Preparation process of crack-free zirconium alloys
A preparation process and zirconium alloy technology, which is applied in the field of preparation process of crack-free deuterium storage zirconium alloy, can solve the problems such as difficult preparation of deuterium (hydrogen) zirconium
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
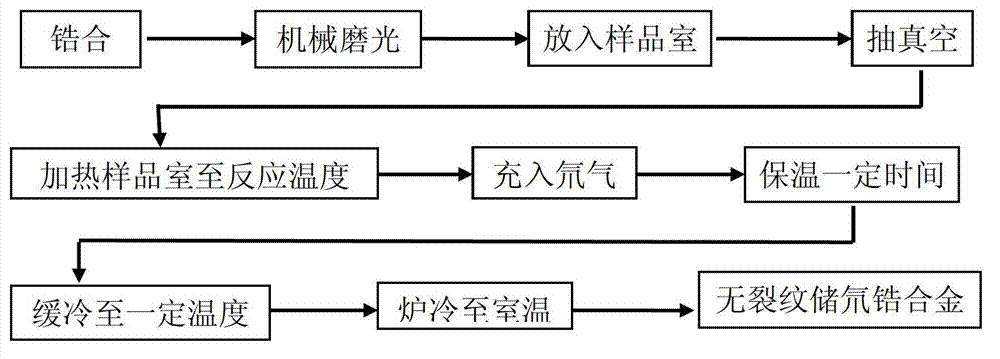
[0029] The atomic level pure zirconium will be processed into a small disc with a diameter of 8mm and a thickness of 1mm, smoothed on sandpaper, and cleaned with absolute ethanol. After the sample is placed in the sample chamber, the sample chamber is evacuated to 10 -3 Pa. After the sample chamber is heated to the reaction temperature of 950°C, it is filled with 0.04 atm deuterium gas to carry out the deuterium absorption reaction. After 20 minutes of heat preservation, the temperature was lowered at a rate of 0.5°C / min, and the furnace was cooled to room temperature after falling to a certain temperature of 500°C, and the samples were taken out to obtain a crack-free deuterium storage zirconium alloy with a deuterium storage content of 2.7% (mass%).
Embodiment 2
[0031] Process Zr-2 into a small disc with a diameter of 8 mm and a thickness of 1 mm, smooth it on sandpaper, and clean it with absolute ethanol. After the sample is placed in the sample chamber, the sample chamber is evacuated to 10 -3 Pa. After the sample chamber is heated to a reaction temperature of 900°C, it is filled with 1 atm of deuterium gas to carry out deuterium absorption reaction. After 30 minutes of heat preservation, the temperature was lowered at a rate of 0.5°C / min, and then furnace cooled to room temperature after falling to a certain temperature of 500°C, and the samples were taken out to obtain a crack-free deuterium-storing zirconium alloy with a deuterium storage capacity of 3.5 (mass%).
Embodiment 3
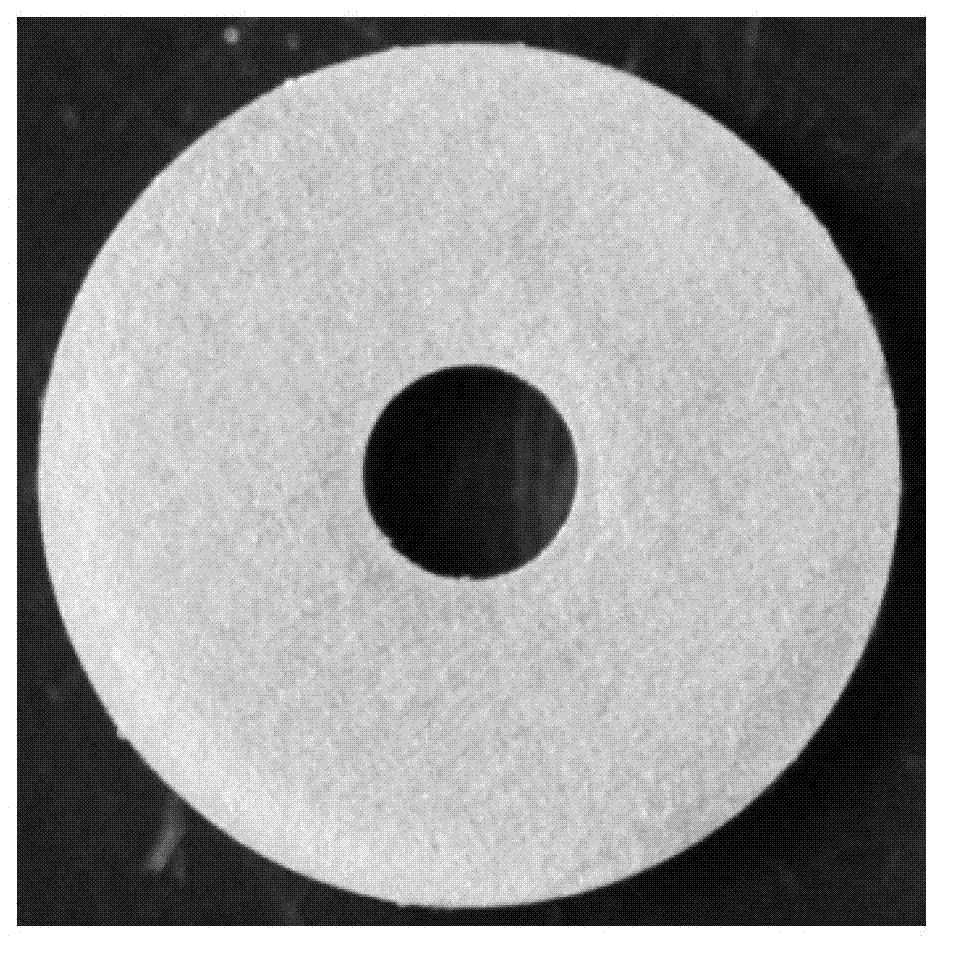
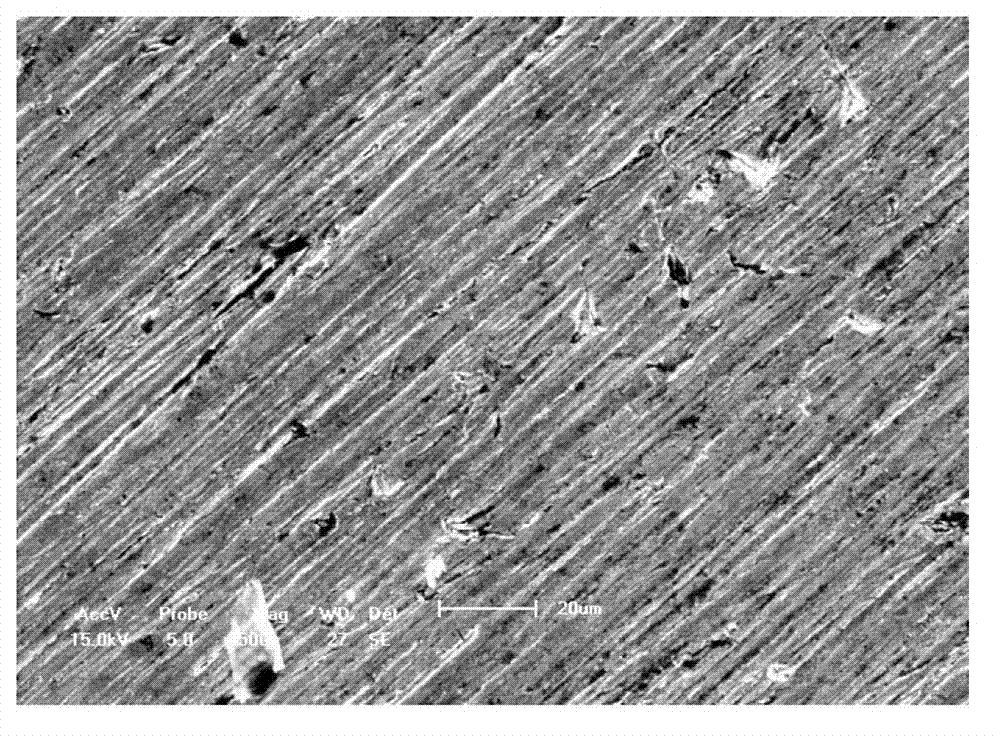
[0033] Process Zr-4 into a small disc with a diameter of 8 mm and a thickness of 1 mm, smooth it on sandpaper, and clean it with absolute ethanol. After the sample is placed in the sample chamber, the sample chamber is evacuated to 10 -3 Pa. After the sample chamber is heated to a reaction temperature of 850°C, it is filled with 2 atm deuterium gas to carry out deuterium absorption reaction. After 40 minutes of heat preservation, the temperature was lowered at a rate of 1°C / min, and the furnace was cooled to room temperature after falling to a certain temperature of 500°C, and the sample was taken out to obtain a crack-free deuterium-storing zirconium alloy with a deuterium storage capacity of 4.0% (mass%). figure 2 A low-magnification schematic diagram of the alloy, image 3 SEM schematic at 500X.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com