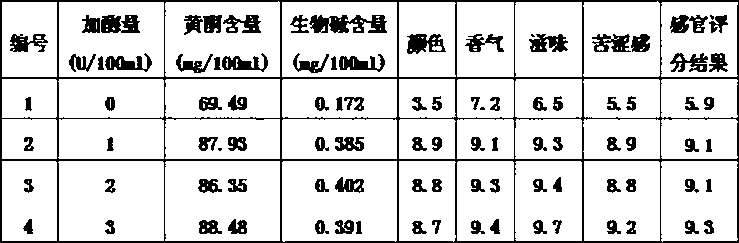
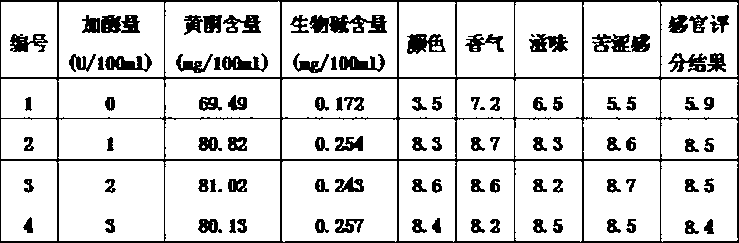
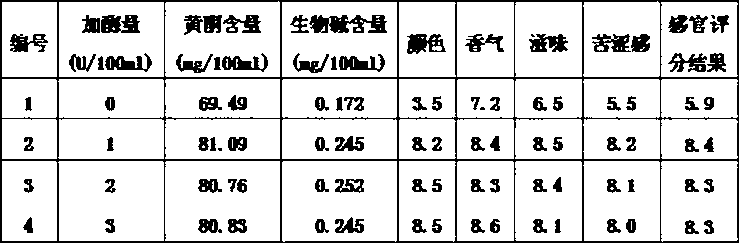
Method for producing aroma enhanced and bitter removed lotus leaf beverage through enzymolysis
The technology of lotus leaf and enzymatic method is applied in the field of plant extraction and plant beverage production to achieve the effects of good smell, long fragrance, and increase of flavonoid content and alkaloid content.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0040] Preparation Example 1: Preparation of phthalic acid-hydrochloric acid buffer
[0041] Measure 5 ml of 0.2 mol / L phthalic acid aqueous solution and 4.070 ml of 0.2 mol / L HCl aqueous solution, mix them, and then dilute to 20 ml with water to obtain a phthalic acid-hydrochloric acid buffer solution with a pH of 2.2.
[0042] Replace the volume of the above 4.07 ml of 0.2 mol / L HCl solution with 3.960 ml, 3.295 ml, 2.642 ml, 2.022 ml, 1.470 ml, 0.990 ml, 0.597 ml, 0.263 ml, respectively, so that the pH is 2.4, 2.6, 2.8 respectively , 3.0, 3.2, 3.4, 3.6 and 3.8 buffer solutions.
preparation example 2
[0043] Preparation Example 2: Extraction of β-glucosidase
[0044] Weigh 9 parts of lotus seeds with the same weight, add polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) with a mass ratio of 1:5 to the lotus seeds, and then add the above-mentioned phthalic acid-hydrochloric acid buffer with a pH of 2.2-3.8 pre-cooled to 4°C solution (9 parts in total), the mass ratio of which to lotus seeds was 1:8, ground into a slurry on an ice bath, centrifuged at 11,000 rpm for 7 minutes at 5°C, and the supernatant was taken, and the same buffer solution was used to dilute to 50 mL, that is, The crude enzyme solution obtained is respectively numbered 1-9, that is, number 1 corresponds to the crude enzyme solution obtained from the pH 2.2 buffer solution, number 2 corresponds to the crude enzyme solution obtained from the pH 2.4 buffer solution, and number 3 corresponds to the obtained crude enzyme solution from the pH 2.6 buffer solution. No. 4 corresponds to the crude enzyme solution obtained from pH 2...
preparation example 3
[0045] Preparation Example 3: Separation and Purification of β-Glucosidase
[0046] According to the method in Zhang Liang (" lotus seed β-glucosidase characteristics and its research on the aroma-enhancing effect of lotus leaf beverage", "Master's Thesis of Huazhong Agricultural University", 2008), the crude enzyme liquid of above-mentioned numbering 1-9 Separation and purification were carried out under the following conditions: the range of ammonium sulfate salting-out was 50-70% saturation, DEAE-5 cellulose was selected for ion exchange column chromatography, and then purified by Sephadex G-100. The specific enzyme activity of the purified β-glucosidase obtained by each number is higher than 965.03 × 10 -3 U / mg
[0047] Enzyme activity test
[0048] According to Zhang Liang ("the characteristics of lotus seed β-glucosidase and its research on the aroma-enhancing effect of lotus leaf beverage", "Master's Thesis of Huazhong Agricultural University", 2008) the test met...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com