Method for improving plant quality
A plant and quality technology, applied in botany equipment and methods, plant growth regulators, animal repellants, etc., can solve problems such as economic losses and plant yield losses, and achieve high machinability effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment A
[0233] Example A Potato Test
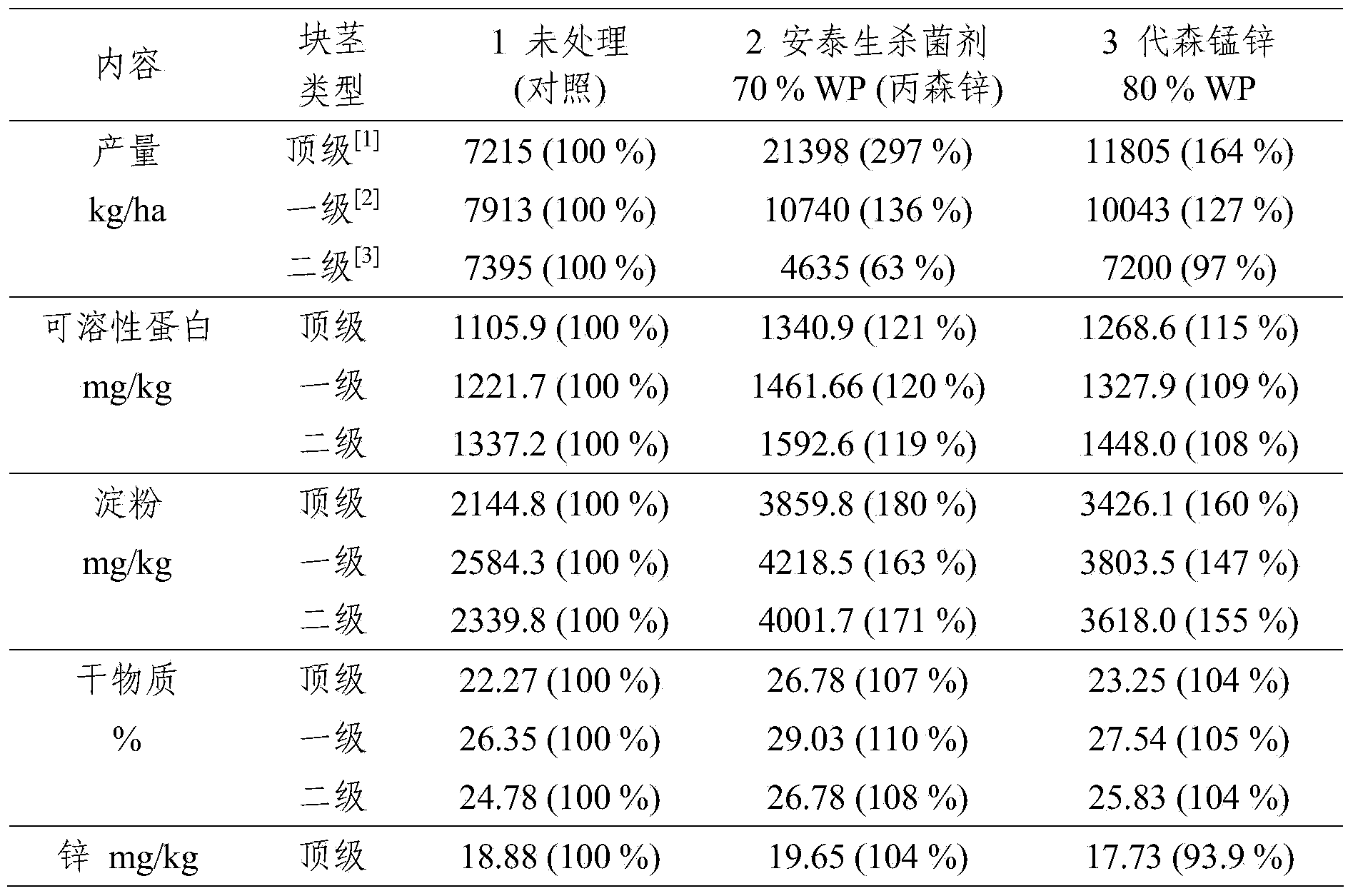
[0234] The potato variety is Xiabodi, planted in the zinc-deficient black soil in Gansu Province (pH8.35, the content of available zinc in the soil is 0.34μg / g, and the organic matter is 8.86%): the altitude is 2050m, the average temperature is 16.4℃~19.7℃, and the rainfall is 18mm ~43.3mm, and the relative humidity between June and September is 34.5%~67.8%. Each treatment has four replicates. Each area has an area of 100m 2 There are 500 mounds. The control product used the commercially available fungicide 80% WP mancozeb. The soil is not infected. The field management in the treatment process is similar: planting on April 28, 2010, soil cultivation on June 25, 2010; three times of irrigation on May 6, June 19, and August 12, 50L each time; Two weedings were carried out on June 9 and July 23. Use 210kg / ha (NH 4 )H 2 PO 3 , 750kg / haCa(H 2 PO 4 )·H 2 O and 165kg / ha CO(NH 2 ) 2 fertilization rate.
[0235] Post-harvest effects of p...
Embodiment B
[0248] Embodiment B rice test (field test)
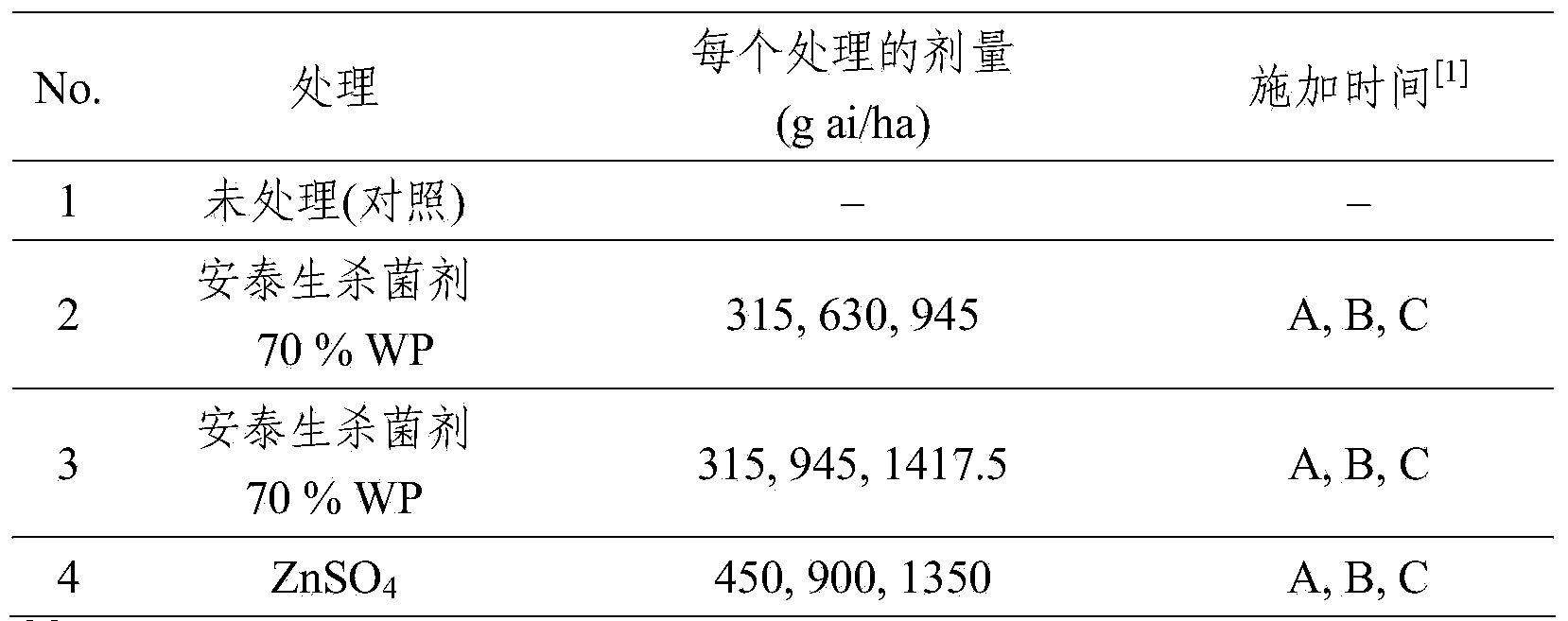
[0249] Rice variety Yang II You 6, planted at 40m 2 The area seeding rate was 22.5kg / ha (3 replicates per treatment). Then use Antaisheng fungicide 70WP (propineb 700g / kg) and zinc fertilizer ZnSO 4 deal with.
[0250] Field management during treatment was routine and similar: previous winter crop rape and rice sown on 15 June 2010. Press 300kg / ha (NH 4 ) 2 PO 3 , 150kg / ha of KCl and 375kg / ha of CO (NH 2 ) 2 Fertilizer application rate.
[0251] The effect of propineb on Zn content in rice grains was evaluated under field conditions in China. Each treatment randomly selected 500g samples to the laboratory for determination of zinc content.
[0252] Detection method of zinc content: refer to the national (P.R.China) standard: Determination of zinc in food (GB / T5009.14-2003, ICS67.040C53).
[0253]
[0254] [1] A: 40DAS (days after sowing), B: 52DAS, C: 66DAS
[0255] Zinc content in leaves and grains measured after harv...
Embodiment C
[0258] Example C Maize Test (Field Test)
[0259] The corn variety is Fuyu No. 2, planted at 80m 2 The regional sowing rate was 60kg / ha (each treatment had three replicates), and this experiment was located at the experimental station of Tianjin Institute of Plant Protection. The soil type is black soil with pH 7.5 and organic matter content 7.54%. Then use Antaisheng fungicide 70WP (propineb 700g / kg) and zinc fertilizer ZnSO 4 Implement processing.
[0260] Field management was routine and similar during the treatment: winter wheat was previously planted, and maize was sown on June 22, 2010; three irrigations were performed during stem elongation, heading and grain filling. Press 225kg / ha (NH 4 ) 2 PO 3 , 150kg / ha of KCl and 150kg / ha of CO(NH 2 ) 2 Fertilizer application rate.
[0261] The effect of propineb on the zinc content of maize kernels was evaluated under field conditions in China. Each treatment randomly selected 1000g samples to the laboratory for determi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com