Electromagnetic force actuator for active support of astronomical telescope mirror face
A technology of astronomical telescopes and force actuators, applied in telescopes, instruments, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as reduced reliability, application limitations, and complex mechanical structures, and achieve coil power supply voltage reduction, output capability improvement, and high control accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
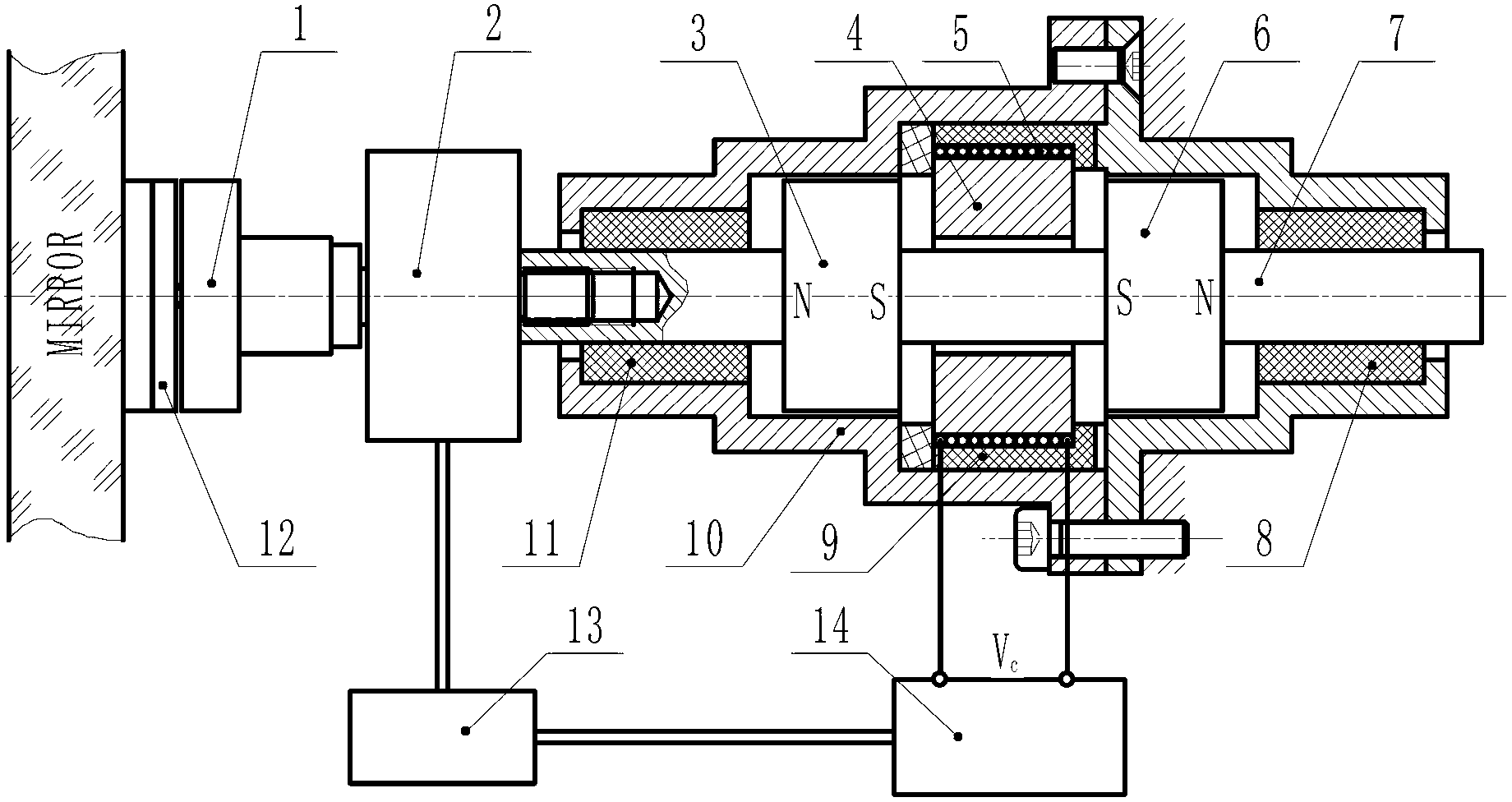
[0020] Embodiment 1, the electromagnetic force actuator structure is as figure 1 Shown. The second permanent magnet 3 and the third permanent magnet 6 are fixed on the shaft 7, and the two permanent magnets are opposite to each other with the same pole. The two ends of the shaft 7 are supported by low-friction materials 8, 11, and the left end of the shaft is connected to the force sensor 2 and connected to the mirror support pad 12 through the first permanent magnet 1. The support pad 12 is fixed to the bottom surface of the mirror by glueing. The coil 5 and the iron core 4 are installed and fixed in the housing 10 through an insulating material 9. When the coil 5 is not energized, the iron core 4 is under the combined action of the permanent magnets 6 and 7 on both sides and is in a balanced state. At this time, the force of the force actuator on the mirror surface is zero. When the coil 5 is energized, the coil 5 and the iron core 4 generate two magnetic poles. If a magnet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com