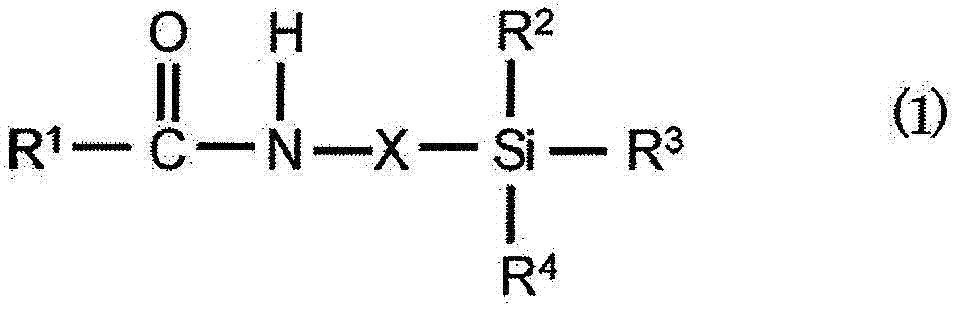Resin compositions for light-scattering layer, light-scattering layer and organic electro luminescence device
An electroluminescent device and resin composition technology, which are applied to optomechanical equipment, photosensitive materials for optomechanical equipment, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of inability to extract, lose light, and insufficient light extraction efficiency, and achieve wavelength dependence. The effect of low performance and high light extraction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
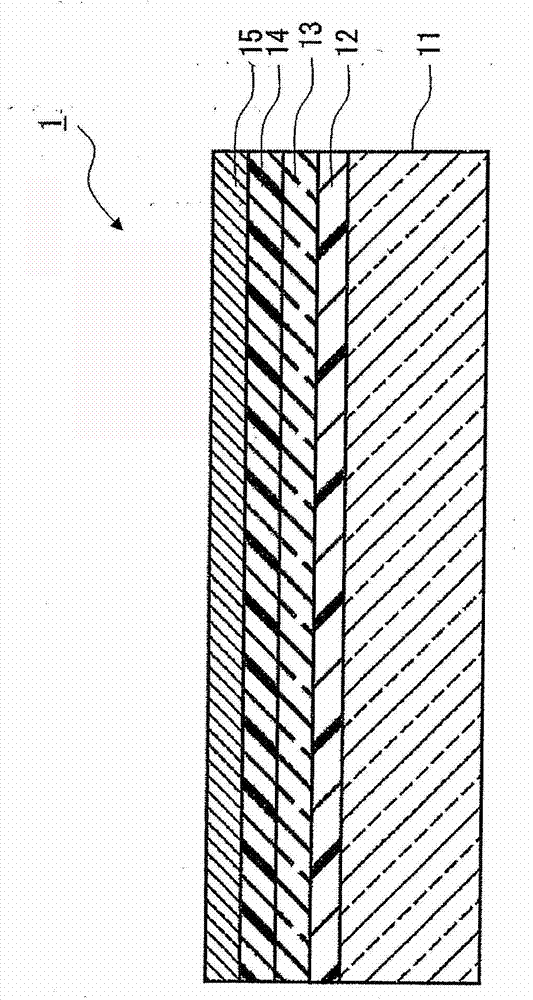
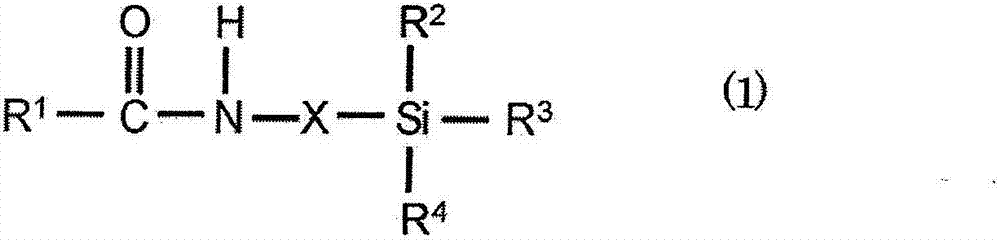
Image
Examples
manufacture example 1-1~1-22
[0337] [Manufacturing Examples 1-1 to 1-22, Examples 1-1 to 1-29, Comparative Examples 1-1 to 1-4]
[0338] (1-1) Preparation of resin (A) solution
manufacture example 1-1
[0340] Process 1:
[0341] 100 parts of PGMEA (propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate: propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate) was added as a solvent to a reaction container equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer, a titration device, a reflux condenser, and a gas introduction tube. It heated to 80 degreeC, injecting nitrogen into this container. Keeping the temperature, add dropwise 5.0 parts of styrene (St), 15.9 parts of cyclohexyl methacrylate (CHMA), 31.7 parts of methacrylic acid (MAA), and 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile 3.0 parts of the mixture and subjected to polymerization. After completion of the titration, it was further reacted at 70° C. for 3 hours, then what dissolved 0.5 part of azobisisobutyronitrile in 40 parts of PGMEA was added, and stirring was continued at the same temperature for 3 hours to obtain a copolymer.
[0342] Process 2:
[0343] Next, dry air was introduced into the reaction vessel, and 50.0 parts of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA), 37.0 parts...
manufacture example 1-2~1-10
[0346] Resin solutions (A1-2) to (A1-10) were obtained in the same manner as in Production Example 1-1 except that the reaction conditions (composition to be charged and reaction temperature) were changed to those shown in Table 1.
[0347] 【Table 1】
[0348]
[0349] Each abbreviation in Table 1 is explained below.
[0350] PGMEA: Propylene Glycol Monomethyl Ether Acetate,
[0351] DCPMA: dicyclopentyl methyl methacrylate,
[0352] CHMA: cyclohexyl methyl methacrylate,
[0353] St: Styrene,
[0354] M-110: p-cumylphenol ethylene oxide modified acrylate,
[0355] HEMA: Hydroxyethyl methacrylate,
[0356] MAA: methacrylic acid,
[0357] GMA: glycidyl methyl methacrylate,
[0358] MMA: methyl methacrylate.
[0359] The unit of the compounding quantity in Table 1 is "part".
[0360] (1-2) Preparation of light-scattering particle (B) dispersion
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com