Organic light emitting diode (OLED) device
A device and structural technology, applied in the field of organic electroluminescence devices, can solve the problems that OLED devices cannot satisfy the requirements of good brightness and long life at the same time, and achieve the effects of wide application range, good service life and improved device life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
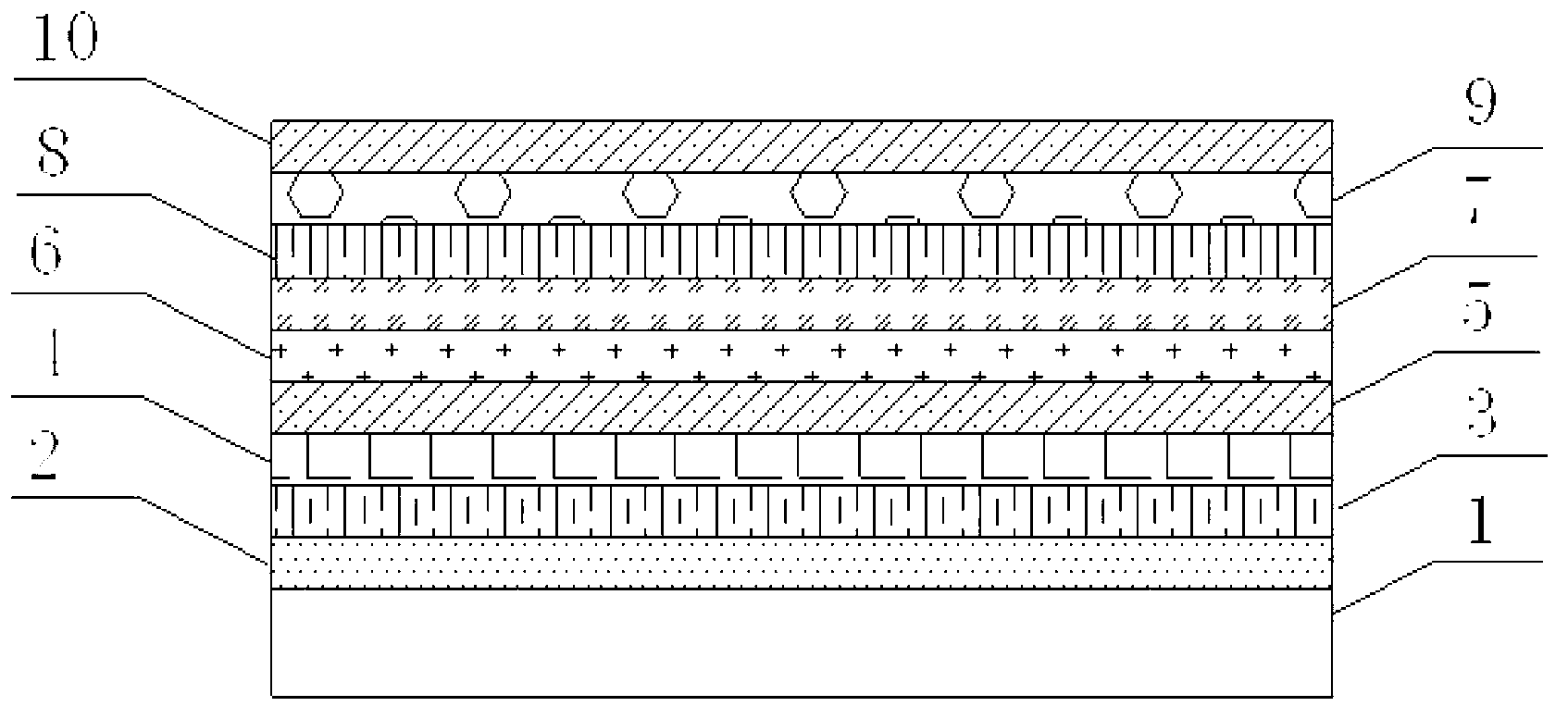
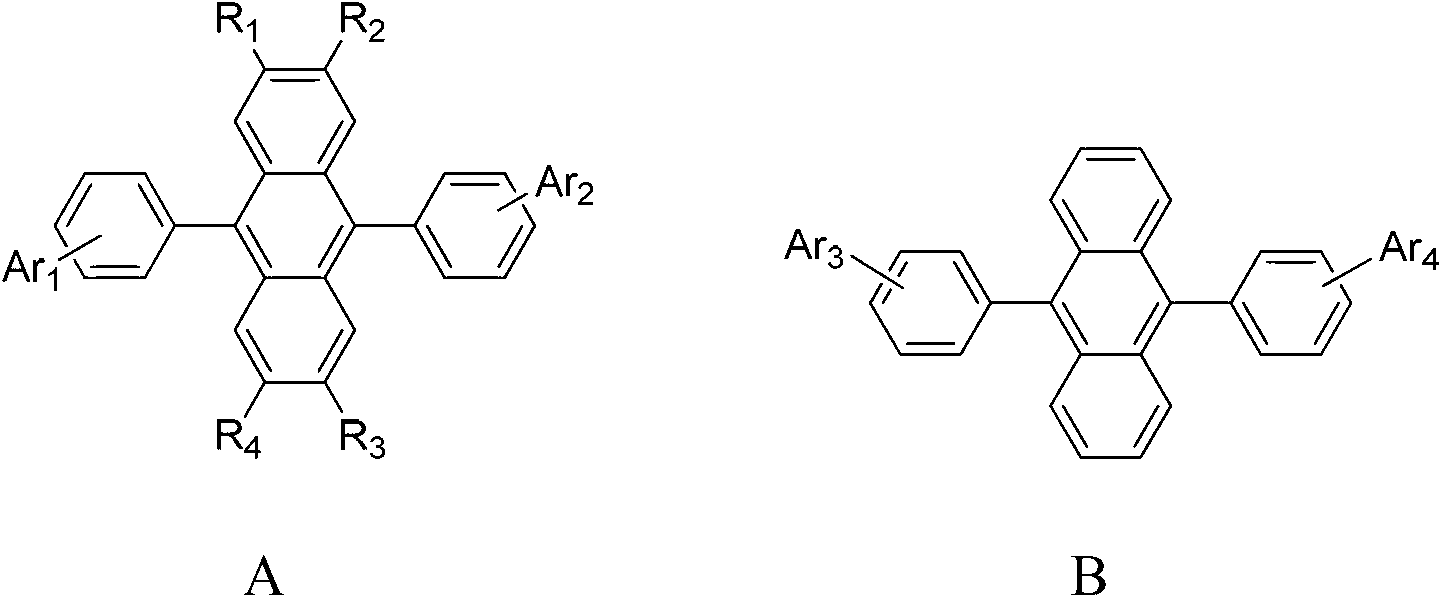
[0057] Red light devices: such as figure 1 As shown, the substrate 1 is a glass substrate. On the substrate 1, Ag is sputtered and deposited as the reflective layer 2 with a thickness of 150nm. ITO of 10nm is sputtered as the anode 3 of the device, and the required pattern is etched out. 3 Plasma treatment for 3 minutes. The resulting substrate 1 was placed in a vacuum, and 130 nm of MTDATA was deposited as a hole injection layer (HIL) 4 by co-evaporation. Next, 10 nm of NPB was deposited as a hole transport layer (HTL) 5 . Then take the compound shown in A1 and the compound shown in B1 according to the mass ratio of 1:1 and mix to obtain the required host material, and add the guest material Ir(piq) which accounts for 5% of the host material by mass 2 (acac), using a double-source co-evaporation method, preheating the two in the evaporation source under a vacuum environment, and vapor-depositing them on the substrate to prepare the light-emitting layer with a thickness of 3...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The structure and specific implementation steps of the OLED device described in this example are the same as those of the red light device in Example 1, the only difference being that the host material is composed of the compound shown in formula A2 and the compound shown in formula B3 in a mass ratio of 5:10 mix.
Embodiment 3
[0065] The structure and specific implementation steps of the OLED device described in this example are the same as those of the red light device in Example 1, the only difference being that the host material is composed of the compound shown in formula A3 and the compound shown in formula B4 in a mass ratio of 6:10 mix.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com