Preparation method and application antimicrobial liquid
A technology of liquid and antibacterial agent, applied in the field of antibacterial liquid containing charge transport catalyst, can solve the problem of high energy consumption, achieve the effects of low energy consumption, simple fixing process and novel antibacterial mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] First mix the catalyst and dispersant at a ratio of 0.3 g / L, and ultrasonically disperse for 15-30 minutes to obtain an antibacterial liquid, and then disperse it evenly on the surface of ceramic products by dipping-lifting process. Finally heat treatment and drying at 100° C. for 15 minutes to obtain the desired functional ceramic product.
[0030] Preparation of test specimen: Take a piece of the same material as the product to be tested (1.5 cm × 4.0 cm), make an antibacterial coating according to the above process, and use it as a specimen to test the antibacterial performance (the same below).
[0031] Then the counting method was used to analyze the antibacterial properties of the functional ceramics against Escherichia coli (E. coli) (the same below). The specific operations are all aseptic operations, as follows: put the bacteria in the Log phase into LB liquid medium at 37 °C for 2 hours, and then adjust the bacterial concentration to 10 3 cells / ml. Dispersi...
Embodiment 2
[0034] First mix the catalyst and dispersant at a ratio of 0 g / L and ultrasonically disperse for 30 minutes to obtain an antibacterial liquid, and then use a spraying process to evenly disperse it on the surface of the glass product. Finally, heat treatment and drying at 100° C. for 30 minutes to obtain the desired glass.
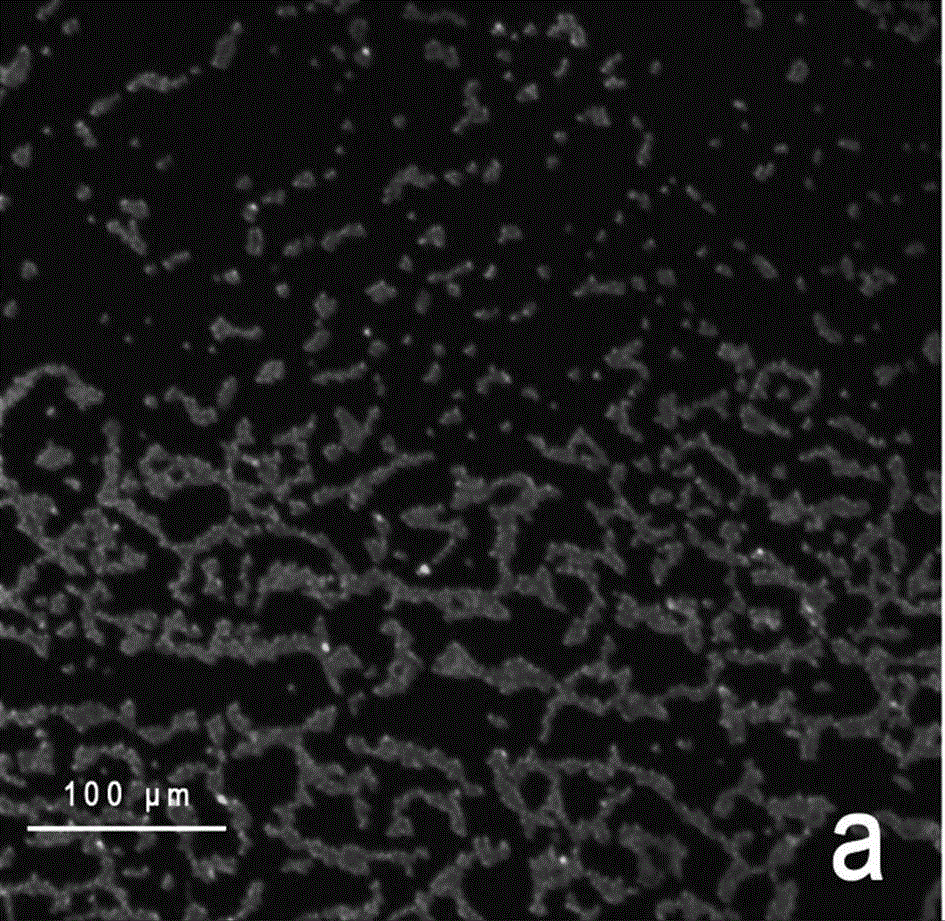
[0035] The effect of glass surface coating on Staphylococcus aureus ( S. aureus ) inhibition of biofilm. From figure 2 and image 3 It can be seen that when the proportion is 0 g / l, the glass surface coating without antibacterial agent has a rough surface, unevenness, and a large amount of bacteria grow.
Embodiment 3
[0037] The functional glass was prepared by the method of Example 2. The difference is that the ratio of catalyst to dispersant is 0.3 g / L.
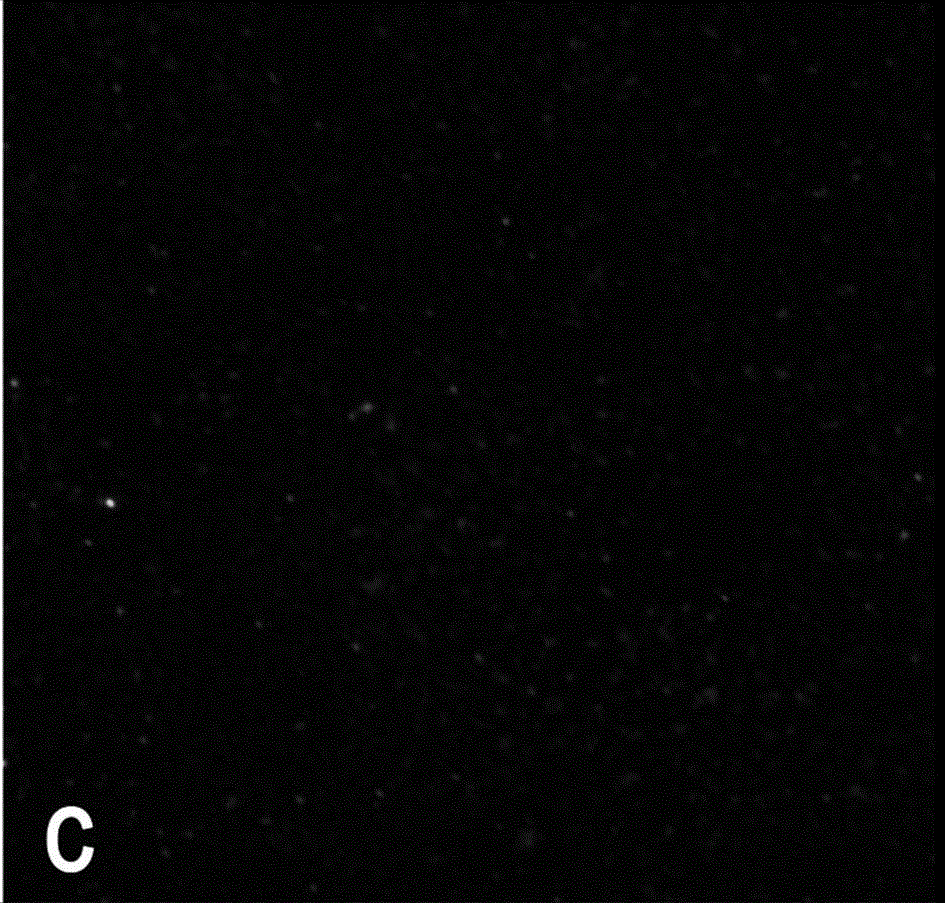
[0038] The effect of glass surface coating on Staphylococcus aureus ( S. aureus ) inhibition of biofilm. From Figure 4 and Figure 5It can be seen that when the proportion is 0.3 g / L, the antibacterial coating of glass has a very smooth surface. This is because the inorganic silicon liquid has good fluidity and can penetrate into the micropores on the surface of the substrate. The two-dimensional and three-dimensional networks formed by its solidification can evenly fix the catalyst particles on the glass surface, which is beneficial to antifouling and antibacterial. Therefore, only a small number of bacteria exist on its surface. This shows that proper control of the ratio of antibacterial liquid can not only improve the antibacterial performance, but also improve the surface finish of the material.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com