Method for recovering metal by use of APT (ammonium paratungstate) waste slag
A waste slag and metal technology, applied in the field of resource recovery and reuse, can solve the problems of resin poisoning, increase labor intensity, waste copper and tungsten, etc., and achieve the effects of improving economic efficiency, reducing resource waste and improving utilization rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
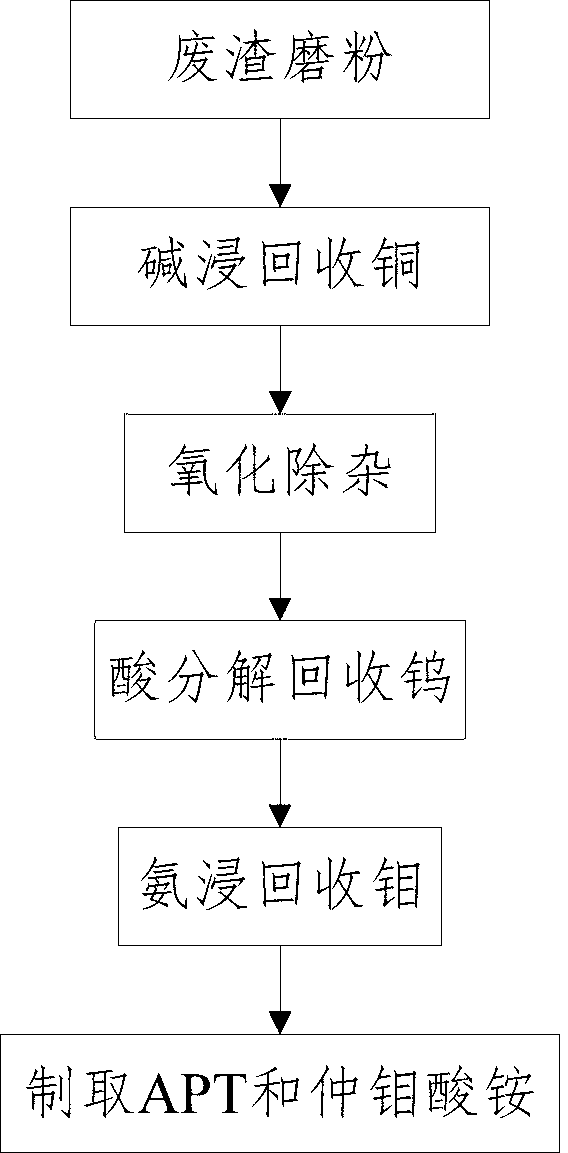
[0028] A kind of method utilizing APT waste slag to recover metal, its steps are as follows:
[0029] a. Waste residue grinding: take 100kg of waste residue, of which WO 3 The content is 6%, the Mo content is 15%, and the Cu content is 24%. The waste residue containing copper, tungsten and molybdenum produced in the production process of ammonium paratungstate is ground to -325 mesh ≥ 90%;
[0030] b. Recovering copper by alkali leaching: filter the waste slag in step a with a water softening material with a pH value of 7.5 to separate the slag containing copper from the filtrate containing tungsten and molybdenum, and leave the filtrate containing tungsten and molybdenum until the next step. The slag material that contains copper carries out alkali boiling leaching, and wherein alkali is NaOH, and when the concentration of alkali is in 35g / L scope, stop adding alkali, boil and keep warm for 1.5h, obtain copper sulfide 23.11kg after washing, in this step Cu The recovery rate ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A kind of method utilizing APT waste slag to recover metal, its steps are as follows:
[0037] a. Waste residue grinding: take 100kg of waste residue, of which WO 3 The content is 6%, the Mo content is 15%, and the Cu content is 24%. The waste residue containing copper, tungsten and molybdenum produced in the production process of ammonium paratungstate is ground to -325 mesh ≥ 90%;
[0038]b. Copper recovery by alkali leaching: filter the waste slag in step a with a softening material with a pH value of 8.5, filter the slag containing copper and the filtrate containing tungsten and molybdenum, and leave the filtrate containing tungsten and molybdenum until the next step. The slag material that contains copper carries out alkali boiling leaching, and wherein alkali is NaOH, when the concentration of alkali is in 45g / L scope, stop adding alkali, boil and keep warm for 2.5h, obtain copper sulfide 23.472kg after washing, in this step Cu The recovery rate is 97.8%;
[003...
Embodiment 3
[0044] A kind of method utilizing APT waste slag to recover metal, its steps are as follows:
[0045] a. Waste residue grinding: take 100kg of waste residue, of which WO 3 The content is 6%, the Mo content is 15%, and the Cu content is 24%. The waste residue containing copper, tungsten and molybdenum produced in the production process of ammonium paratungstate is ground to -325 mesh ≥ 90%;
[0046] b. Copper recovery by alkali leaching: filter the waste slag in step a with a demineralized material with a pH value of 8.0 to separate the slag containing copper from the filtrate containing tungsten and molybdenum, and leave the filtrate containing tungsten and molybdenum until the next step. The slag material that contains copper carries out alkali boiling leaching, and wherein alkali is NaOH, when the concentration of alkali is in 40g / L scope, stop adding alkali, boil and keep warm 2.0h, obtain copper sulfide 23.352kg after washing, in this step Cu The recovery rate is 97.3%; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com