Fluorescent in-situ hybridization method for detecting plant rhizosphere microbe
A fluorescent in situ hybridization and microbial technology, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to find target microorganisms, interfere with microbial observation, and difficult observation, so as to avoid spontaneous fluorescent effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1, adopt the method of the present invention to carry out fluorescence in situ hybridization
[0040] 1. Take the root tissue of a Juncus acutiflorus from the wetland. After sampling for 48 hours, wash it with deionized water to remove excess wetland sediment and soil residue attached to the surface; then cut the root tissue into about 2cm in length root fragments.
[0041] 2. Soak the root fragments obtained in step 1 in 2-5ml (whichever is sufficient to completely submerge the root fragments) solution A for 12 hours of fixation.
[0042] The solution A is obtained by mixing 3 parts by volume of fixative solution and 1 part by volume of PBS buffer solution.
[0043] The preparation method of fixative solution is as follows (taking 100ml volume as an example): (1) Take 66ml of ultrapure water and heat it to 60°C in a water bath; (2) Add 4g of paraformaldehyde to the water, the mixture will become turbid; (3) Slowly add 2mol / L NaOH aqueous solution to the mi...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2, adopt the method of the present invention to carry out fluorescence in situ hybridization
[0061] 1. Same as step 1 in Example 1.
[0062] 2. Same as step 2 of embodiment 1.
[0063] 3. Adopt 0.0001mol / L tetrasodium pyrophosphate aqueous solution, incubate in 20 ℃ water bath for 15 minutes, others are the same as step 3 of embodiment 1.
[0064] 4. Same as step 4 in Example 1.
[0065] 5. Same as Step 5 of Example 1.
[0066] 6. Same as step 6 of embodiment 1.
[0067] 7. Same as Step 7 of Example 1.
[0068] 8. Same as step 8 in Example 1.
[0069] 9. Same as step 9 in Example 1.
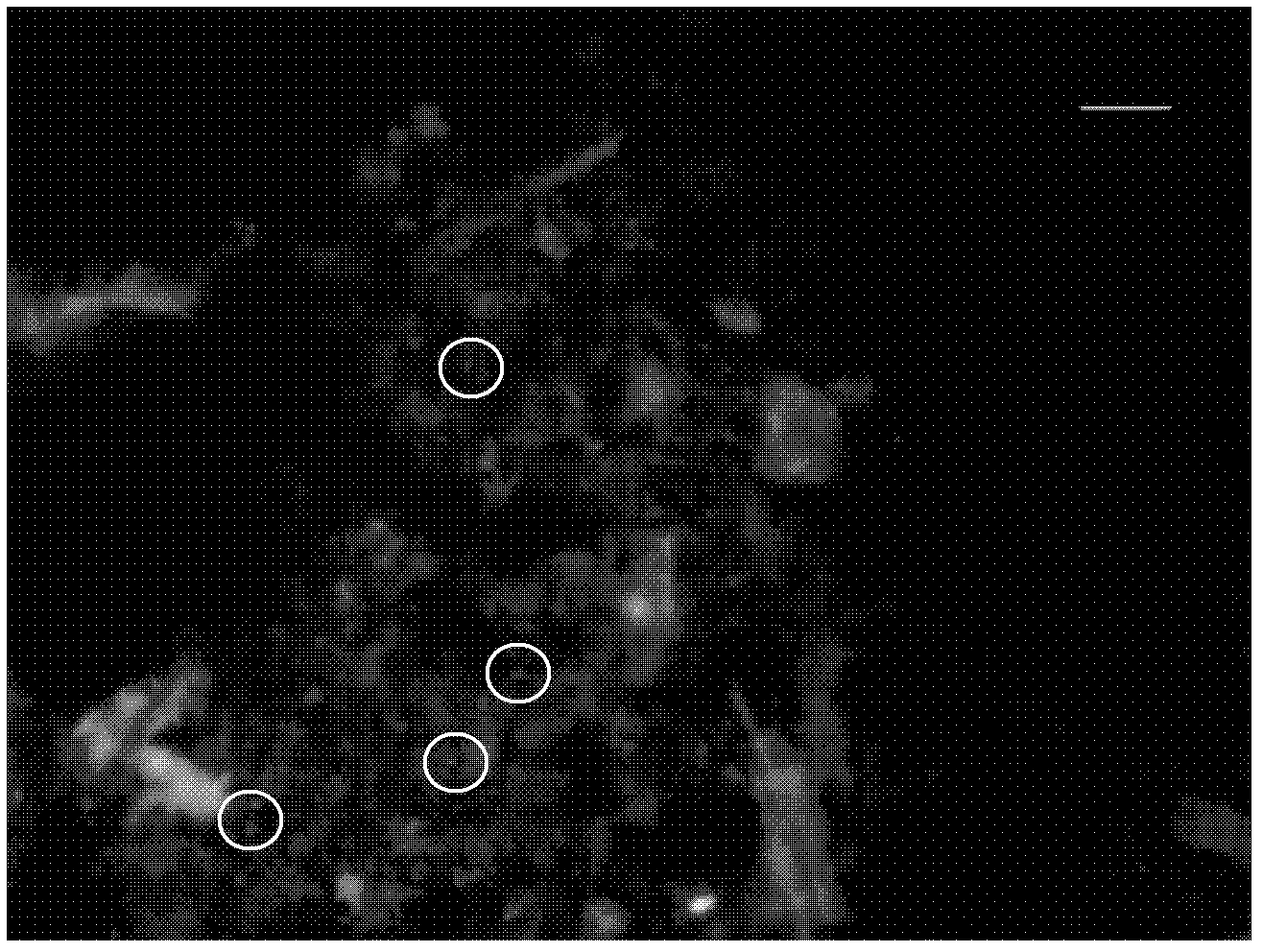
[0070] See figure 2 . The target microorganisms with fluorescence can be clearly observed.
Embodiment 3
[0071] Embodiment 3, adopt the method of the present invention to carry out fluorescence in situ hybridization
[0072] 1. Same as step 1 in Example 1.
[0073] 2. Same as step 2 of embodiment 1.
[0074] 3. Adopt 0.1 mol / L tetrasodium pyrophosphate aqueous solution, incubate in 30° C. water bath for 60 minutes, and other steps are the same as step 3 of embodiment 1.
[0075] 4. Same as step 4 in Example 1.
[0076] 5. Same as Step 5 of Example 1.
[0077] 6. Same as step 6 of embodiment 1.
[0078] 7. Same as Step 7 of Example 1.
[0079] 8. Same as step 8 in Example 1.
[0080] 9. Same as step 9 in Example 1.
[0081] See image 3 . The target microorganisms with fluorescence can be clearly observed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com