Method for on-line synthesizing glucose-6-palmitate by lipase catalysis
A technology of palmitate and glucose, which is applied in the field of lipase-catalyzed online controllable selective synthesis of glucose-6-palmitate, which can solve the problems of low conversion rate and selectivity, long reaction time, etc., and shorten the reaction time , reduced usage, high conversion and reaction selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
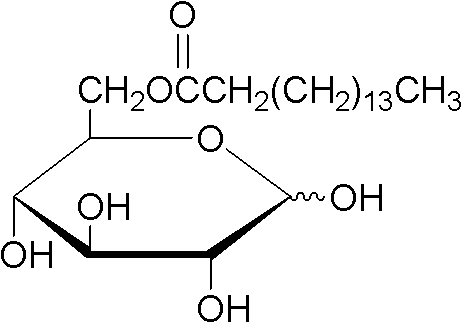
[0027] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of glucose-6-palmitate
[0028]
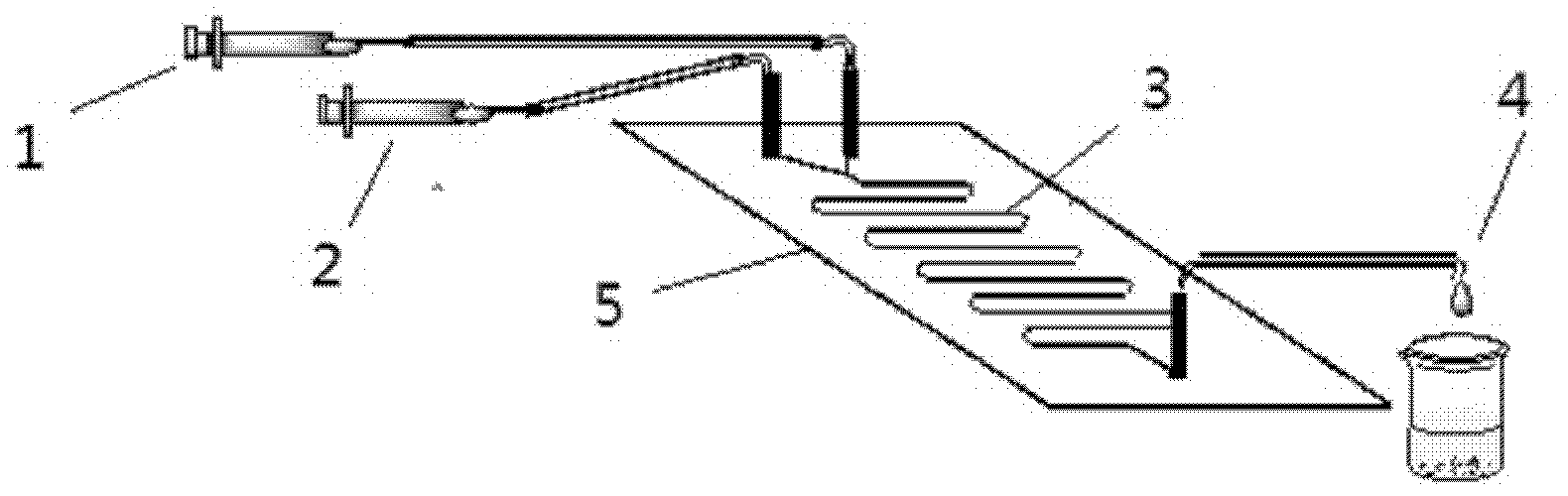
[0029] device reference figure 1 : Glucose (0.4mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of tert-amyl alcohol: DMSO=4:1 (v / v) mixed solvent, vinyl palmitate (2.0mmol) was dissolved in 10mL of tert-amyl alcohol, and then packed in 10mL Ready to use in the syringe. 0.87g of lipase Lipozyme TLIM was evenly filled in the reaction channel, driven by the PHD2000 syringe pump, the two reaction solutions were separated at 10.4 μL min -1 The flow rate enters the reaction channel through the "Y" joint for reaction, and the temperature of the reactor is controlled at 52°C by a water bath thermostat. The reaction solution flows continuously in the reaction channel for 30 minutes, and the reaction results are tracked and detected by thin-layer chromatography (TLC).
[0030] The reaction solution was collected online by the product collector, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the column was wet-packed with 2...
Embodiment 2-5
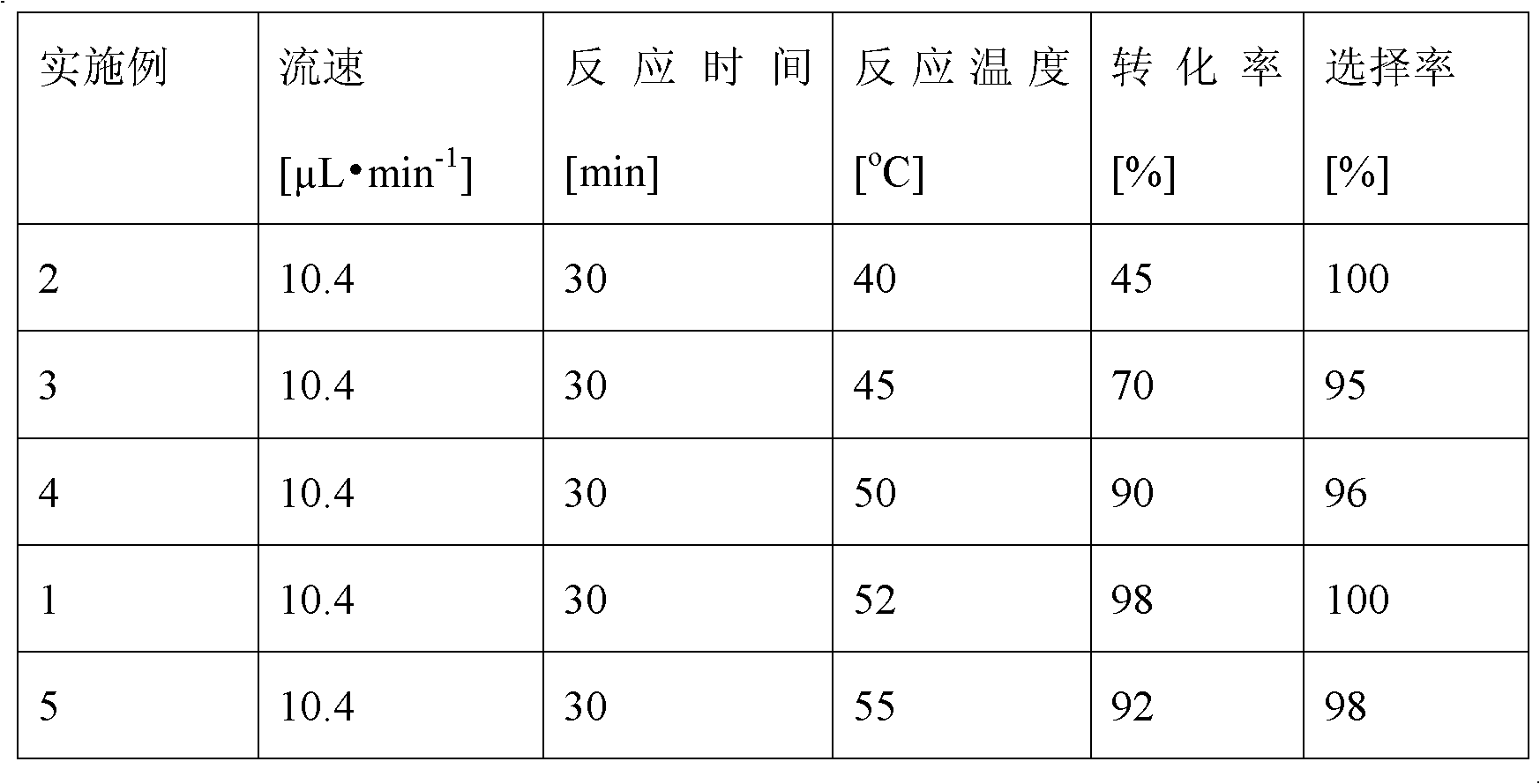
[0034] Change the temperature of the microfluidic channel reactor, others are the same as in Example 1, and the reaction results are as shown in Table 1:
[0035] Table 1: Effect of Temperature on Reaction
[0036]
[0037] The results in Table 1 show that when the flow rate is 10.4 μL min -1 , when the reaction time is 30min, the conversion rate increases obviously with the increase of the reaction temperature. When the reaction temperature reaches 52°C, the conversion rate and selectivity of the reaction are the best. The reduction in enzyme activity leads to a reduction in the conversion rate and selectivity of the reaction, so the optimum reaction temperature of glucose palmitate in the microfluidic microchannel reactor in the present invention is 52°C.
Embodiment 6-10
[0039] Change the substrate ratio of vinyl palmitate and glucose in the microfluidic microchannel reactor to be 3: 1 (Example 6), 4: 1 (Example 7), 6: 1 (Example 8), 7: 1 (Example 9), 8:1 (Example 10), others are the same as Example 1, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0040] Table 2: Effect of glucose to vinyl palmitate substrate ratio on the reaction
[0041] Example
[0042] 8
[0043] The result of table 2 shows, along with the increase of reactant vinyl palmitate, the conversion rate of reaction also thereupon increases, and when substrate ratio is 5: 1, the conversion rate of reaction and selectivity are optimal, and glucose has basically been quantified Complete conversion to glucose-6-palmitate. Now if continue to increase the consumption of reactant vinyl palmitate, will cause the conversion rate of reaction and selectivity to reduce, thereby, the optimum substrate ratio of this reaction is 5: 1, under this reaction condition, glucose is q...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com