Novel low-temperature rare earth-chromium-boronizing agent
A technology of co-penetrating agent and rare earth, applied in metal material coating process, coating, solid diffusion coating, etc., can solve the problems of heavy pollution, large gas volume, long time, etc., and achieve wide application fields and small deformation of workpieces. , the effect of no internal stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: A new type of boron-chromium-rare earth low-temperature co-infiltration agent, the content of the co-infiltration agent components is: 4.8 parts of high-carbon ferrochrome, 3.8 parts of rare earth, 6.8 parts of potassium fluoroborate, and 21.3 parts of aluminum oxide , 5.9 parts of thiourea, 53.0 parts of ferroboron.
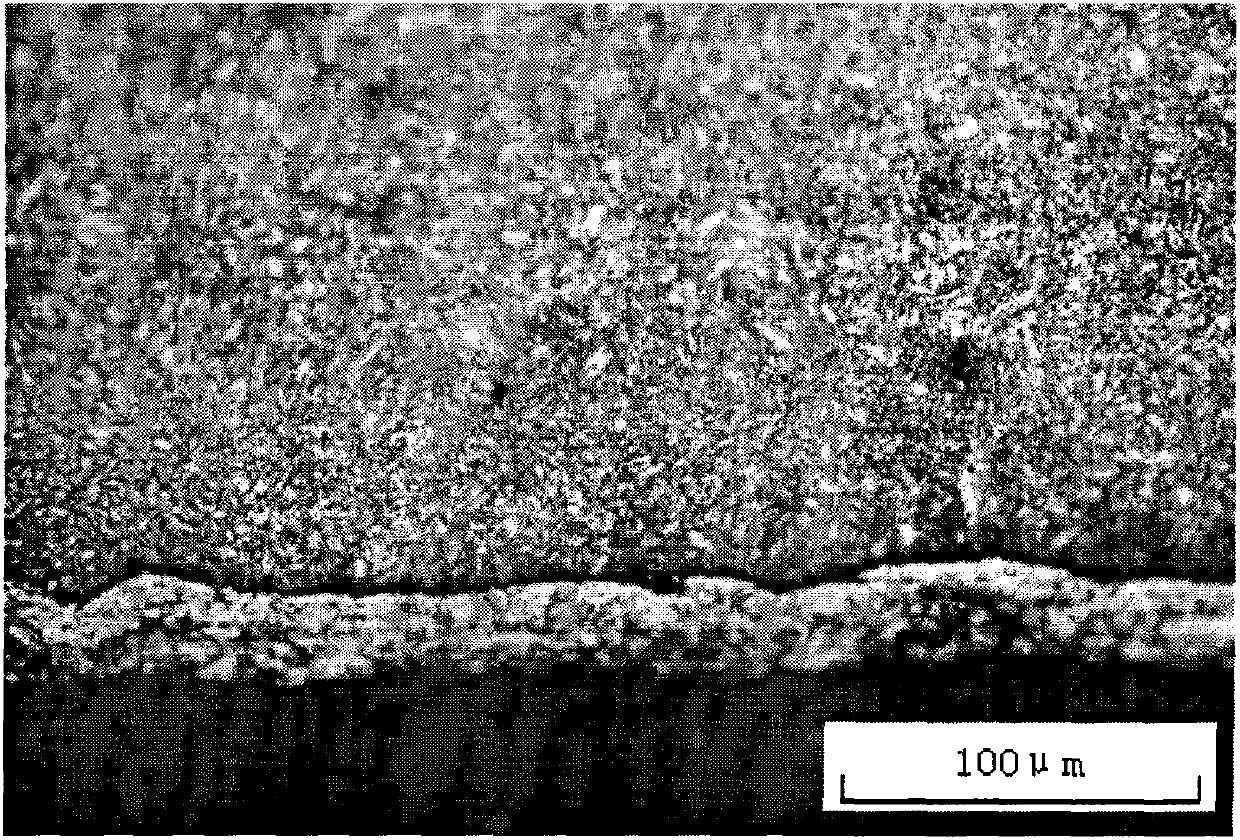
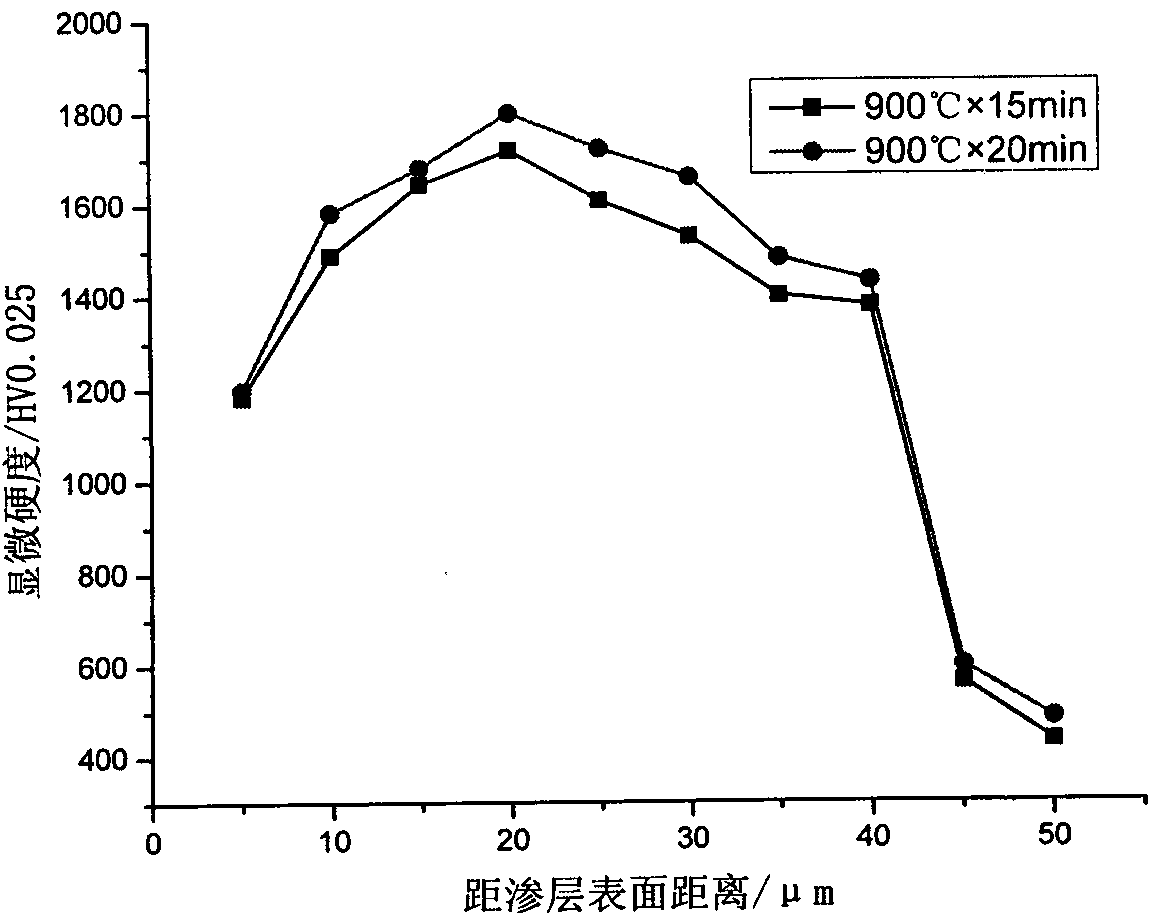
[0028] No. 20 steel sample was quenched before infiltration, and then co-infiltrated with boron-chromium-rare earth at 600℃×6h, and observed and tested the sample after infiltration. The process is as follows:
[0029] 1. Carry out pre-infiltration quenching treatment on the workpiece
[0030] The workpiece is quenched at 900°C, the holding time is 15 minutes, and then water quenched.
[0031] 2. Co-infiltration agent preparation
[0032] The penetrating agent is a boron-iron type co-penetrating agent with the above ratio, and its preparation process is as follows:
[0033] a. Grinding ferroboron, high-carbon ferrochrome, rare earth and alu...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: A new type of boron-chromium-rare earth low-temperature co-infiltration agent, the content of the co-infiltration agent components is: 4.9 parts of high-carbon ferrochrome, 3.9 parts of rare earth, 7.0 parts of potassium fluoroborate, and 23.5 parts of aluminum oxide , 7.2 parts of thiourea, 53.5 parts of boron iron.
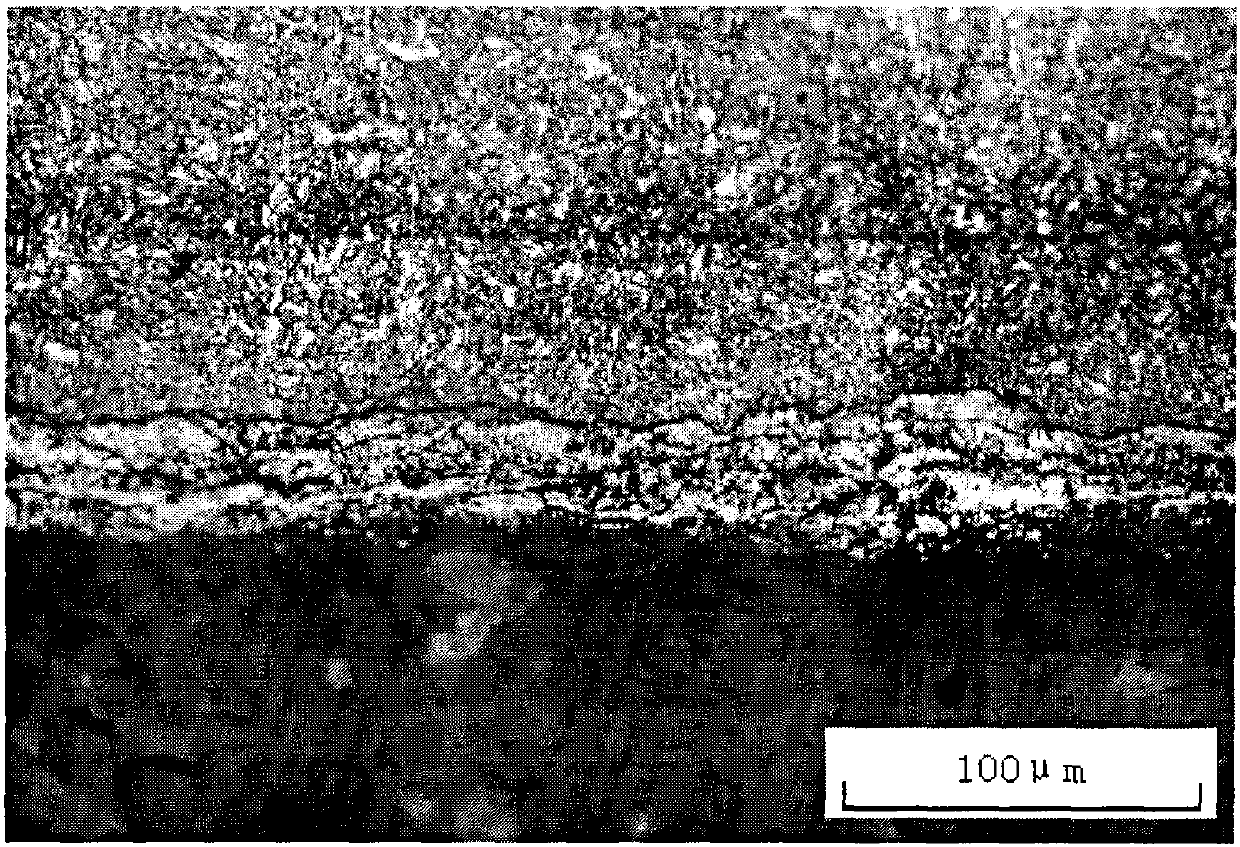
[0042]No. 20 steel sample was quenched before infiltration, and then co-infiltrated with boron-chromium-rare earth at 600℃×6h, and observed and tested the sample after infiltration. The process is as follows:
[0043] 1. Carry out pre-infiltration quenching treatment on the workpiece
[0044] The workpiece is quenched at 900°C, holding time is 20 minutes, and quenched in water.
[0045] 2. Co-infiltration agent preparation
[0046] The penetrating agent is a boron-iron type co-penetrating agent with the above ratio, and its preparation process is as follows:
[0047] a. Grinding ferroboron, high-carbon ferrochrome, rare earth and aluminum o...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3: A new type of boron-chromium-rare earth low-temperature co-infiltration agent, the content of the co-infiltration agent components is: 4.9 parts of high-carbon ferrochrome, 3.9 parts of rare earth, 8.2 parts of potassium fluoroborate, and 22.2 parts of aluminum oxide , 7.0 parts of thiourea, 53.8 parts of boron iron.
[0056] No. 45 steel sample was quenched before infiltration, and then co-infiltrated with boron-chromium-rare earth at 600°C×6h, and the sample was observed and tested after infiltration. The process is as follows:
[0057] 1. Carry out pre-infiltration quenching treatment on the workpiece
[0058] The workpiece is quenched at 860°C, the holding time is 20 minutes, and then water quenched.
[0059] 2. Co-infiltration agent preparation
[0060] The penetrating agent is a boron-iron type co-penetrating agent with the above ratio, and its preparation process is as follows:
[0061] a. Grinding ferroboron, high carbon ferrochrome, rare earth an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| microhardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com