Woodland cultivating method for pleurotus edible mushrooms
A cultivation method and technology for edible fungi, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, application, horticulture, etc., can solve the problems of large cultivated land occupation, high investment in facilities, residual toxins, etc., and achieve high fruiting yield and biological efficiency improvement. , the overall effect of matrix nutrition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Embodiment 1: the woodland cultivation method of flat mushroom
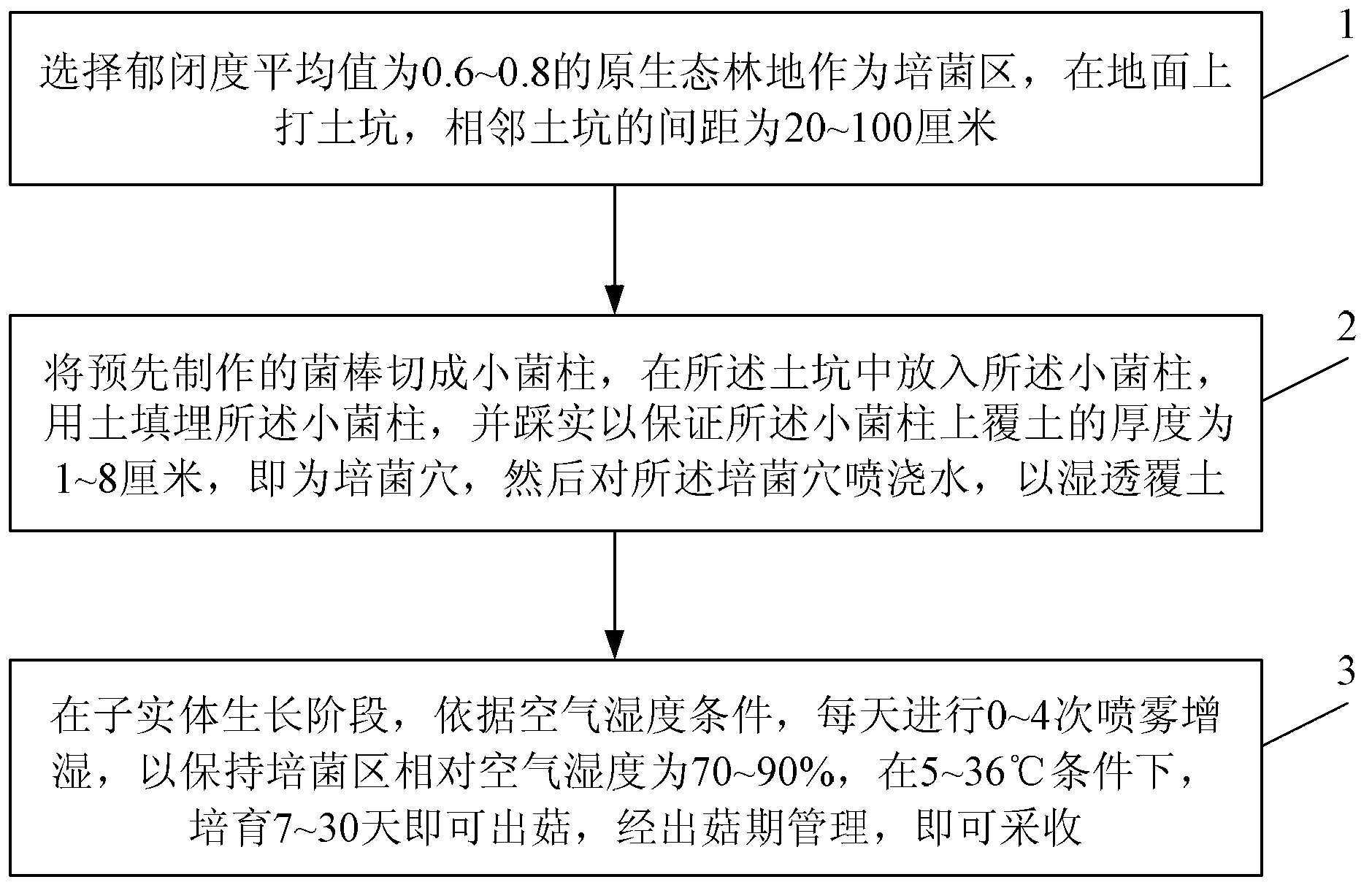
[0049] The selected forest land is 30-year-old original ecological forest land, with an area of about 2,000 mu, mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest land, the main tree species are black pine and arborvitae, and the average canopy density in the forest is 0.7.
[0050] After the fungus sticks have germinated, remove the plastic film, and when the temperature is 5-10°C, after-ripening and cultivating for about 30 days, the woodland cultivation can be carried out.
[0051] The forest cultivation method is as follows:
[0052] First of all, under the tree, start from more than 0.8 meters away from the trunk, and use a special one-time pit maker to dig a cuboid soil pit with a depth of 25 cm and a length and width of 20 cm at a distance of 60 cm.
[0053] Secondly, cut the mushroom stick into two small mushroom columns, put a small mushroom column into a soil pit, which is the cultivation hole, fill the...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2: the woodland cultivation method of pocket mushroom
[0058] The selected forest land is 30-year-old original ecological forest land, with an area of about 1500 mu, mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest land, the main tree species is Pinus massoniana, and the average canopy density in the forest is 0.7.
[0059] Bacteria sticks are made except that bacterial classification uses pocket mushroom, other is identical with embodiment 1.
[0060] The forest cultivation method is as follows:
[0061] First of all, start under the tree from more than 0.5 meters away from the trunk, and use a special one-time pit forming device to make a cube-shaped soil pit with a depth, length and width of 20 centimeters at a distance of 30 centimeters.
[0062] Secondly, cut the fungus sticks into small mushroom columns, put a small mushroom column into a soil pit, which is the cultivation hole, fill the small bacteria column with the excavated soil and step on it slightly,...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3: the woodland cultivation method of oyster mushroom
[0067] The selected forest land is 50-year-old original ecological forest land, with an area of about 5,000 mu, mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest land, the main tree species are masson pine and arborvitae, and the average canopy density in the forest is 0.7.
[0068] Bacteria rod is made except that bacterial classification uses little oyster mushroom, and other is identical with embodiment 1.
[0069] The forest cultivation method is as follows:
[0070] First of all, start under the tree from more than 0.7 meters away from the trunk, and use a special one-time pit maker to make a cube-shaped soil pit with a depth, length and width of about 22 centimeters at a distance of 50 centimeters.
[0071] Secondly, cut the mushroom stick into two small mushroom columns, put a small mushroom column into a soil pit, which is the cultivation hole, fill the small mushroom column with the excavated soil and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Altitude | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com