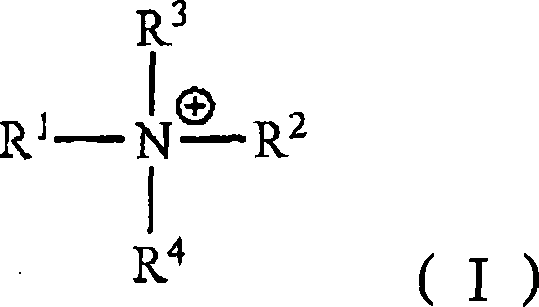Process for producing oxymethylene polymers
A technology of formaldehyde polymers and polymers, which is applied in the field of production of formaldehyde polymers, and can solve problems such as the limitation of formaldehyde removal effectiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0107] Polymerization was carried out in a gastight, pressure-resistant twin-screw extruder with 7 independently adjustable heating zones of approximately equal length. The starting compounds are metered with HPLC pumps and efficiently mixed by static mixing elements in the premix zone before they are delivered to the extruder for polymerization. In the sixth zone, triethylamine is supplied as a passivating agent to quench the reaction.
[0108] Make 4kg / h of trioxane containing 3.5% dioxolane and 1500ppm formal The alkane was mixed with an initiator solution containing trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and a salt formed from triethylamine and trifluoromethanesulfonic acid in a weight ratio of 1:2. The concentration of free triflic acid was 1 ppm based on the monomer feed.
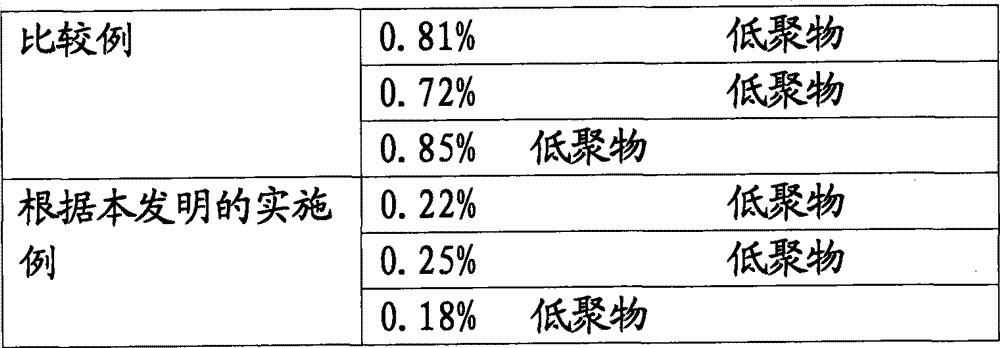
[0109] The temperature profile in the polymer exit is listed in the table below:
[0110] District 1
[0111] The reaction was carried out at 30 bar. Pressure was maintained by a control valve a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com