Multi-stage single switch boost converter
A boost converter, single-switch technology, applied in instruments, converting DC power input to DC power output, adjusting electrical variables, etc., can solve the problems of high voltage stress of switching tubes, low input voltage utilization rate, and many inductive components. , to meet the requirements of reducing the capacity of the capacitor withstanding voltage, high utilization of power supply voltage, and simple control circuit.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 2
[0037] Embodiment 1 Two-stage single-switch boost converter
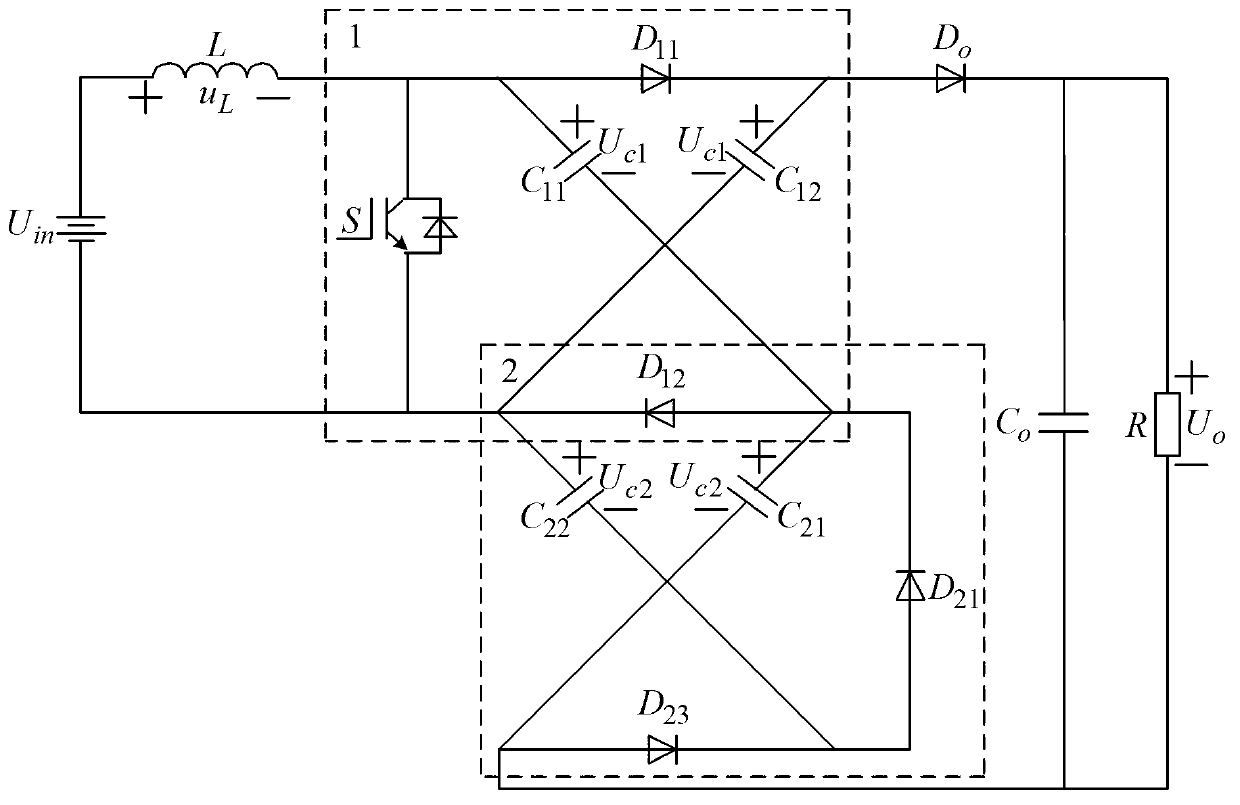
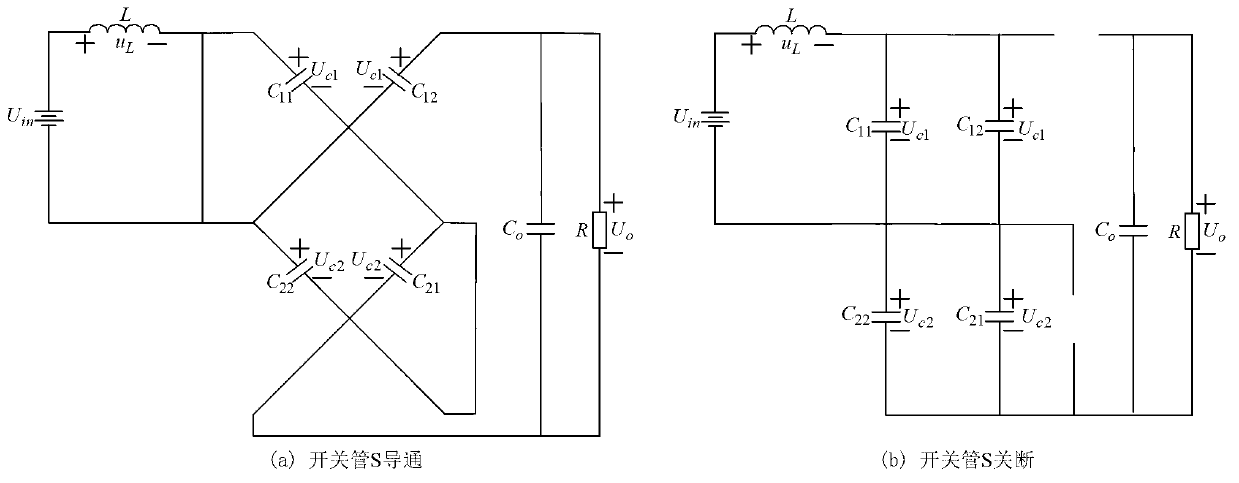
[0038] Add a Switch-Capacitor network to the pre-stage Boost network to form a secondary single-switch boost converter, such as figure 1 shown. Denote these two nets as net 1 and net 2, where net 1 and net 2 share diode D 12 . The equivalent circuit of the two-stage single-switch boost converter is shown as figure 2 shown.
[0039] When the active switch S is turned on, the diode D 11 、D 12 、D 23 Deadline, D 21 、D o conduction, the equivalent circuit of the secondary single-switch boost converter is as figure 2 (a) shown. At this point, the capacitor C in network 1 11 with C 12 and capacitor C in network 2 21 with C 22 respectively interleaved in series, while the capacitance C 11 with C 22 in parallel.
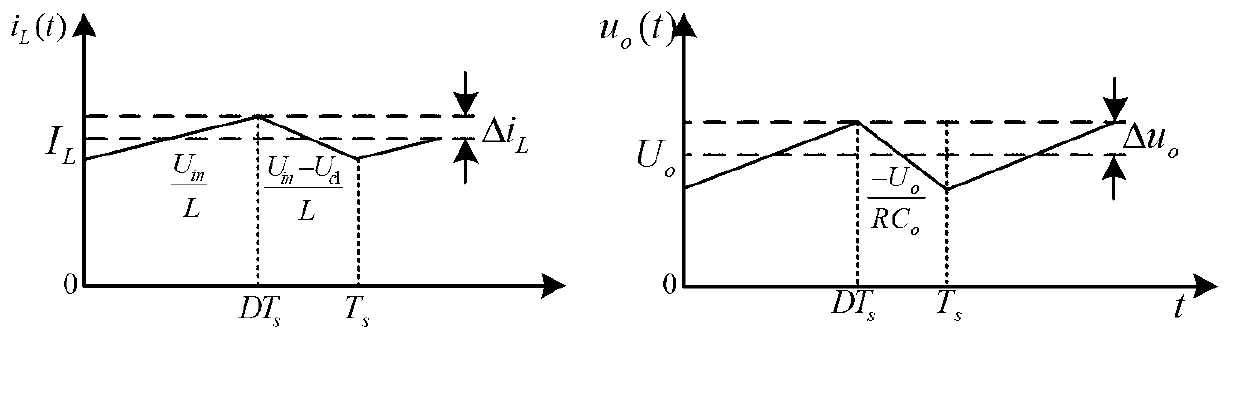
[0040] The voltage across the inductor L is:
[0041] u L =U in (1-1)
[0042] due to C 11 with C 22 In parallel, so the capacitor voltages in network 1 and network 2 are equal, that is:...
Embodiment 2 3
[0059] Embodiment 2 Three-stage single-switch boost converter
[0060] If a Switch-Capacitor network is added on the basis of Embodiment 1, a three-stage single-switch boost converter can be formed, such as Figure 4 shown, where net 1 and net 2 share diode D 12 , net 2 and net 3 share diode D 23 . Its equivalent circuit is as Figure 5 shown.
[0061] When the active switch S is turned on, the diode D 11 、D 12 、D 23 、D 34 Deadline, D 21 、D 31 、D o conduction, its equivalent circuit is as Figure 5 (a) shown. At this point, the capacitor C in network 1 11 with C 12 , the capacitor C in network 2 21 with C 22 and capacitor C in network 3 31 with C 32 respectively interleaved in series, while C 11 with C 22 、C 21 with C 32 respectively in parallel.
[0062] The voltage across the inductor L is:
[0063] u L =U in (2-1)
[0064] due to C 11 with C 22 、C 21 with C 32 They are connected in parallel respectively, so the capacitance voltages in these...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Embodiment 3 Multi-level single-switch boost converter
[0079] Based on the composition law and working principle of the two-stage single-switch boost converter and the three-stage single-switch boost converter, if (n-1) Switch-Capacitor networks are added to the previous Boost network, we can get A boost converter with n networks is referred to as an n-level single-switch boost converter, also known as a multi-level single-switch boost converter. Its circuit topology is as follows: Figure 7 shown.
[0080] Depending on the number of Switch-Capacitor networks interleaved in series, the converter structure will be different, but generally speaking, it can be divided into two topological structures, such as Figure 7 shown. Note that the number of interleaved networks is n, when n=2k (k is a positive integer), the topology is as follows Figure 7 As shown in (a), there are an even number of Switch-Capacitor networks interleaved in series; when n=2k+1 (k is a positive...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com