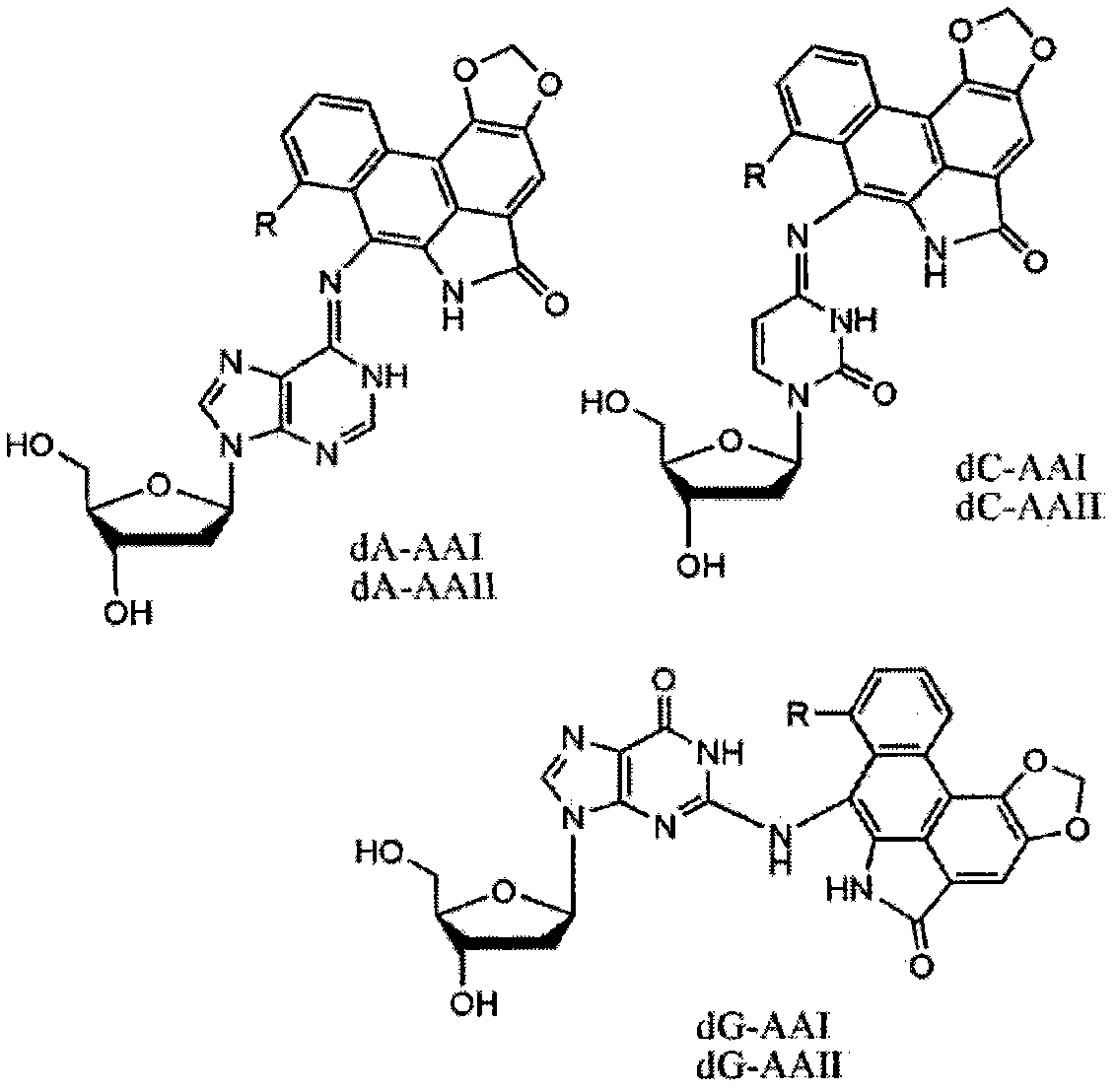
Laser confocal microscrope method for analyzing aristolochic acid nephropathy biomarker
A technique for aristolochic acid and an analysis method, which is applied in the biological technology and medical fields, and can solve the problems of complex processing methods, inability to intuitively reflect the actual distribution state of adducts, and the like.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
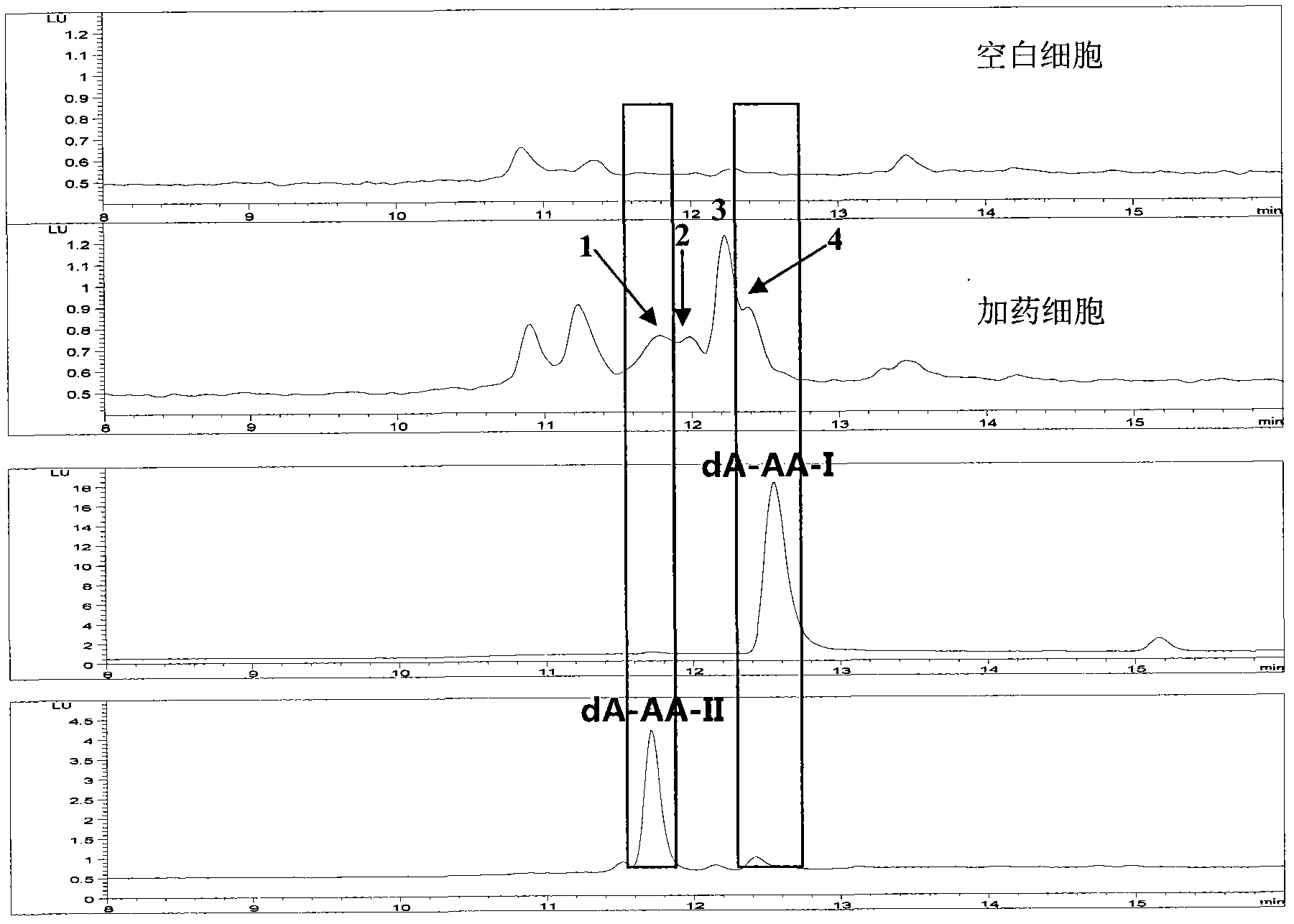
[0031] Take the renal tubular epithelial cells cultured in vitro, culture them with DMEM medium containing no more than 0.5% fetal bovine serum, inoculate the cells into a 35mm glass-bottom dish, and when they grow to 80% confluence, use 0.5 μg / ml The culture medium of AA-I was stimulated for 24h. AA-DNA adducts can be detected in the nucleus using confocal laser microscopy using an excitation wavelength of 300 nm and an emission wavelength of 580 nm. The fluorescence intensity of the adduct was significantly stronger than the autofluorescence intensity in HK-2 cells of the blank control group ( image 3 ), the same below.
Embodiment 2
[0033] HK-2 cells cultured in vitro were stimulated with AA-I at a concentration of 1 μg / ml for 24 hours, and AA-DNA adducts could be detected in the nucleus by laser confocal microscopy. The excitation wavelength is 310nm and the emission wavelength is 550nm.
Embodiment 3
[0035] HK-2 cells cultured in vitro were stimulated with AA-I at a concentration of 5 μg / ml for 6 hours, and AA-DNA adducts could be detected in the nucleus by laser confocal microscopy. The excitation wavelength is 340nm and the emission wavelength is 520nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com