catalytic amount of palladium may be used in the reaction if an oxidant is present. The reactions is also compatible with a variety of organic solvent as well as aqueous solution. Both intermolecular and intramolecular reactions have been demonstrated. This novel carbon-carbon bond forming reaction is particularly useful in the synthesis of macrocycles. Kits, reagents, catalysts, solvents, oxidants, salts, acids, instructions, and other materials useful in the practice of the inventive reaction are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Dinuclear nickel cross-coupling reaction catalyst supported by nitrogen heterocycle carbine ligand and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101284247AImprove catalytic performanceGood catalyticOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsNickel organic compoundsShortest distanceDual core
The invention discloses a dual-core nickel cross-coupling reaction catalyst supported by N-heterocyclic carbine and a preparation method. Acetonitrile is taken as a solvent, N-heterocyclic carbine ligand and silver oxide in the molar ratio of 1: 3 to 1: 6 are added and stirred, the reaction is carried out for 10 to 15 hours away from light; Ni(DME)Cl2 or Ni(PPh3)2Cl2, Ni(DME)Cl2 or Ni(PPH3)2Cl2 and the N-heterocyclic carbine ligand in the molar ratio of 2: 1 to 3: 1 are added and filtered, the filtrate is condensed, ether is added for precipitation of yellow solids, the yellow solids are sequentially washed by ethanol and ether for 2 to 3 times, the acetonitrile is then used for dissolution, the ether is slowly added, and the dual-core nickel cross-coupling reaction catalyst supported by the N-heterocyclic carbine is obtained by crystallization. The novel dual-core nickel catalyst synthesized by the invention can play the synergy due to the shorter distance between two nickel atoms, the catalytic effect thereof is higher than the common palladium catalyst, thus having very ideal catalytic effect on chlorinated aryl compounds with cheap price and wide application prospect in fine chemical and pharmaceutical industries and being environment-friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Mesoporous carbon supported N-heterocyclic carbene-palladium catalyst as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN104511310AHigh catalytic activityEasy to useOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic substitutionPalladium catalystCarbene
The invention discloses a mesoporous carbon supported N-heterocyclic carbene-palladium catalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst carrier is hydroxylated mesoporous carbon; the ligand is N-heterocyclic carbine; the active ingredient is palladium chloride; the load capacity of the palladium in the active ingredient is 5.0-10.0% of the total mass of the catalyst; the surface hydroxyl group content of the hydroxylated mesoporous carbon is 1.9-2.2 mmol / g; the BET specific surface area of the hydroxylated mesoporous carbon is 700-1000m<2> / g; the BJH pore diameter is 5-7 nm; the BJH pore volume is 0.8-1.8 ml / g. According to the mesoporous carbon supported N-heterocyclic carbene-palladium catalyst, the palladium can be prevented from loss in the catalytic process; the mesoporous carbon has an ordered mesoporous structure, so that the surface dispersing performance of the palladium nano-particles can be improved to prevent the palladium from gathering in the catalytic process and improve the catalytic activity of the supported catalyst. The mesoporous carbon supported N-heterocyclic carbene-palladium catalyst has relatively high catalytic activity and relatively good reusability.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Popular searches
Hydroxy compound preparation Amino-carboxyl compound preparation Phosphorus organic compounds Metallocenes Amino-hyroxy compound preparation Group 4/14 element organic compounds Isocyanic acid derivatives preparation Hydrocarbon from halogen organic compounds Hydrazone preparation Carbonyl compound preparation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com