Light emitting diode and production method thereof
A technology of light-emitting diodes and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the direction of vacuum evaporation plating, coating, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as difficulties and adjustment of process parameters, and achieve the effects of ensuring adhesion, ensuring stress release, and reducing ohmic contact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
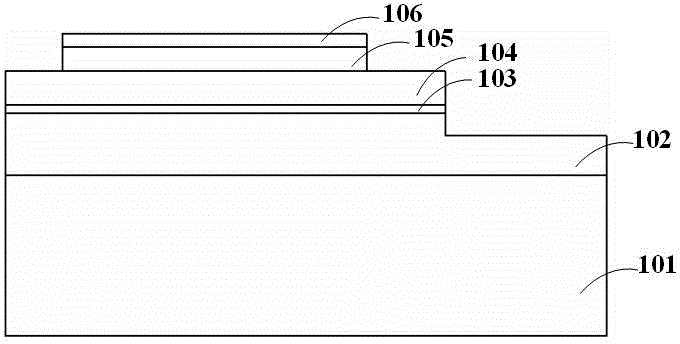
[0037] Such as Figure 6 As shown, a light-emitting diode device with a transparent conductive layer includes: a substrate 101; a light-emitting epitaxial layer, which is stacked from bottom to top with semiconductor material layers of a first confinement layer 102, a light-emitting layer 103 and a second confinement layer 104 formed on the substrate 101; the current blocking layer 105 is formed on the partial area of the second confinement layer 104 of the light-emitting epitaxial layer; the first transparent conductive layer 106 is formed on the current blocking layer 105 , and the contact area between the first transparent conductive layer 106 and the current blocking layer 105 is equal to the upper surface area of the current blocking layer 105; the second transparent conductive layer 107 is coated on the first transparent conductive layer 106 and the current blocking layer 105 and extend to the surface of the second confinement layer 104 of the light-emitting epitaxia...
Embodiment 2
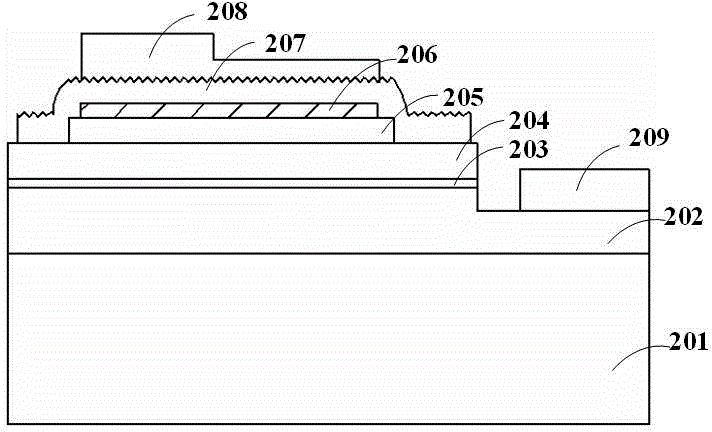
[0045] Such as Figure 12 As shown, another light-emitting diode device with a transparent conductive layer has the same general structure as the light-emitting diode device in Embodiment 1. The difference between the two mainly lies in: the first transparent conductive layer 206 and the current blocking layer of this embodiment The contact area of 205 is smaller than the upper surface area of the current blocking layer 205; the upper surface of the first transparent conductive layer 206 has no roughness.
[0046] Such as Figure 7~12 As shown, another method for manufacturing a light-emitting diode device with a transparent conductive layer is roughly the same as that of the light-emitting diode device in Example 1, the difference mainly lies in: the first transparent conductive layer 206 and the second transparent conductive layer 207 The coating method is different. Specifically:
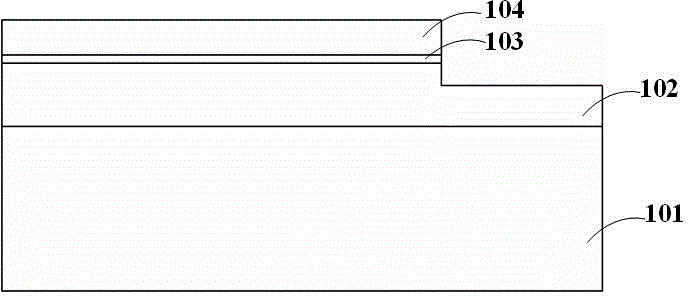
[0047] Such as Figure 7 As shown, a sapphire substrate 201 is provided; a firs...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com