Application of rhamnolipid in serving as printing and dyeing auxiliary
A technology of rhamnolipid and printing and dyeing auxiliaries, which is applied in the fields of dyeing, textiles and papermaking, fiber treatment, etc., can solve the problems that have not been reported on the application of printing and dyeing auxiliaries, reduce the harm to the human body and the environment, and improve the development level , The effect of overcoming green barriers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
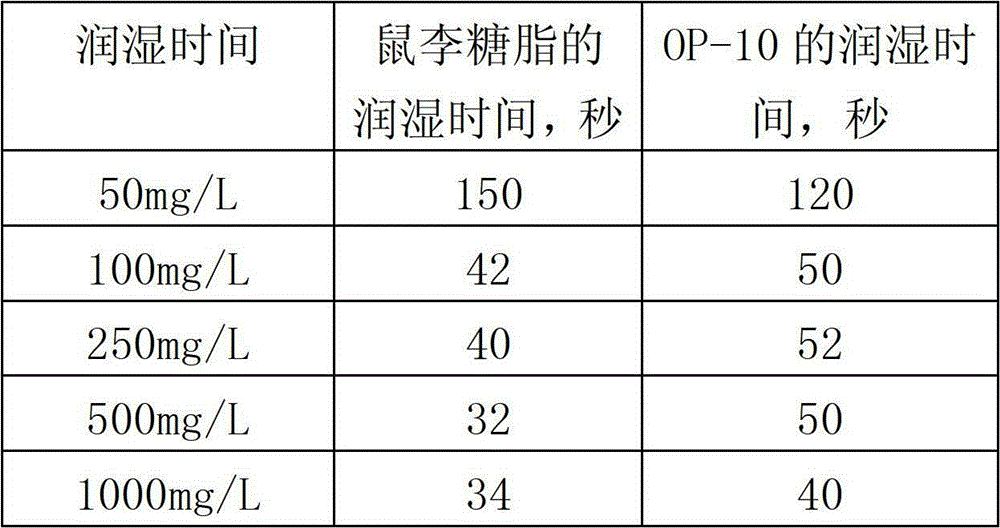
[0018] Embodiment 1: the wetting effect of debacterial body rhamnolipid to fabric
[0019] The rhamnolipid solution is prepared from paste-like rhamnolipid and tap water with a mass percentage of about 85%, and the concentration is 35g / L. Another chemical surfactant for comparison is nonylphenol polyoxyethylene ether ( OP-10). The wetting target is a commercially available cotton gray cloth which is difficult to wet with water. The gray cloth is cut into discs with a diameter of 50 mm, and each disc weighs about 0.43 g. Insert the pin into the canvas test piece at a distance of 2mm from the edge, gently clamp the cotton gray cloth disc with tweezers, place it at the bottom of the center of a 250mL beaker containing 200ml of water with or without surfactant, and start the stopwatch. Initially, the disc floats from the bottom to the top of the test solution, and as the test solution enters the fiber gap and the air bubbles are driven out, the test piece begins to sink. When t...
Embodiment 2
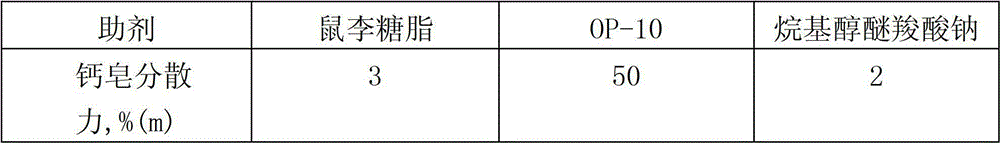
[0023] Embodiment 2: the dispersing action of rhamnolipid to dyestuff
[0024] Calcium soap dispersibility is an important index to characterize the dispersant ability of dispersant, that is, the minimum gram of dispersant that needs to be added to disperse 100g sodium oleate in 3 hard water. First prepare 1000ppm hard water (CaCl2.033g / L, MgSO4.049g / L), use a micropipette to draw 1mL of sodium oleate solution (5g / L) into a 10ml stoppered colorimetric tube, and then add microvolumes of Rhamnolipid solution (200g / l, prepared with 40% mass percentage of concentrated glycolipid), OP-10 solution (100g / L) and sodium alkyl alcohol ether carboxylate (100g / L), add 2mL hard water to each , and then diluted to 6mL with distilled water, vibrated up and down 20 times vigorously and stood for 1min to observe the dispersion state of the calcium soap particles. As the amount of dispersant increases, the amount of calcium soap suspended matter gradually decreases until the calcium soap just ...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Embodiment 3: the retardation effect of rhamnolipid
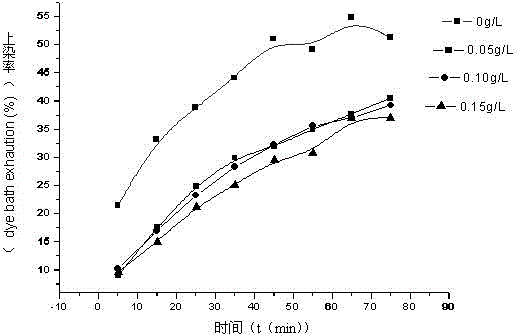
[0029] Drop into 50g fabric at 50 ℃ in the 250ml acid scarlet solution of 0.3% (mass), add or do not add the rhamnolipid solution prepared in Example 2 in advance in this solution so that its final concentration is 0-0.15g / L, Then the temperature was raised to 80°C at a rate of about 1°C / min. Samples are taken every 10 minutes after the fabric is put into the dye solution, and the percentage of dye uptake is determined. Detected uptake rates see figure 1 .
[0030] From figure 1 It can be seen that, compared with the control blank group, rhamnolipid has slow staining effect, and with the increase of concentration, the slow staining effect increases. It can be seen that rhamnolipid has the effect of slowing down the coloring of dyes on fabrics, that is, it has a slowing effect, and the effect is very significant.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com