Metallurgical method for refining grains of steel by modifying inclusions through addition of magnesium and aluminum
A technology of thinning steel and smelting methods, applied in the field of iron and steel smelting, can solve the problems of limited performance improvement, high operating cost, and no more than 20%
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] In order to better understand the purpose, features and advantages of the present invention, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
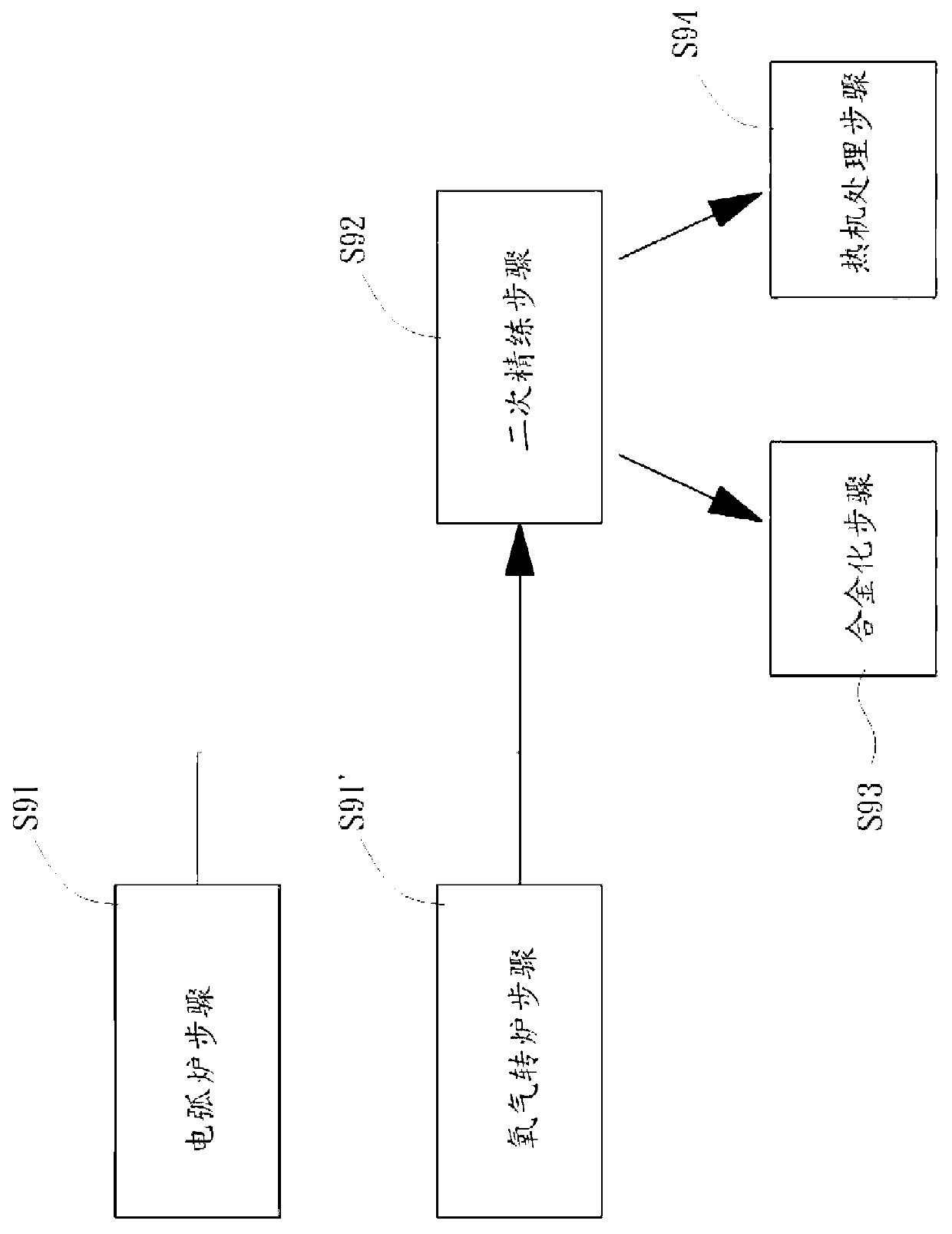
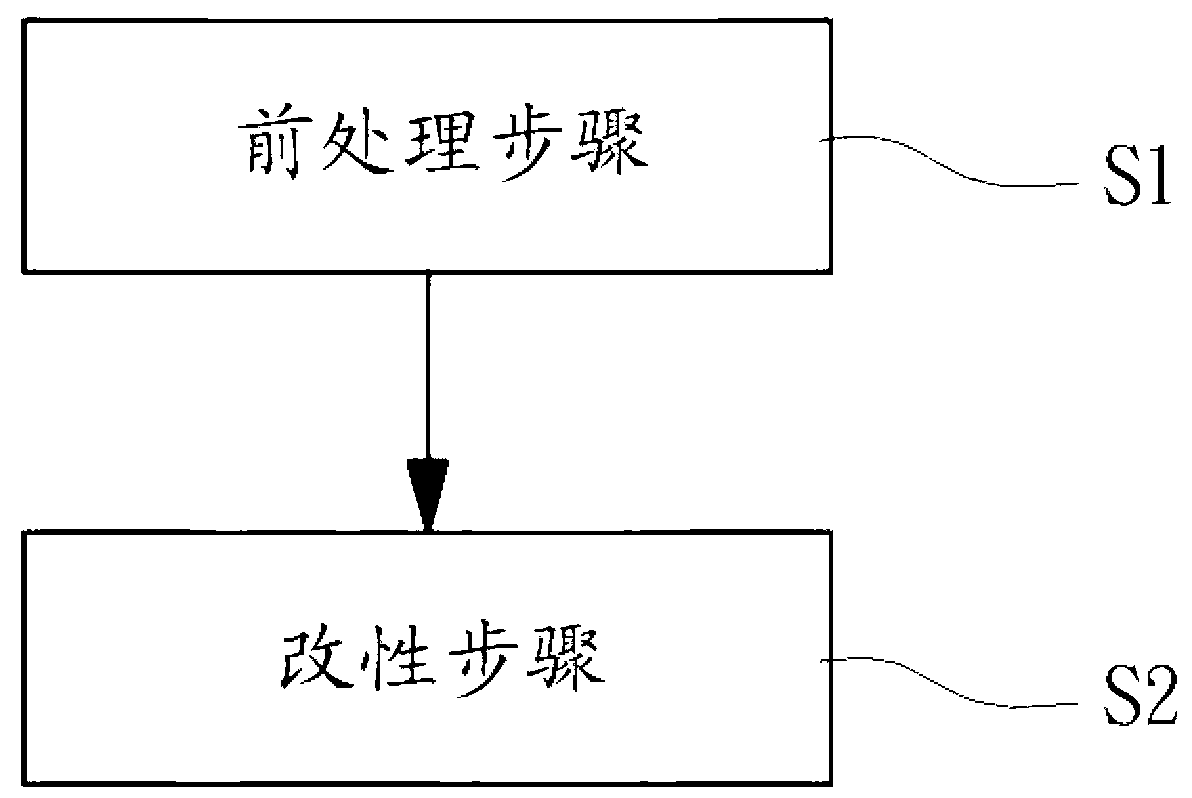
[0028] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a preferred embodiment of the present invention. The smelting method for refining steel grains with magnesium-aluminum modified inclusions includes a pretreatment step S1 and a modification step S2. Among them, the smelting method of the present invention uses magnesium-aluminum modified inclusions to refine steel grains, and is used to process the molten steel produced by secondary refining. The molten steel after scouring and tapping is the so-called molten steel with high cleanliness.
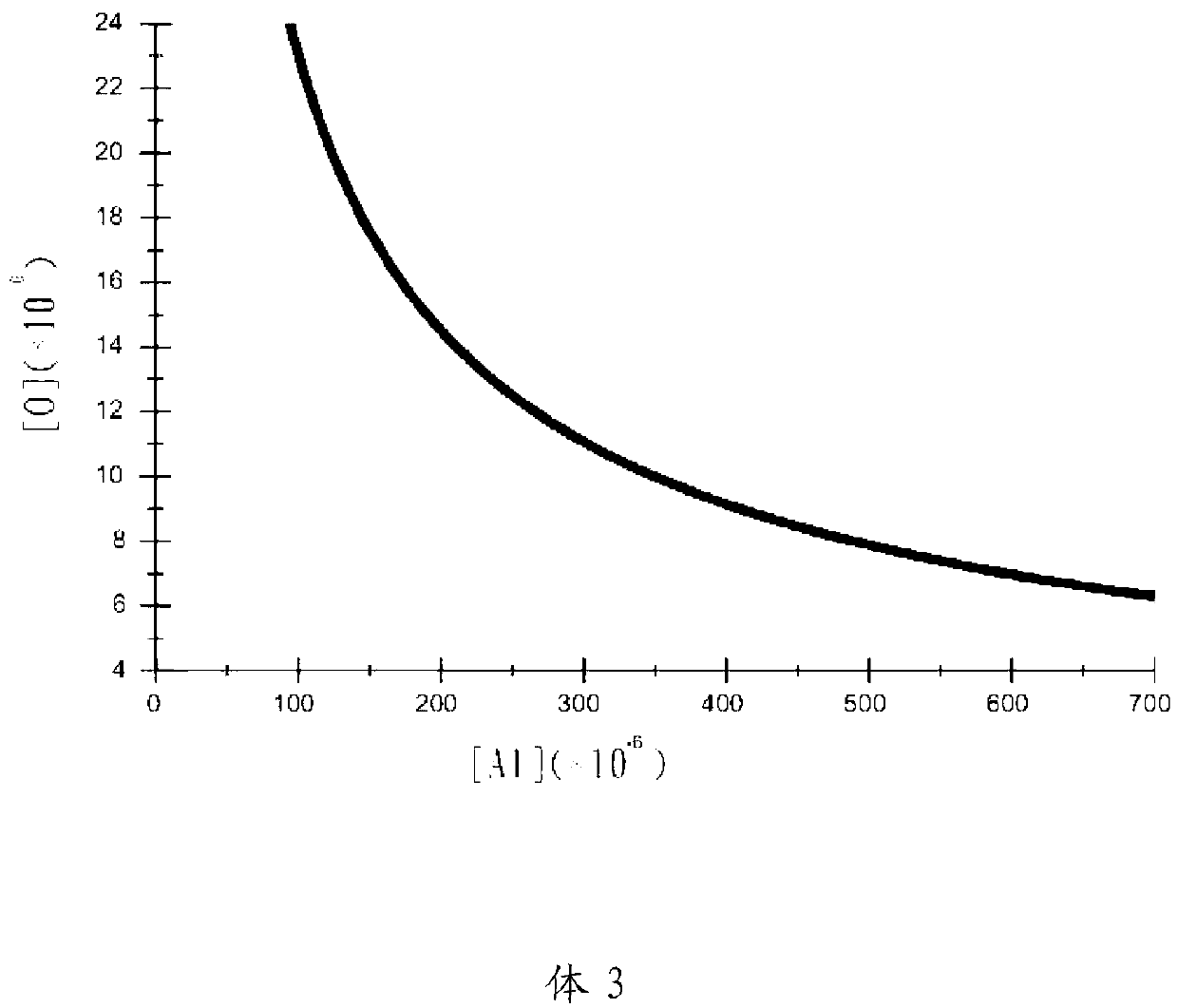
[0029] It should be noted that ΔGθ shown in each of the following chemical formulas refers to the change of free energy by chemical reaction in the standard state; a refers to the activity of each element in the standard sta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com