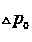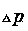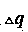Instantaneous-power-based single phase ground fault line selection method of resonant grounded system
A single-phase-to-ground fault, instantaneous power technology, applied in the direction of electric power measurement, measurement devices, instruments, etc. through current/voltage, can solve the problems of difficult power theory, interpretation and description, and the effect is not very ideal, and achieve anti-interference ability. Strong, eliminate the large gap between the length of the line and the effect of high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0132] Embodiment 1: A cable hybrid resonance grounding system simulation model such as image 3 , in the figure, , , They are overhead lines with lengths of 9㎞, 15㎞ and 10㎞ respectively; , , are cables, the lengths are 4.3㎞, 6㎞ and 8㎞ respectively; The first 5㎞ is an overhead line, and the last 2㎞ is a cable; the load ranges from 0.2 to 1.5MVA, the power factor is 0.8, and the arc suppression coil is grounded through a Z-shaped transformer. set line A ground fault occurs at 4㎞ of B phase, the fault closing angle is 20°, and the transition resistance is 50 . The failure occurred at 0.04s, and the simulation time was 0.08s.
[0133] Due to space limitations, only sound lines are taken and the fault line for comparison.
[0134] (1) Instantaneous zero-sequence power comparison
[0135] 1) if Figure 4 Line l when the system shown is in normal operation 1 The instantaneous zero-sequence power waveform diagram; such as Figure 5 Line l when the system sh...
Embodiment 2
[0147] Example 2: Also for the simulation model such as image 3 , a bus ground fault occurs. At this time, the waveform diagrams of instantaneous zero-sequence power, instantaneous real power, and instantaneous virtual power of each line are similar, and the difference is not obvious. calculated for each line (p.u.) see table below:
[0148]
[0149] The top three lines with the largest variation are , and , its corresponding The values, in order of magnitude, are: =3.853p.u., =3.811p.u., =3.786 p.u.. dissatisfied , so it is determined to be a bus fault.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com