Normal olefin isomerization catalyst and preparation method
A technology for olefin isomerization and catalysts, which is applied in the field of olefin isomerization catalysts and its preparation, can solve problems such as the complexity of the reaction process, and achieve the effects of increased yield, easy control, and simple preparation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0014] The preparation method of the catalyst provided by the present invention includes mixing molecular sieves and binders, drying and roasting to obtain a carrier, and then impregnating with an aqueous solution of a modified compound. dry.
[0015] The molecular sieve is preferably one or any two of ZSM-35, ZSM-22 and SAPO-11, and the binder is preferably alumina.
[0016] The method of mixing molecular sieve and binder in the method of the present invention is extruding, dropping ball, rolling ball or tableting method, preferably extruding. The extruding method is as follows: uniformly mix the molecular sieve with the binder or its precursor, add an appropriate amount of extrusion aid and / or peptizer and knead, and then extrude. The extrusion aid is preferably squash powder, and the peptizing agent is preferably an inorganic acid, such as hydrochloric acid or nitric acid. After the wet strip is cut into pellets, the carrier is obtained by drying and roasting. The temper...
example 1
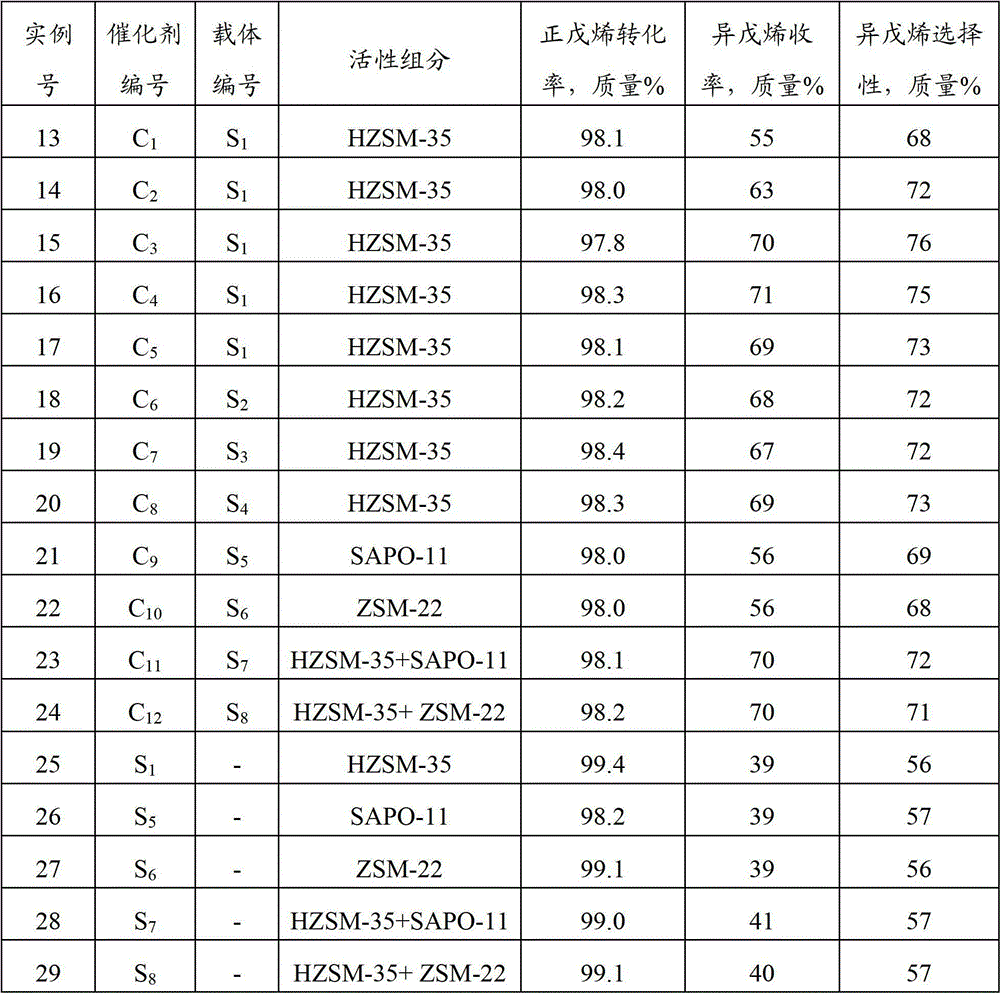
[0027] Mix 10,788 grams of HZSM-35 molecular sieve with a molar ratio of silica to alumina of 25 and 1,638 grams of pseudoboehmite, add 65.5 grams of nitric acid with a concentration of 65% by mass and 10,770 grams of water, and extrude with a twin-screw extruder. The trefoil-shaped strips with a diameter of 1.1 mm were cut into pellets, then dried at 120°C for 4 hours, and roasted at 550°C for 2 hours to obtain the carrier S 1 , which contains 90% by mass of HZSM-35 molecular sieve and 10% by mass of alumina.
[0028] Take 2000 grams of carrier S 1 , impregnated with 1939 ml of an aqueous solution containing 100.2 g (0.506 mol) of D-glucose at 25°C for 0.5 hours, and dried the impregnated solid at 90°C and 0.01MPa for 2 hours to obtain catalyst C 1 , whose weight is 2100 g, indicating that the catalyst C 1 Contains 100 grams of D-glucose, D-glucose and carrier S 1 The mass ratio is 0.05.
example 2
[0030] Take 2000 grams of carrier S 1 , impregnated with 1939 ml of an aqueous solution containing 147.3 grams (0.743 mol) of D-glucose at 25 ° C for 0.5 hours, and dried the solid at 90 ° C and 0.01 MPa for 2 hours after impregnation to obtain catalyst C 2 , whose weight is 2147 g, indicating that the catalyst C 2 Contains 147 grams of D-glucose, D-glucose with carrier S 1 The mass ratio is 0.074.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com