Ferrum oxyhydroxide and ferrum oxide hierarchical nanostructured material, preparation methods and applications thereof
A technology of nanomaterials and iron oxides, which is applied in the field of iron oxyhydroxide and iron oxide hierarchical nanostructure materials and their preparation and application, can solve problems such as application difficulties, and achieve large application prospects, high specific surface area, and good removal The effect of the ability of organic pollutants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0029] The preparation method of iron oxyhydroxides and oxide nanomaterials having a sea urchin-like three-dimensional self-assembled hierarchical structure includes the following steps:
[0030] a) mixing sulfur-saturated alcoholic organic solvent and iron salt aqueous solution, and stirring rapidly to obtain a mixed colloidal suspension of iron salt and sulfur;
[0031] b) at a certain temperature, ultrasonic treatment with a certain power for a period of time to obtain a mixed colloidal dispersion of iron oxyhydroxide and sulfur;
[0032] c) centrifuging the above-mentioned dispersion liquid, and obtaining the iron oxyhydroxide nanomaterial of the present invention after repeated washing and drying;
[0033] d) calcining the above-mentioned iron oxyhydroxide nanomaterial to obtain the iron oxide nanomaterial of the present invention.
[0034] Iron oxides are obtained by calcining iron oxyhydroxides. Specifically, in a muffle furnace, heat from room temperature to 400-450°C...
Embodiment 1
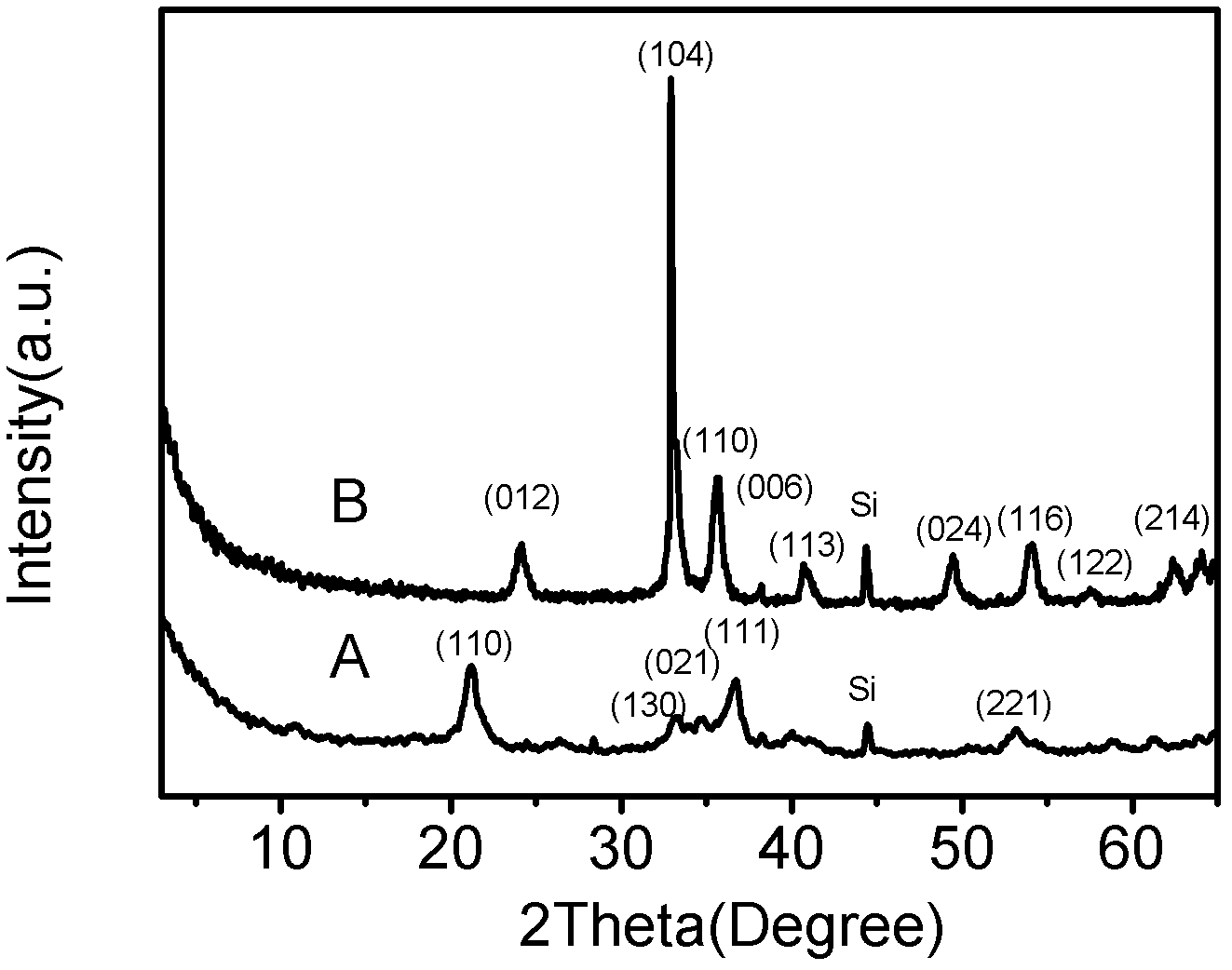
[0039] 2.78 g of ferrous sulfate hexahydrate was dissolved in 50 mL of double distilled water. Add 50 mL of saturated solution of sublimed thioethanol quickly. Sonicate at 70°C for 60 minutes (power 80w). After cooling to room temperature, the sulfur was removed by six times of centrifugal water washing and centrifugal ethanol washing respectively, and dried at 25° C. to obtain α-FeOOH nanomaterials. Then place the obtained α-FeOOH nanomaterials in a muffle furnace, raise the temperature from room temperature to 450°C at a rate of 50°C / min in an air atmosphere, keep the temperature for 4 hours, and cool naturally to obtain red α-Fe 2 o 3 nanomaterials.
[0040] figure 1 The SEM and TEM images of different magnifications representatively represent the as-prepared α-FeOOH nanomaterials. from figure 1 It can be seen from A and 1B that most of the prepared iron oxyhydroxide nanomaterials are urchin-like. Specifically, they are three-dimensional hierarchical nanostructures c...
Embodiment 2
[0042] 5 g of ammonium ferrous sulfate hexahydrate was dissolved in 50 mL of double distilled water. 60 mL of a saturated solution of settled thioethanol was quickly added thereto. Sonicate at 60°C for 20 minutes (power 90w). After cooling to room temperature, the sulfur was removed by six times of centrifugal washing with water and centrifugal ethanol, and dried at 30° C. to obtain α-FeOOH nanomaterials. Then the obtained α-FeOOH nanomaterials were placed in a muffle furnace, and the temperature was raised from room temperature to 400°C at a rate of 45°C / min in an air atmosphere. After 6 hours of heat preservation, the red α-Fe 2 o 3 nanomaterials. Its morphology features are similar to the iron oxyhydroxide and iron oxide nanomaterials in Example 1, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com