A biological artificial hip joint femoral stem
A technology of hip joint and femoral stem, which is applied in the field of hip joint surface replacement, can solve problems such as prosthesis loosening, negative local bone tissue shaping, and periprosthetic fractures, so as to increase long-term stability, avoid prosthesis loosening, and reduce The effect of bone resorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
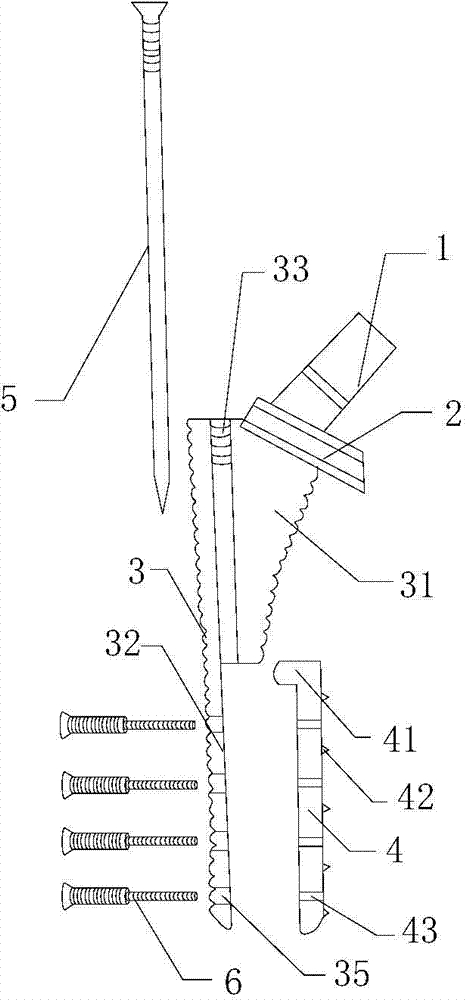
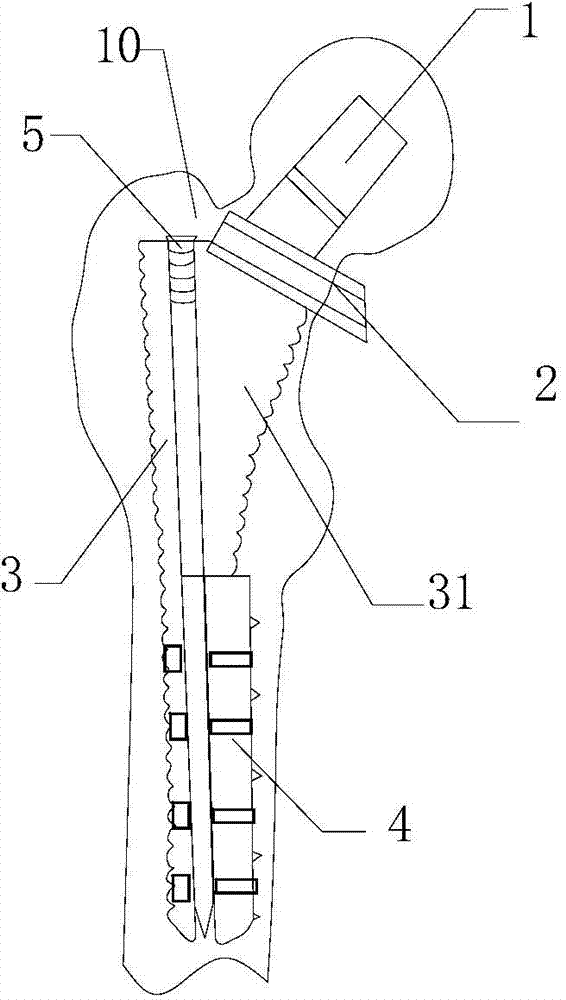
[0022] Such as figure 1 As shown, on the basis of the above scheme, the internal support device includes a main screw 5, and the fixed end 31 of the prosthesis handle 3 is provided with a threaded hole 33 matching the main screw 5, and the main screw 5 extends into the main screw 5 through the threaded hole 33. Between the endosteal separating steel plate 4 and the endosteal receiving steel plate 32 , the endosteal steel plate 4 is stretched toward the inner side of the femoral shaft 10 during the tightening process of the main screw 5 . The main screw 5 can not only expand the intima separation plate 4, but also fix the endosteal receiving plate 32 in the femur. This structure is mainly used for general replacement surgery, and the bone quality near the greater trochanter and the upper part of the femur is still relatively strong in patients without obvious osteoporosis ; At this time, the ordinary replacement structure of Example 1 is used during the operation, and no addit...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Such as Figure 4 As shown on the basis of the above-mentioned scheme, the internal support device includes at least two special-shaped screws 6; the special-shaped screw 6 includes a first diameter thread segment and a second diameter thread segment, and the diameter of the first diameter thread segment is larger than the second The diameter of the diameter thread section; the endosteal receiving steel plate 32 is provided with the first screw hole 35 matched with the first diameter thread section, and the described endosteal separation steel plate 4 is provided with the second diameter thread section matching The second screw hole 43 ; during the tightening process of the special-shaped screw 6 , the intima plate 4 is stretched toward the medial cortex of the femur 10 . On the basis of this embodiment, as a further improvement, the number of the special-shaped screws 6 is 4-8. Because the special-shaped screw 6 is made up of two thread segments with different diamete...
Embodiment 3
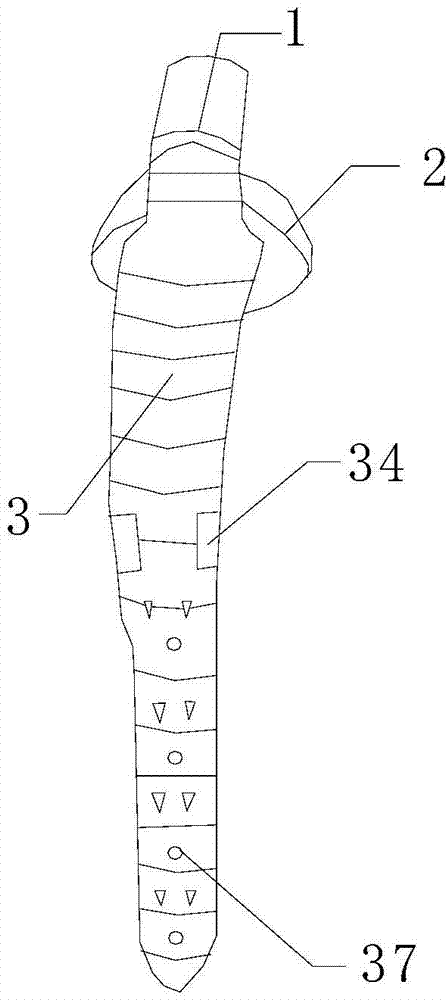
[0026] Such as Figure 5 As shown, on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiment 1 or 2, the prosthesis handle is lengthened as a whole, and several small screw holes 36 are provided on the surface of the fixed end 31 . The femoral stem with this structure is suitable for revision surgery. This structure is usually used for patients with osteoporosis around the greater trochanter, or even comminuted fractures. Short-stem prostheses cannot be used for repair. Small screw holes 36 on the proximal surface can be used to secure bone fragments 40 . The extra holes are conducive to the growth of new bone. The endosteal bearing plate and the endosteal separating plate can be fixed to the femoral shaft with stronger bone that is far away from the greater trochanter by using this long-handle prosthesis, which is suitable for osteoporosis around the greater trochanter and It is suitable for revision surgery of patients with periprosthetic fractures. Since there is no need to use bon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com