Deep hydrodesulfurization method for catalytic gasoline
A technology of catalytic gasoline and deep hydrogenation, which is applied in the fields of hydrotreating process, petroleum industry, and hydrocarbon oil treatment, etc. It can solve the problems of poor adaptability of raw materials and different process flow, so as to reduce investment and operating costs and reduce energy consumption , Reduce equipment investment and operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
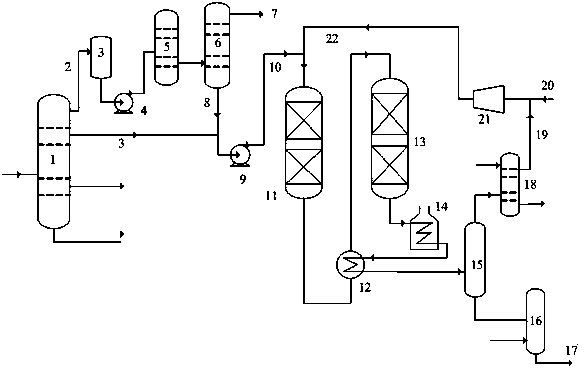
[0037] Gasoline is pre-separated in the fractionation tower of the catalytic cracking unit to obtain light fractions and heavy fractions. The separation temperature of the light fractions and heavy fractions is 73°C; the light fractions are deodorized without alkali, and then enter the hydrogenation pre-fractionation tower for separation. The division temperature of the obtained light gasoline and medium gasoline was 65°C. The prehydrogenation reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 1.8MPa, volume space velocity 3.8 h -1 , The reaction temperature is 178°C; the hydrodesulfurization reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 1.6MPa, volume space velocity 2.8h -1 , The reaction temperature is 282°C; the total hydrogen to oil volume ratio is 350:1.
[0038] The alkali-free deodorization conditions are: the operating pressure of the reactor is 0.6MPa, the reaction temperature is 35°C, and the feed space velocity is 0.9h -1 , the air flow / feed volume ratio is 0...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Gasoline is pre-separated in the fractionation tower of the catalytic cracking unit to obtain light fractions and heavy fractions; the division temperature of the light fractions and heavy fractions is 76°C; the light fractions are deodorized without alkali, and then enter the hydrogenation pre-fractionation tower for separation. The division temperature of the obtained light gasoline and medium gasoline was 62°C. The prehydrogenation reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 2.0 MPa, volume space velocity 3.5 h -1 , The reaction temperature is 183°C; the hydrodesulfurization reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 1.8MPa, volume space velocity 3.0 h -1 , The reaction temperature is 288°C; the total hydrogen to oil volume ratio is 380:1.
[0042] The alkali-free deodorization conditions are: the operating pressure of the reactor is 0.5MPa, the reaction temperature is 45°C, and the feed space velocity is 0.8h -1 , the air flow / feed volume ratio is 0...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Gasoline is pre-separated in the fractionation tower of the catalytic cracking unit to obtain light fractions and heavy fractions; the division temperature of the light fractions and heavy fractions is 80°C; the light fractions are deodorized without alkali, and then enter the hydrogenation pre-fractionation tower for separation. The division temperature of the obtained light gasoline and medium gasoline was 67°C. The prehydrogenation reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 1.8MPa, volume space velocity 4.2 h -1 , Reaction temperature 180℃; hydrodesulfurization reaction conditions: hydrogen partial pressure 1.6MPa, volume space velocity 3.2 h -1 , The reaction temperature is 277°C; the total hydrogen to oil volume ratio is 320:1.
[0046] The conditions for alkali-free deodorization are: the operating pressure of the reactor is 0.5MPa, the reaction temperature is 40°C, and the feed space velocity is 1.1h -1 , the air flow / feed volume ratio is 1.0. The oper...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com